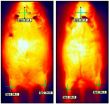
(Press-News.org) February 5, 2013—Ottawa—Ottawa scientists have discovered a trigger that turns muscle stem cells into brown fat, a form of good fat that could play a critical role in the fight against obesity. The findings from Dr. Michael Rudnicki's lab, based at the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, were published today in the prestigious journal Cell Metabolism.
"This discovery significantly advances our ability to harness this good fat in the battle against bad fat and all the associated health risks that come with being overweight and obese," says Dr. Rudnicki, a senior scientist and director for the Regenerative Medicine Program and Sprott Centre for Stem Cell Research at the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. He is also a Canada Research Chair in Molecular Genetics and professor in the Faculty of Medicine at the University of Ottawa.
Globally, obesity is the fifth leading risk for death, with an estimated 2.8 million people dying every year from the effects of being overweight or obese, according to the World Health Organization. The Public Health Agency of Canada estimates that 25% of Canadian adults are obese.
In 2007, Dr. Rudnicki led a team that was the first to prove the existence of adult skeletal muscle stem cells. In the paper published today, Dr. Rudnicki now shows (again for the first time) that these adult muscle stem cells not only have the ability to produce muscle fibres, but also to become brown fat. Brown fat is an energy-burning tissue that is important to the body's ability to keep warm and regulate temperature. In addition, more brown fat is associated with less obesity.
Perhaps more importantly, the paper identifies how adult muscle stem cells become brown fat. The key is a small gene regulator called microRNA-133, or miR-133. When miR-133 is present, the stem cells turn into muscle fibre; when reduced, the stem cells become brown fat.
Dr. Rudnicki's lab showed that adult mice injected with an agent to reduce miR-133, called an antisense oligonucleotide or ASO, produced more brown fat, were protected from obesity and had an improved ability to process glucose. In addition, the local injection into the hind leg muscle led to increased energy production throughout the body—an effect observed after four months.
Using an ASO to treat disease by reducing the levels of specific microRNAs is a method that is already in human clinical trials. However, a potential treatment using miR-133 to combat obesity is still years away.
"While we are very excited by this breakthrough, we acknowledge that it's a first step," says Dr. Rudnicki. "There are still many questions to be answered, such as: Will it help adults who are already obese to lose weight? How should it be administered? How long do the effects last? Are there adverse effects we have not observed yet?"
INFORMATION:
The full article, "MicroRNA-133 Controls Brown Adipose Determination in Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells by Targeting Prdm16," was published by Cell Metabolism online ahead of print on February 5, 2013. The article's authors are: Hang Yin, Alessandra Pasut, Vahab D. Soleimani, C. Florian Bentzinger, Ghadi Antoun, Stephanie Thorn, Patrick Seale, Pasan Fernando, Wilfred van IJcken, Frank Grosveld, Robert A. Dekemp, Robert Boushel, Mary-Ellen Harper, and Michael A. Rudnicki.
This research was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the National Institutes of Health, the Ontario Research Fund and EuTRACC, a European Commission 6th Framework grant. It was a collaboration that included researchers from the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, University of Ottawa, University of Ottawa Heart Institute, Nordion, Erasmus Medical Centre in the Netherlands and University of Copenhagen.
Media contacts
Paddy Moore
Manager, Communications and Public Relations,
Ottawa Hospital Research Institute
613-737-8899 x 73687
613-323-5680 (cell)
padmoore@ohri.ca
Néomie Duval
Media Relations Officer
University of Ottawa
613-562-5800 x2981
613-863-7221 (cell)
neomie.duval@uOttawa.ca
About the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute (OHRI)
The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute (OHRI) is the research arm of The Ottawa Hospital and is an affiliated institute of the University of Ottawa, closely associated with the university's Faculties of Medicine and Health Sciences. OHRI includes more than 1,700 scientists, clinical investigators, graduate students, postdoctoral fellows and staff conducting research to improve the understanding, prevention, diagnosis and treatment of human disease. Research at OHRI is supported by The Ottawa Hospital Foundation. www.ohri.ca
Research Bringing you Tomorrow's Health Care Today
About the University of Ottawa
The University of Ottawa is committed to research excellence and encourages an interdisciplinary approach to knowledge creation, which attracts the best academic talent from across Canada and around the world. It is an important stakeholder in the National Capital Region's economic development.
Fighting fat with fat: Stem cell discovery identifies potential obesity treatment
2013-02-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mammogram every 2 years has same benefit as yearly mammogram for older women, UCSF study finds
2013-02-05
Among older women, getting a mammogram every two years was just as beneficial as getting a mammogram annually, and led to significantly fewer false positive results, according to a study led by UC San Francisco.
The national study of more than 140,000 women between the ages of 66 and 89 appears online February 5, 2013, in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
"Screening every other year, as opposed to every year, does not increase the probability of late-stage breast cancer in older women," said lead author Dejana Braithwaite, PhD, a UCSF assistant professor ...
Cargo container research to improve buildings' ability to withstand tsunamis
2013-02-05
Anyone who has seen the movie "Impossible" or watched footage from the Japanese tsunami has learned the terror that can strike with little warning. In those cases, when there is no time to flee, there may still be time to reach higher ground, called vertical evacuation.
But as you race to the third floor, how do you know if the building will hold up? Walls of water are not the only danger. Another potentially lethal challenge is water-driven debris - such as 60,000-pound fully loaded cargo containers - transformed into projectiles. Often pulled behind semi-trucks on highways, ...
Olive oil component alleviates intestinal ischemia and reperfusion
2013-02-05
Here's another reason why you should include olive oil in your diet: A new research report published in the Journal of Leukocyte Biology suggests that at least one compound in olive oil significantly reduces intestinal ischemia (restricted blood supply) and the resulting reperfusion injury (tissue damage caused when blood supply returns). The compound, called "oleuropein aglycone," is the most prominent polyphenol found in olive oil and could become a novel therapeutic target aimed at treating intestinal ischemia and reperfusion injury in humans. Ultimately, this research ...
Flexible classroom design saves money, improves flexibility, accessibility of instruction
2013-02-05
Researchers at North Carolina State University have developed a classroom design that gives instructors increased flexibility in how to teach their courses and improves accessibility for students, while slashing administrative costs.
Specifically, the new classrooms take advantage of the fact that students are bringing their own technology – such as laptops – to class. The classrooms also include mobile infrastructure, where whiteboards, desks and tables can be reconfigured according to the needs of students and instructors.
"These classrooms work really well in terms ...
Chest pain prior to a heart attack can protect the heart
2013-02-05
MINNEAPOLIS, MN – Feb. 5, 2013 – Patients who experience chest pain in the 24 hours preceding a heart attack, also called preinfarction angina, have smaller heart attacks and improved cardiac function in the contemporary cardiac stenting era, researchers found in a study published Jan. 22 in Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions.
"Even before we began treating heart attack patients with angioplasty and stenting, physicians recognized that patients with chest pain prior to their heart attack seem to have better outcomes," says the study's senior author, Jay H. Traverse, ...
Precise Point Positioning and real-time positioning accuracy for COMPASS satellite navigation
2013-02-05
COMPASS uses the Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) and Inclined Geosynchronous Satellite Orbit (IGSO) satellites, which are more suitable for regional services. Its constellation is composed of 14 satellites, including 5 GEO, 5 IGSO satellites and 4 Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellites. As of 2012, 13 satellites have been launched. Except for G2 (unusable) and M1 (testing only), the remaining 11 satellites, including 4GEO+5IGSO+2MEO, have successfully transmitted signals and broadcasted navigational messages, to prepare for full operation starting in 2013.
Positioning accuracy ...
The zebrafish revealed a central regulator for the development of the brain histamine system
2013-02-05
Research has shown that mutations in the psen1 gene are common in the familial forms of Alzheimer's disease, and the Presenilin-1 protein that the gene encodes is known to be involved in the cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein. In Alzheimer's disease the amyloid precursor protein is not cleaved the normal way, and the protein accumulates in the brain damaging neuronal tracts and neurons. It is still unknown if the psen1 gene is involved in the etiology of Alzheimer's disease via another mechanism.
Professor Pertti Panula's research team at the University of Helsinki ...
Growth arrest in prostate cancer
2013-02-05
A previously poorly investigated signalling pathway is crucial for the growth and proliferation of prostate cancer cells. An international research team discovered this when studying the enzyme "soluble adenylyl cyclase" that produces the second messenger molecule cAMP. When the scientists inhibited the enzyme, the cancer cell proliferation was suppressed. The team led by Dr. Yury Ladilov from the Department of Clinical Pharmacology at the Ruhr-Universität Bochum reported together with colleagues from the Department of Urology at the RUB and the Cornell University in New ...
A review of the rapidly evolving field of topological insulator hybrid structures
2013-02-05
Topological insulators are novel materials that are insulating in the bulk but have surface states that are conducting. These surface states are topologically protected and possess several intriguing properties with the promise of potential applications. As a result, topological insulators have attracted many theoretical and experimental studies in the last few years. More recently, the potential of interfacing topological insulators with other materials with quantum states to make hybrid structures has been recognized and a slew of new studies are underway. Professor Jian ...
1 out of 4 lung cancer patients in Andalusia does not receive the radiotherapy they need
2013-02-05
A study conducted by University of Granada and Virgen de las Nieves U.H. researchers has revealed that in Andalusian public hospitals radiotherapy is provided to lung cancer patients with a frequency 25 % below that established by clinical protocols. Failure to provide such treatment results in a total of 3,000 survival-day loss for all lung cancer patients.
To carry out this study –recently published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology–, the researchers reviewed the medical records and radiotherapy provided to all lung cancer patients in 2007 in the 12 Andalusian public ...