(Press-News.org) Malaria in pregnancy causes a range of adverse effects, including abortions, stillbirths, premature delivery and low infant birth weight. Many of these effects are thought to derive from a placental inflammatory response resulting from interaction of infected red blood cells with the placental tissue. In a study published in the latest issue of the journal PLOS Pathogen*, a researchers' team led by Carlos Penha-Gonçalves at the Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (IGC), Portugal, observed, for the first time, the mouse placental circulation and showed how it can influence the malaria parasite behavior and infection. Their results indicate a higher accumulation of parasites in placental regions with low blood flow, being these areas more prone to an inflammatory response.
In humans, red blood cells infected with the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, accumulate in the placenta via interaction with a molecule expressed on the placental tissue – a process called sequestration. In response to this event, placental cells secrete substances that recruit inflammatory cells leading to placental damage and negatively impacting fetal growth. Until now placental circulation has not been linked to the infected red blood cell sequestration. In fact, it is not trivial to investigate this hypothesis in human placenta, due to technical constraints
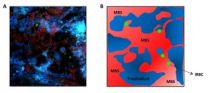
Luciana Moraes, an investigator of Carlos Penha-Gonçalves laboratory, has provided new insights to this issue by developing an experimental system that allowed the live observation of the blood flow in the mouse placenta. Mating two strains of mice, one of them with cells stained with a colorful marker, Luciana was able to identify the placental tissue (fetus origin). In collaboration with Carlos Tadokoro's laboratory at the IGC, the investigators developed a microscopy technique that allowed the observation of the placenta in a living mouse. Immediately before exposure to the microscope the mouse was injected with a fluorescent substance that labels the blood. With this set-up it was possible to distinguish maternal blood and placental tissue. The results showed for the first time how the circulation occurs in the placenta, and that the blood flows with different speeds in different regions of the placenta.
Next, the investigators infected red blood cells with the malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei, stained with a different color, and observed – live – the behavior of the parasite inside the placenta. They observed that in the areas with higher blood flow, the parasite never stops moving and does not interact with the placental tissue. The accumulation of parasite just occurs in areas of low or absence of flow. In these regions, placental macrophages engulf the infected red blood cells to attempt parasite clearance. Their observations also suggest that movements of the placental tissue may control the blood flow.
Luciana Moraes says: "Our results indicate that binding of infected red blood cells to a molecule expressed in the placenta may not be the only mechanism of parasite sequestration. The dynamics of placental circulation may also play an important role, and should be considered when designing therapeutics."
Carlos Penha-Gonçalves adds: "This is the first study done that shows live how placental blood circulation impacts on the local infection by the malaria parasite. It would be interesting and worthwhile to explore if a similar process occurs in the placenta of humans, taking in consideration that microcirculation in human placenta is quite different."
INFORMATION:
This study was done in collaboration with University of Vigo, Spain, and was funded by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, Portugal.
* de Moraes LV, Tadokoro CE, Gómez-Conde I, Olivieri DN, Penha-Gonçalves C (2013) Intravital Placenta Imaging Reveals Microcirculatory Dynamics Impact on Sequestration and Phagocytosis of Plasmodium-Infected Erythrocytes. PLoS Pathog 9(1): e1003154.
doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003154.
Placental blood flow can influence malaria during pregnancy
2013-02-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sequencing hundreds of chloroplast genomes now possible
2013-02-01
Researchers at the University of Florida and Oberlin College have developed a sequencing method that will allow potentially hundreds of plant chloroplast genomes to be sequenced at once, facilitating studies of molecular biology and evolution in plants.
The chloroplast is the compartment within the plant cell that is responsible for photosynthesis and hence provides all of the sugar that a plant needs to grow and survive. The chloroplast is unusual in containing its own DNA genome, separate from the larger and dominant genome that is located in every cell's nucleus. ...
Examining the so-called Basque mutation of Parkinson's
2013-02-01
This press release is available in Spanish.
The relationship between genetics and Parkinson's has been investigated for more than a decade, but it is only over the last few years that significant results have begun to be obtained. The first mutations related to the development of this disease were found in 2004. A team from the UPV/EHU-University of the Basque Country came across a mutation of the LRRK2 gene, which is particularly prevalent among the population of Gipuzkoa. It is the R1441G mutation and is known as the Basque mutation. Now, Doctor Javier Ruiz, a doctor ...
NASA sees a coronal mass ejection erupt from the sun
2013-02-01
On Jan. 31, 2013 at 2:09am EST, the sun erupted with an Earth-directed coronal mass ejection or CME. Experimental NASA research models, based on observations from the Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) and ESA/NASA's Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, show that the CME left the sun at speeds of around 575 miles per second, which is a fairly typical speed for CMEs. Historically, CMEs at this speed are mild.
Not to be confused with a solar flare, a CME is a solar phenomenon that can send solar particles into space and reach Earth one to three days later.
Earth-directed ...
The effective collective: Grouping could ensure animals find their way in a changing environment
2013-02-01
For social animals such as schooling fish, the loss of their numbers to human activity could eventually threaten entire populations, according to a finding that such animals rely heavily on grouping to effectively navigate their environment.
Princeton University researchers report in the journal Science that collective intelligence is vital to certain animals' ability to evaluate and respond to their environment. Conducted on fish, the research demonstrated that small groups and individuals become disoriented in complex, changing environments. However, as group size is ...
Evidence of geological 'facelift' in the Appalachians
2013-02-01
How does a mountain range maintain its youthful, rugged appearance after 200 million years without tectonic activity? Try a geological facelift – courtesy of the earth's mantle.
Researchers from North Carolina State University noticed that a portion of the Appalachian Mountains in western North Carolina near the Cullasaja River basin was topographically quite different from its surroundings. They found two distinct landscapes in the basin: an upper portion with gentle, rounded hills, where the average distance from valley to mountain top was about 500 feet; and a lower ...
Genome-wide atlas of gene enhancers in the brain online
2013-02-01
Future research into the underlying causes of neurological disorders such as autism, epilepsy and schizophrenia, should greatly benefit from a first-of-its-kind atlas of gene-enhancers in the cerebrum (telencephalon). This new atlas, developed by a team led by researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) is a publicly accessible Web-based collection of data that identifies and locates thousands of gene-regulating elements in a region of the brain that is of critical importance for cognition, motor functions ...
New role for DNA methylation in subset of premature aging disorder patients
2013-02-01
Scientists at the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute in Barcelona, Spain have found new evidence for the role of epigenetic changes (those heritable alterations in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in DNA sequence) on premature aging diseases. A new study published in the journal Epigenetics on Jan. 1, 2013, identified a role for DNA methylation changes in a subset of Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria and Werner Syndrome patients, for which no genetic cause (such as DNA mutation) had been associated with onset disease. The study, titled "Aberrant DNA ...
Safe sex practices among African American women
2013-02-01
Los Angeles, CA (January 31, 2013) Researchers have found that African American women exhibit a higher risk for sexually transmitted infections including HIV/Aids. But what motivates this group of women to have sex? And when are they more likely to use protection?
A new study published today in Health Education & Behavior (a SAGE journal) found that regardless of motivations for having sex, condom use expectations were less than 50% for all types of sexual encounters, including the riskiest types of sex.
Researchers Julianna Deardorff et. al used a combination of interviews ...
Men taking long-acting chronic pain meds 5xs more likely to have low testosterone levels
2013-02-01
OAKLAND, Calif., January 31, 2013 — Low testosterone levels occur five times more often among men who take long-acting instead of short-acting opioids for chronic pain, according to a new Kaiser Permanente study published in The Clinical Journal of Pain.
While it has been known that opioids cause low testosterone in men, this study is the first to show a significant difference in risk between short-acting (immediate release) and long-acting opioids.
The 81 men in the retrospective study were between 26 and 79 years old (median age 51) and were seen in the chronic-pain ...
New device traps particulates, kills airborne pathogens
2013-02-01
A new device called a soft x-ray electrostatic precipitator protected immunocompromised mice from airborne pathogenic bacteria, viruses, ultrafine particles, and allergens, according to a paper published online ahead of print in the journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology. This device, known for short as a SXC ESP, is highly versatile, with multiple potential uses, and Washington University is working on licensing the technology.
"Small particles are difficult to remove, and our device overcomes that barrier," says Pratim Biswas of Washington University, St. Louis. ...