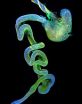
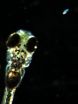
(Press-News.org) A cure for congenital sight impairment caused by lens damage is closer following research by scientists at Monash University.
Associate Professor Tiziano Barberi and Dr Isabella Mengarelli from the Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute at Monash University are closer to growing parts of the human eye in the lab. They have, for the first time, derived and purified lens epithelium - the embryonic tissue from which the lens of the eye develops. The purity of the cells paves the way for future applications in regenerative medicine.
Further, the researchers caused these precursor cells to differentiate further into lens cells, providing a platform to test new drugs on human tissue in the lab.
Pluripotent stem cells have the ability to become any cell in the human body including, skin, blood and brain matter. Once the stem cells have begun to differentiate, the challenge for researchers is to control the process and produce only the desired, specific cells.
Using a technology known as fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS), Associate Professor Barberi and his team were able to identify the precise combination of protein markers expressed in the lens epithelium that enabled them to isolate those cells from the rest of the cultures. Most markers are common to more than one type of cell, making it challenging to determine the exact mix of markers unique to the desired cells.
Associate Professor Barberi said this breakthrough would eventually help cure visual impairment caused by congenital cataracts or severe damage to the lens from injury through lens transplants.
"The lens has, to some extent, the ability to heal well following surgical intervention. However, with congenital cataracts, the fault is wired into the DNA, so the lens will re-grow with the original impairment. This problem is particularly prevalent in developing countries," he said.
Combined with advances in producing pluripotent stem cells from fully-differentiated adult cells, the research will also progress treatments for eye diseases.
"In the future, we will be able to take adult skin cells, for example, and turn back the clock to produce stem cells. From there, using processes like we have developed for lens epithelium, we will be able to produce diseased cells - an invaluable asset for medical research," Associate Professor Barberi said.
The researchers will now focus on creating a lens more closely resembling a human eye in the lab.
"The lens cells that we created in the petri dish are organised differently to those in a human eye. The next challenge is mimicking nature more perfectly," Associate Professor Barberi said.
### Published in Stem Cells Translational Medicine, the study was partly funded by the Australian Research Council.
'Petri dish lens' gives hope for new eye treatments
2013-01-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Aztec conquest altered genetics among early Mexico inhabitants, new DNA study shows
2013-01-31
AUSTIN, Texas — For centuries, the fate of the original Otomí inhabitants of Xaltocan, the capital of a pre-Aztec Mexican city-state, has remained unknown. Researchers have long wondered whether they assimilated with the Aztecs or abandoned the town altogether.
According to new anthropological research from The University of Texas at Austin, Wichita State University and Washington State University, the answers may lie in DNA. Following this line of evidence, the researchers theorize that some original Otomies, possibly elite rulers, may have fled the town. Their exodus ...
Disease not a factor in Tassie Tiger extinction
2013-01-31
Humans alone were responsible for the demise of Australia's iconic extinct native predator, the Tasmanian Tiger or thylacine, a new study led by the University of Adelaide has concluded.
Using a new population modelling approach, the study contradicts the widespread belief that disease must have been a factor in the thylacine's extinction.
The thylacine was a unique marsupial carnivore found throughout most of Tasmania before European settlement in 1803. Between 1886 and 1909, the Tasmanian government encouraged people to hunt thylacines and paid bounties on over 2000 ...
Stanford experiment shows that virtual superpowers encourage real-world empathy
2013-01-31
If you give people superpowers, will they use those abilities for good?
Researchers at Stanford recently investigated the subject by giving people the ability of Superman-like flight in the university's Virtual Human Interaction Laboratory (VHIL). While several studies have shown that playing violent videogames can encourage aggressive behavior, the new research suggests that games could be designed to train people to be more empathetic in the real world.
To test this hypothesis, the group – which included Jeremy Bailenson, an associate professor of communication; Robin ...
Hit by 2 hammers
2013-01-31
KANSAS CITY, MO—Mutations in single genes can cause catastrophic diseases, such as Huntington's Disease or sickle cell anemia. However, many conditions, including cancer, diabetes and birth defects are multigenic, arising from the collective failure of the function of more than one gene.
Researchers know that mutations in at least twelve individual genes are associated with the congenital defect Hirschprung Disease (HSCR), in which children are born lacking nerves that innervate the large intestine. Now two companion studies published in Human Molecular Genetics by Paul ...
Study rebuts hypothesis that comet attacks ended 9,000-year-old Clovis culture
2013-01-31
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — Rebutting a speculative hypothesis that comet explosions changed Earth's climate sufficiently to end the Clovis culture in North America about 13,000 years ago, Sandia lead author Mark Boslough and researchers from 14 academic institutions assert that other explanations must be found for the apparent disappearance.
"There's no plausible mechanism to get airbursts over an entire continent," said Boslough, a physicist. "For this and other reasons, we conclude that the impact hypothesis is, unfortunately, bogus."
In a December 2012 American Geophysical ...
Research unlocks mystery surrounding the harnessing of fusion energy
2013-01-31
The research of a multi-institutional team from the U.S., Japan, and France, led by Predrag S. Krstic of the Joint Institute for Computational Sciences and Jean Paul Allain of Purdue University has answered the question of how the behavior of plasma—the extremely hot gases of nuclear fusion—can be controlled with ultra-thin lithium films on graphite walls lining thermonuclear magnetic fusion devices.
"It is remarkable that seemingly insignificant lithium depositions can profoundly influence the behavior of something as powerful as fusion plasmas," Krstic said.
Krstic ...
Outdoor fast food ads could promote obesity, study finds
2013-01-31
Past studies have suggested a relationship between neighborhood characteristics and obesity, as well as a connection between obesity and advertisements on television and in magazines.
Now, new research from UCLA has identified a possible link between outdoor food ads and a tendency to pack on pounds. The findings, researchers say, are not encouraging.
In a study published online in the peer-reviewed journal BMC Public Health, Dr. Lenard Lesser and his colleagues suggest that the more outdoor advertisements promoting fast food and soft drinks there are in a given ...
UCI team finds new target for treating wide spectrum of cancers
2013-01-31
Irvine, Calif., Jan. 30, 2013 — UC Irvine biologists, chemists and computer scientists have identified an elusive pocket on the surface of the p53 protein that can be targeted by cancer-fighting drugs. The finding heralds a new treatment approach, as mutant forms of this protein are implicated in nearly 40 percent of diagnosed cases of cancer, which kills more than half a million Americans each year.
In a study published online this week in Nature Communications, the UC Irvine researchers describe how they employed a computational method to capture the various shapes ...
This is what a fish thought looks like
2013-01-31
VIDEO:
A double-transgenic larva was embedded in agarose, and a spot was presented on an LCD display placed on the right-eye side. Ca2+ signals were detected on the left tectum upon...
Click here for more information.
For the first time, researchers have been able to see a thought "swim" through the brain of a living fish. The new technology is a useful tool for studies of perception. It might even find use in psychiatric drug discovery, according to authors of the study, ...
More links found between schizophrenia and cardiovascular disease
2013-01-31
A new study, to be published in the Feb. 7, 2013 issue of the American Journal of Human Genetics, expands and deepens the biological and genetic links between cardiovascular disease and schizophrenia. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of premature death among schizophrenia patients, who die from heart and blood vessel disorders at a rate double that of persons without the mental disorder.
"These results have important clinical implications, adding to our growing awareness that cardiovascular disease is under-recognized and under-treated in mentally ill ...