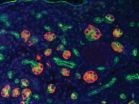
(Press-News.org) Miniaturized laboratory-on-chip systems promise rapid, sensitive, and multiplexed detection of biological samples for medical diagnostics, drug discovery, and high-throughput screening. Using micro-fabrication techniques and incorporating a unique design of transistor-based heating, researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign are further advancing the use of silicon transistor and electronics into chemistry and biology for point-of-care diagnostics.
Lab-on-a-chip technologies are attractive as they require fewer reagents, have lower detection limits, allow for parallel analyses, and can have a smaller footprint.
"Integration of various laboratory functions onto microchips has been intensely studied for many years," explained Rashid Bashir, an Abel Bliss Professor of electrical and computer engineering and of bioengineering at Illinois. "Further advances of these technologies require the ability to integrate additional elements, such as the miniaturized heating element, and the ability to integrate heating elements in a massively parallel format compatible with silicon technology.
"In this work, we demonstrated that we can heat nanoliter volume droplets, individually and in an array, using VLSI silicon based devices, up to temperatures that make it interesting to do various biochemical reactions within these droplets."
"Our method positions droplets on an array of individual silicon microwave heaters on chip to precisely control the temperature of droplets-in-air, allowing us to perform biochemical reactions, including DNA melting and detection of single base mismatches," said Eric Salm, first author of the paper, "Ultralocalized thermal reactions in subnanoliter droplets-in-air," published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) on February 12.
According to Salm, approaches to perform localized heating of these individual subnanoliter droplets can allow for new applications that require parallel, time-, and space multiplex reactions on a single integrated circuit. Within miniaturized laboratory-on-chips, static and dynamic droplets of fluids in different immiscible media have been used as individual vessels to perform biochemical reactions and confine the products.
"This technology makes it possible to do cell lysing and nucleic acid amplification reactions within these individual droplets – the droplets are the reaction vessels or cuvettes that can be individually heated," Salm added.
"We also demonstrate that ssDNA probe molecules can be placed on heaters in solution, dried, and then rehydrated by ssDNA target molecules in droplets for hybridization and detection," said Bashir, who is director of the Micro and Nanotechnology Laboratory at Illinois. "This platform enables many applications in droplets including hybridization of low copy number DNA molecules, lysing of single cells, interrogation of ligand–receptor interactions, and rapid temperature cycling for amplification of DNA molecules.
"Notably," Bashir added, "our miniaturized heater could also function as dual heater/sensor elements, as these silicon-on-insulator nanowire or nanoribbon structures have been used to detect DNA, proteins, pH, and pyrophosphates.
By using microfabrication techniques and incorporating the unique design of transistor-based heating with individual reaction volumes, 'laboratory-on-a-chip' technologies can be scaled down to 'laboratory-on-a-transistor' technologies as sensor/heater hybrids that could be used for point-of-care diagnostics."
###
In addition to Salm and Bashir, co-authors of the study included Carlos Duarte Guevara, Piyush Dak, Brian Ross Dorvel, and Bobby Reddy, Jr. at the University of Illinois; and Muhammad Ashraf Alam, Birck Nanotechnology Center and the School of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Purdue University.
Building a biochemistry lab on a chip
2013-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows that problem-solving training helps mothers cope with child's cancer diagnosis
2013-02-13
A multi-site clinical trial including the University of Colorado Cancer Center shows that the benefit of Bright IDEAS problem-solving skills training goes beyond teaching parents to navigate the complex medical, educational, and other systems that accompany a child's diagnosis of cancer – the training also leads to durable reduction in mothers' levels of anxiety and symptoms of posttraumatic stress, and improves overall coping with a child's illness. Results of the study were published online last week in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
"Earlier research shows that ...
Molecular master switch for pancreatic cancer identified, potential predictor of treatment outcome
2013-02-13
PHILADELPHIA – A recently described master regulator protein may explain the development of aberrant cell growth in the pancreas spurred by inflammation
A team from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania profiled gene expression of mouse pancreatic ductal and duct-like cells from different states - embryonic development, acute pancreatitis and K-ras mutation-driven carcinogenesis - to find the molecular regulation of these processes.
Broadly speaking, two cellular compartments are important in a normal pancreas, endocrine cells, which produce ...
Marketing technique: Activating gender stereotypes just to knock 'em down
2013-02-13
In certain circles, such as publishing, it has been well-documented that female authors have taken male pen names to attract a larger audience and/or get their book published. But should marketers actually highlight gender and activate stereotypes to sell more products?
A new study by USC Marshall Professor Valerie Folkes and Ohio State University Professor Shashi Matta looks at the issue of product perception of consumers through the lens of gender stereotypes. The researchers conclude that while traditional gender stereotypes can still have a significant influence on ...
Cities can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 70 percent, says U of T researcher
2013-02-13
TORONTO, ON – Cities around the world can significantly reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by implementing aggressive but practical policy changes, says a new study by University of Toronto Civil Engineering Professor Chris Kennedy and World Bank climate change specialist Lorraine Sugar, one of Kennedy's former students.
Kennedy and Sugar make the claim in 'A low carbon infrastructure plan for Toronto, Canada,' published in the latest issue of The Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering. The paper aims to show how cities can make a positive difference using realistic, ...
Stanford scientist uncovers the reproductive workings of a harvester ant dynasty
2013-02-13
Ants are just about everywhere you look, and yet it's largely unknown how they manage to be so ubiquitous. Scientists have understood the carnal mechanism of ant reproduction, but until now have known little of how successful the daughters of a colony are when they attempt to found new colonies.
For the first time, Stanford biologists have been able to identify specific parent ants and their own children in wild ant colonies, making it possible to study reproduction trends.
And in a remarkable display of longevity, an original queen ant was found to be producing new ...
Major clinical trial finds no link between genetic risk factors and 2 top wet AMD treatments
2013-02-13
SAN FRANCISCO – February 12, 2013 – New findings from a landmark clinical trial show that although certain gene variants may predict whether a person is likely to develop age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a potentially blinding eye disease that afflicts more than nine million Americans, these genes do not predict how patients will respond to Lucentis™ and Avastin™, the two medications most widely used to treat the "wet" form of AMD. This new data from the Comparison of AMD Treatment Trials (CATT), published online in Ophthalmology, the journal of the American Academy ...
Explosive breakthrough in research on molecular recognition
2013-02-13
Edmonton—Ever wonder how sometimes people still get through security with explosives on their person? Research done in the University of Alberta's Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering has revealed a new way to better detect these molecules associated with explosive mixtures.
A team of researchers including post-doctoral fellows Seonghwan Kim, Dongkyu Lee and Xuchen Liu, with research associate Charles Van Neste, visiting professor, Sangmin Jeon from the Pohang University of Science and Technology (South Korea), and Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering ...
Lower autism risk with folic acid supplements in pregnancy
2013-02-13
Women who took folic acid supplements in early pregnancy almost halved the risk of having a child with autism. Beginning to take folic acid supplements later in pregnancy did not reduce the risk. This is shown in new findings from the ABC Study and Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study published in the Journal of The American Medical Association (JAMA).
Women who took folic acid supplements from four weeks before conception to eight weeks into pregnancy had a 40 per cent lower risk of giving birth to children with childhood autism (classic autism). Use of folic acid ...
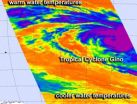
NASA sees Cyclone Gino wind up to wind down later
2013-02-13
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Cyclone Gino as the storm continues to wind up in the southern Indian Ocean, consolidating and strengthening. Infrared data shows the storm has strengthened but it is headed for cooler waters which will weaken it in coming days.
On Feb. 12 at 0841 UTC, NASA Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard the Aqua satellite captured infrared imagery of Cyclone Gino that showed the storm developed a large area of very cold, high cloud top temperatures around its center indicating powerful thunderstorms. Cloud top temperatures ...
NASA provides satellite views of nor'easter lifespan
2013-02-13
NASA and NOAA satellites have provided animations and images of the coupling of two low pressure areas that created the now historic winter-time nor'easter that brought more than two feet of snow to portions of the New England states on Feb. 8 and 9, 2013. NASA released an animation of NOAA satellite imagery that shows the lifetime of the historic nor'easter.
The nor'easter dropped between 2 and 3 feet of snowfall over the U.S. Northeast and left more than 650,000 without power in eight states, according to the Associated Press. Several governors established travel bans ...