(Press-News.org) This press release is available in German.
Unlike the brain and spinal cord, the peripheral nervous system has an astonishing capacity for regeneration following injury. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Experimental Medicine in Göttingen have discovered that, following nerve damage, peripheral glial cells produce the growth factor neuregulin1, which makes an important contribution to the regeneration of damaged nerves.
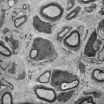
From their cell bodies to their terminals in muscle or skin, neuronal extensions or axons in the peripheral nervous system are surrounded along their entire length by glial cells. These cells, which are known as Schwann cells, envelop the axons with an insulating sheath called myelin, which enables the rapid transmission of electrical impulses. Following injury to a peripheral nerve, the damaged axons degenerate. After a few weeks, however, they regenerate and are then recovered with myelin by the Schwann cells. For thus far unexplained reasons, however, the Schwann cells do not manage to regenerate the myelin sheaths completely. Thus the function of damaged nerves often remains permanently impaired and certain muscles remain paralysed in affected patients.
In a current research study, the scientists have succeeded in showing that the growth factor neuregulin1 supports nerve repair and the redevelopment of the myelin layer. This protein is usually produced by neurons and is localised on axons where it acts as an important signal for the maturation of Schwann cells and myelin formation. Because the axons rapidly degenerate after injury, the remaining Schwann cells lose their contact with the axons. They thus lack the neuregulin1 signal of the nervous fibres. "In the phase following nerve damage, in which the axons are missing, the Schwann cells must carry out many tasks without the help of axonal signals. If the Schwann cells cannot overcome this first major obstacle in the aftermath of nerve injury, the nerve cannot be adequately repaired," explains Ruth Stassart, one of the study authors.
To prevent this, the Schwann cells themselves take over the production of the actual neuronal signal molecule. After nerve damage, they synthesise the neuregulin1 protein until the axons have grown again. With the help of genetically modified mice, the researchers working on this study were able to show that the neuregulin1 produced in Schwann cells is necessary for the new maturation of the Schwann cells and the regeneration of the myelin sheath after injury. "In mice that lack the neuregulin1 gene in their Schwann cells, the already incomplete nerve regeneration process is extensively impaired," explains co-author Robert Fledrich.
The researchers would now like to examine in greater detail how the Schwann cells contribute to the complete repair of myelinated axons after nerve damage, so that this information can also be used for therapeutic purposes.
INFORMATION:
Glial cells assist in the repair of injured nerves
When a nerve is damaged, glial cells produce the protein neuregulin1 and thereby promote the regeneration of nerve tissue
2013-01-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
EARTH: Drinking toilet water
2013-01-29
Alexandria, VA – Would you drink water from a toilet? What if that water, once treated, was cleaner than what comes out of the faucet? Although the imagery isn't appealing, as climate change and population growth strain freshwater resources, such strategies are becoming more common around the world — and in the United States.
Over the last several decades, local and regional water shortages have become increasingly common. These shortages have led to increased friction over water resources. Technologies are currently being developed to help make wastewater recycling ...
1 in, 2 out: Simulating more efficient solar cells
2013-01-29
Using an exotic form of silicon could substantially improve the efficiency of solar cells, according to computer simulations by researchers at the University of California, Davis, and in Hungary. The work was published Jan. 25 in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Solar cells are based on the photoelectric effect: a photon, or particle of light, hits a silicon crystal and generates a negatively charged electron and a positively charged hole. Collecting those electron-hole pairs generates electric current.
Conventional solar cells generate one electron-hole pair ...
Study finds eating deep-fried food is associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer
2013-01-29
SEATTLE – Regular consumption of deep-fried foods such as French fries, fried chicken and doughnuts is associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer, and the effect appears to be slightly stronger with regard to more aggressive forms of the disease, according to a study by investigators at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center.
Corresponding author Janet L. Stanford, Ph.D., and colleagues Marni Stott-Miller, Ph.D., a postdoctoral research fellow and Marian Neuhouser, Ph.D., all of the Hutchinson Center's Public Health Sciences Division, have published their findings ...
Study shows climate change could affect onset and severity of flu seasons
2013-01-29
The American public can expect to add earlier and more severe flu seasons to the fallout from climate change, according to a research study published online Jan. 28 in PLOS Currents: Influenza.
A team of scientists led by Sherry Towers, research professor in the Mathematical, Computational and Modeling Sciences Center at Arizona State University, studied waves of influenza and climate patterns in the U.S. from the 1997-1998 season to the present.
The team's analysis, which used Centers for Disease Control data, indicates a pattern for both A and B strains: warm winters ...
Research: Military women may have higher risk for STIs
2013-01-29
As the number of women in the military increases, so does the need for improved gynecologic care. Military women may be more likely to engage in high-risk sexual practices, be less likely to consistently use barrier contraception, and, therefore, more likely to contract sexually transmitted infections (STIs), according to research recently released by a physician at Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island.
Vinita Goyal, MD, MPH, followed up earlier research into the rates of contraception use and unintended pregnancy by today's military women and veterans with her latest ...
USGS-NOAA: Climate change impacts to US coasts threaten public health, safety and economy
2013-01-29
According to a new technical report, the effects of climate change will continue to threaten the health and vitality of U.S. coastal communities' social, economic and natural systems.
The report, Coastal Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerabilities: a technical input to the 2013 National Climate Assessment, authored by leading scientists and experts, emphasizes the need for increased coordination and planning to ensure U.S. coastal communities are resilient against the effects of climate change.
The recently released report examines and describes climate change impacts ...
When food porn holds no allure: The science behind satiety
2013-01-29
New research from the University of British Columbia is shedding light on why enticing pictures of food affect us less when we're full.
"We've known that insulin plays a role in telling us we're satiated after eating, but the mechanism by which this happens is unclear," says Stephanie Borgland, an assistant professor in UBC's Dept. of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics and the study's senior author.
In the new study published online this week in Nature Neuroscience, Borgland and colleagues found that insulin – prompted by a sweetened, high-fat meal – affects ...
Power helps you live the good life by bringing you closer to your true self
2013-01-29
How does being in a position of power at work, with friends, or in a romantic relationship influence well-being? While we might like to believe the stereotype that power leads to unhappiness or loneliness, new research indicates that this stereotype is largely untrue: Being in a position of power may actually make people happier.
Drawing on personality and power research, Yona Kifer of Tel Aviv University in Israel and colleagues hypothesized that holding a position of authority might enhance subjective well-being through an increased feeling of authenticity. The researchers ...
Artificial pancreas: The way of the future for treating type 1 diabetes
2013-01-29
Montréal, January 28, 2013 – IRCM researchers, led by endocrinologist Dr. Rémi Rabasa-Lhoret, were the first to conduct a trial comparing a dual-hormone artificial pancreas with conventional diabetes treatment using an insulin pump and showed improved glucose levels and lower risks of hypoglycemia. Their results, published today in the Canadian Medical Association Journal (CMAJ), can have a great impact on the treatment of type 1 diabetes by accelerating the development of the external artificial pancreas.
The artificial pancreas is an automated system that simulates ...
Why are there redheads? Birds might hold the clues
2013-01-29
Red coloration—historically seen as costly in vertebrates—might represent some physiological benefit after all, according to research published in the journal Physiological and Biochemical Zoology.
Pheomelanin, which is responsible for red hair and freckles in humans and orange and chestnut coloration in other animals, is known to increase the damage to skin cells and melanoma risk when present in large amounts. Furthermore, its creation involves the consumption of glutathione, a beneficial antioxidant.
In an attempt to unearth the factors favoring the evolution of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Glial cells assist in the repair of injured nervesWhen a nerve is damaged, glial cells produce the protein neuregulin1 and thereby promote the regeneration of nerve tissue