(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR—Women in developed countries survive roughly 10 years longer after a breast cancer diagnosis compared to women in poor-to-middle-income countries, a new University of Michigan study suggests.
The report demonstrates the lack of access to good health care faced by women in poor countries, said the study's principal investigator Rajesh Balkrishnan, an associate professor at the U-M schools of Pharmacy and Public Health.
Early diagnosis and sustained treatment were the biggest hurdles and also the main indicators of patient survival, he said.
Balkrishnan and colleagues looked at roughly 300 women in the southern rural district of Udupi, India. Patients received one of three chemotherapy drug regimens depending on the stage of cancer. Only about 27 percent of patients were diagnosed in the early stages of cancer, and they survived an average of 11 years. The majority of patients were diagnosed in later or advanced stages, and they survived from about one to two-and-a-half years after diagnosis and treatment.
Many diagnoses occur at later stages because screening isn't available in those rural areas, Balkrishnan said. Fear, poverty and ignorance about breast cancer also delay treatment and diagnosis. And, if the diagnosis does come early, access and use of breast cancer chemotherapy treatments—even the generic inexpensive options—aren't readily available. Only the latest-stage patients receive the most current and expensive treatments, he said.
"I think if the tumor is diagnosed early and treated aggressively, a patient can expect an additional decade of survival," Balkrishnan said. "But access and adherence to optimal treatment remains very difficult for women in poorer countries."
Breast cancer is a growing problem in India, with estimates as high as 1 in 22 women predicted to develop the disease. While the breast cancer rate is much higher in the United States at 1 in 8 women, the survival rate is also much higher. For instance, the five-year survival rate for Indian women is about 60 percent; in developed countries, it is 79-85 percent. Additionally, studies have shown that Indian women develop breast cancer roughly a decade earlier than women in Western countries.
There are about 1.4 million new cases of breast cancer worldwide annually, and it comprises 10 percent of all cancers, making it the second most common cancer in the world.
Other researchers included: Daisy Augustine, Anantha Naik Nagappa, Nayanibhirama Udupa and B.M. Vadiraja, all affiliated with Manipal University in India.
INFORMATION:
Rajesh Balkrishnan: http://sitemaker.umich.edu/rajesh.balkrishnan/home
END
VIDEO:
NIMH's Dr. Maura Furey talks about how a functional brain imaging measure may help predict a patient's response to a rapid-acting experimental antidepressant.
Click here for more information.
A telltale boost of activity at the back of the brain while processing emotional information predicted whether depressed patients would respond to an experimental rapid-acting antidepressant, a National Institutes of Health study has found.
"We have discovered a potential ...
Healthy eating not only promotes growth and development, but also provides important opportunities for children to socialize during meals. A new, comprehensive analysis of feeding behavior in children with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) indicates that these children are five times more likely to have a feeding problem, including extreme tantrums during meals, severe food selectivity and ritualistic mealtime behaviors.
Researchers at Marcus Autism Center and the Department of Pediatrics at Emory University School of Medicine conducted a comprehensive meta-analysis of ...
A new NOAA research report finds that both fish populations and commercial and recreational anglers have benefited from "no-take" protections in the Tortugas Ecological Reserve in the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary.
The report, "An Integrated Biogeographic Assessment of Reef Fish Populations and Fisheries in Dry Tortugas: Effects of No-take Reserves," is the first to evaluate how the 151-square nautical mile Tortugas Ecological Reserve affects the living marine resources of the region and the people whose livelihoods are connected to them.
The report's analysis ...
Boston, MA – Having adequate levels of vitamin D during young adulthood may reduce the risk of adult-onset type 1 diabetes by as much as 50%, according to researchers at Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH). The findings, if confirmed in future studies, could lead to a role for vitamin D supplementation in preventing this serious autoimmune disease in adults. The study was published online February 3, 2013 and will appear in the March 1 print edition of the American Journal of Epidemiology.
"It is surprising that a serious disease such as type 1 diabetes could perhaps ...
According to a new technical report, the effects of climate change will continue to threaten the health and vitality of U.S. coastal communities' social, economic and natural systems. The report, Coastal Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerabilities: a technical input to the 2013 National Climate Assessment, authored by leading scientists and experts, emphasizes the need for increased coordination and planning to ensure U.S. coastal communities are resilient against the effects of climate change.
The recently-released report examines and describes climate change impacts on ...
LA JOLLA, CA – February 4, 2013 – A team led by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) has identified specific cellular events that appear key to lupus, a debilitating autoimmune disease that afflicts tens of millions of people worldwide. The findings suggest that blocking this pathway in lupus-triggering cells could be a potent weapon against the disease.
In the new study, described in an online Early Edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences the week of February 4, 2013, the researchers determined that the absence of a certain type ...
(Edmonton) A University of Alberta polar bear researcher along with eleven international co-authors are urging governments to start planning for rapid Arctic ecosystem change to deal with a climate change catastrophe for the animals.
U of A professor Andrew Derocher co-authored a policy perspective in the journal Conservation Letters urging governments with polar bear populations to accept that just one unexpected jump in Arctic warming trends could send some polar bear populations into a precipitous decline.
"It's a fact that early sea ice break-up and late ice freeze-up ...
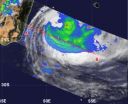
Cyclone Felleng traveled through the Mozambique Channel during the week of Jan. 28, 2013 and emerged south into the Southern Indian Ocean where it transitioned into a cold core low pressure area. NASA's TRMM satellite captured a look at the rainfall rates occurring in Felleng as it was making that transition on Feb. 1.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite flew over Cyclone Felleng on Feb. 1 at 1648 UTC (11:48 a.m. EST) as it was exiting the Mozambique Channel and becoming extra-tropical. TRMM measured a small area of heavy rainfall east of the center ...
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Researchers long have evaluated the roles parents play in children's development. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have found that mothers' directiveness, the extent to which they try to control the content and pace of young children's play, varies based on the children's ages and the mothers' ethnicities. In addition, the study found that the more directive the mothers were during play, the less engaged children were with them and the more negative emotion the children displayed toward their mothers.
"Children flourish when they have opportunities ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. – A five-year study by researchers at three universities has established that providing tangible assistance to others protects our health and lengthens our lives.
This, after more than two decades of research failed to establish that the same benefits accrue to the recipients of such help.
Principal investigator Michael J. Poulin, PhD, assistant professor of psychology at the University at Buffalo, says, "This study offers a significant contribution to the research literature on the relationship between social environment and health, and specifically to ...