(Press-News.org)
VIDEO:
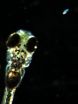
A double-transgenic larva was embedded in agarose, and a spot was presented on an LCD display placed on the right-eye side. Ca2+ signals were detected on the left tectum upon...
Click here for more information.
For the first time, researchers have been able to see a thought "swim" through the brain of a living fish. The new technology is a useful tool for studies of perception. It might even find use in psychiatric drug discovery, according to authors of the study, appearing online on January 31 in Current Biology, a Cell Press publication.
"Our work is the first to show brain activities in real time in an intact animal during that animal's natural behavior," said Koichi Kawakami of Japan's National Institute of Genetics. "We can make the invisible visible; that's what is most important."
VIDEO:
Calcium signals are evoked by a swimming paramecium.
Click here for more information.
The technical breakthrough included the development of a very sensitive fluorescent probe to detect neuronal activity. Kawakami, along with Junichi Nakai of Saitama University and their colleagues, also devised a genetic method for inserting that probe right into the neurons of interest. The two-part approach allowed the researchers to detect neuronal activity at single-cell resolution in the zebrafish brain.
Akira Muto, the study's lead author from the Kawakami lab, used the new tool to map what happens when a zebrafish sees something good to eat, in this case a swimming paramecium. The researchers were also able to correlate brain activity with that prey's capture.
The new tool now makes it possible to ask which brain circuits are involved in complex behaviors, from perception to movement to decision making, the researchers say, noting that the basic design and function of a zebrafish brain is very much like our own.
"In the future, we can interpret an animal's behavior, including learning and memory, fear, joy, or anger, based on the activity of particular combinations of neurons," Kawakami said.
By monitoring neuronal activity in the zebrafish brain, Kawakami thinks that researchers may also be able to screen chemicals that affect neuronal activity in the brain. "This has the potential to shorten the long processes for the development of new psychiatric medications," he said.
INFORMATION:
Current Biology, Muto et al.: "Real-time visualization of neuronal activity during perception."
This is what a fish thought looks like
2013-01-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
More links found between schizophrenia and cardiovascular disease
2013-01-31
A new study, to be published in the Feb. 7, 2013 issue of the American Journal of Human Genetics, expands and deepens the biological and genetic links between cardiovascular disease and schizophrenia. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of premature death among schizophrenia patients, who die from heart and blood vessel disorders at a rate double that of persons without the mental disorder.
"These results have important clinical implications, adding to our growing awareness that cardiovascular disease is under-recognized and under-treated in mentally ill ...
Identifying all factors modulating gene expression is actually possible!
2013-01-31
It was in trying to answer a question related to the functioning of our biological clock that a team lead by Ueli Schibler, a professor at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, has developed a method whose applications are proving to be countless. The researchers wanted to understand how 'timed' signals, present in the blood and controlled by our central clock, located in the brain, act on peripheral organs. In order to identify gene activator proteins, called transcription factors, involved in this process, they have developed an original screening technique called ...
Discovery opens the door to a potential 'molecular fountain of youth'
2013-01-31
Berkeley — A new study led by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, represents a major advance in the understanding of the molecular mechanisms behind aging while providing new hope for the development of targeted treatments for age-related degenerative diseases.
Researchers were able to turn back the molecular clock by infusing the blood stem cells of old mice with a longevity gene and rejuvenating the aged stem cells' regenerative potential. The findings will be published online Thursday, Jan. 31, in the journal Cell Reports.
The biologists found ...
Marriage reduces the risk of heart attack in both men and women and at all ages
2013-01-31
Sophia Antipolis, 31 January 2013. A large population-based study from Finland has shown that being unmarried increases the risk of fatal and non-fatal heart attack in both men and women whatever their age. Conversely, say the study investigators, especially among middle-aged couples, being married and cohabiting are associated with "considerably better prognosis of acute cardiac events both before hospitalization and after reaching the hospital alive".
The study, published today in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, was based on the FINAMI myocardial infarction ...
Jocks beat bookworms on brain test
2013-01-31
This press release is available in French.
English Premier League soccer players, NHL hockey players, France's Top 14 club rugby players, and even elite amateur athletes have better developed cognitive functions than the average university student, according to a perception study undertaken by Professor Jocelyn Faubert of the University of Montreal's School of Optometry. The study demonstrates a possible outcome of the increased cortical thickness that has been found in areas of trained athletes' brains. It also offers researchers new avenues for exploring the treatment ...
Scientists identify culprit in obesity-associated high blood pressure
2013-01-31
Obesity and its related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and stroke are among the most challenging of today's healthcare concerns.
Together, they constitute the biggest killer in western society. New findings, published in Cell, have identified a target that could hold the key to developing safe therapies to treat obesity and its associated conditions.
Although recent research has begun to unravel some of the pathways that control how information is processed by our nervous system regulating body weight and cardiovascular function, the exact ...
How cancer cells rewire their metabolism to survive
2013-01-31
LA JOLLA, Calif., January 31, 2013 – Cancer cells need food to survive and grow. They're very good at getting it, too, even when nutrients are scarce. Many scientists have tried killing cancer cells by taking away their favorite food, a sugar called glucose. Unfortunately, this treatment approach not only fails to work, it backfires—glucose-starved tumors actually get more aggressive. In a study published January 31 in the journal Cell, researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute discovered that a protein called PKCζ is responsible for this paradox. The ...
Leading researchers warn of 'brain drain' as scientists struggle to find funding
2013-01-31
Clarksburg, Md. – BrightFocus Foundation, a nonprofit organization that funds research worldwide to save sight and mind, today released the results of a survey of more than 170 leading biomedical scientists that explores the most significant barriers to progress in ending brain and eye diseases. The survey indicates that a lack of dependable funding is threatening to create a deficit of highly skilled scientists at a time when the nation could soon face a health care crisis brought on by devastating disorders like Alzheimer's, macular degeneration, and glaucoma.
"Cures ...
A 'neurosteroid' found to prevent brain injury caused by HIV/AIDS
2013-01-31
Bethesda, MD—A team of scientists from Canada, Thailand and Morocco have found that DHEA-S may prevent neurocognitive impairment that affects a significant percentage of AIDS patients. In a report appearing in the February 2013 issue of The FASEB Journal, they describe how a network of steroid molecules found in the brain, termed "neurosteroids," is disrupted during HIV infection leading to brain damage. This suggests that treatment with one of these steroid molecules, called DHEA-S, may offset the disruption caused by the virus to prevent or reduce brain damage.
"From ...
Health care providers may be at greater risk of flu exposure
2013-01-31
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Jan. 31, 2013 – Some people with the flu emit more of the air-borne virus than others, suggesting that the current recommendations for infection control among health care providers may not be adequate, according to a new study from researchers at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center.
The study is published in the Jan. 31 online edition of The Journal of Infectious Disease.
"Our study provides new evidence that infectiousness may vary between influenza patients and questions the current medical understanding of how influenza spreads," said Werner Bischoff, ...