(Press-News.org) PITTSBURGH—When faced with a difficult decision, it is often suggested to "sleep on it" or take a break from thinking about the decision in order to gain clarity.
But new brain imaging research from Carnegie Mellon University, published in the journal "Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience," finds that the brain regions responsible for making decisions continue to be active even when the conscious brain is distracted with a different task. The research provides some of the first evidence showing how the brain unconsciously processes decision information in ways that lead to improved decision-making.
"This research begins to chip away at the mystery of our unconscious brains and decision-making," said J. David Creswell, assistant professor of psychology in CMU's Dietrich College of Humanities and Social Sciences and director of the Health and Human Performance Laboratory. "It shows that brain regions important for decision-making remain active even while our brains may be simultaneously engaged in unrelated tasks, such as thinking about a math problem. What's most intriguing about this finding is that participants did not have any awareness that their brains were still working on the decision problem while they were engaged in an unrelated task."
For the study, Creswell, recent CMU graduate James K. Bursley and Northeastern University's Ajay B. Satpute presented 27 healthy adults with information about cars and other items while undergoing neuroimaging. Then, before being asked to make decisions about the items, the participants had to complete a difficult distractor task — memorizing sequences of numbers — to prevent them from consciously thinking about the decision information.
The results included three main findings. First, the team confirmed previous research demonstrating that a brief period of distraction — in this case two minutes — produced higher quality decisions about the cars and other items. But did this effect occur because the distraction period provided an opportunity for the brain to take a break from decision-making and then return to the problem with a fresh look? Or alternatively, does the brain continue to unconsciously process decision information during this distraction period? This research supports the latter unconscious processing explanation.
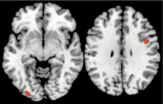
When the participants were initially learning information about the cars and other items, the neuroimaging results showed activation in the visual and prefrontal cortices, regions that are known to be responsible for learning and decision-making. Additionally, during the distractor task, both the visual and prefrontal cortices continued to be active — or reactivated — even though the brain was consciously focused on number memorization.
Third, the results showed that the amount of reactivation within the visual and prefrontal cortices during the distractor task predicted the degree to which participants made better decisions, such as picking the best car in the set.
"We all face difficult problems we need to solve on a regular basis," Creswell said. "Whether it's buying a new car, finding a new apartment to rent, or seeking out a new dating partner on social networking sites. This study provides some of the first clues for how our brains process this information for effective problem-solving and decision-making."
Bursley (DC'12), who joined CMU's Health and Human Performance Laboratory as a freshman, spent his undergraduate career working on this research and related studies. To support his work, he received a Small Undergraduate Research Grant (SURG) and Summer Undergraduate Research Fellowship (SURF). Bursley also received a Rothberg Research Award in Human Brain Imaging, made possible by Carnegie Mellon alumnus and trustee Jonathan M. Rothberg (E'85), founder of four genetics companies aimed at improving human health.
"Carnegie Mellon was the perfect place to carry out this work because there's a significant focus here on pursuing new directions in mind-brain research," Bursley said. "This study is really a starting point. We also are using brain imaging to see if we find the same reactivation patterns in learning tasks that we saw here in decision-making."
INFORMATION:
CMU's Department of Psychology has helped to establish Carnegie Mellon as a world leader in brain sciences. The university recently launched a Brain, Mind and Learning initiative to build from its research excellence in psychology, computer science and computation to continue to solve real-world problems.
For more information on how distraction improves decision-making, watch this video: http://youtu.be/eFX5S0tpTUA.
The Pittsburgh Life Sciences Greenhouse Opportunity Fund supported this research.
Carnegie Mellon brain imaging research shows how unconscious processing improves decision-making
Findings reveal that unconscious brain activity leads to better decisions
2013-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study in mice yields Angelman advance
2013-02-13
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — In a new study in mice, a scientific collaboration centered at Brown University lays out in unprecedented detail a neurological signaling breakdown in Angelman syndrome, a disorder that affects thousands of children each year, characterized by developmental delay, seizures, and other problems. With the new understanding, the team demonstrated how a synthesized, peptide-like compound called CN2097 works to restore neural functions impaired by the disease.
"I think we are really beginning to understand what's going wrong. That's what's ...
A neural basis for benefits of meditation
2013-02-13
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Why does training in mindfulness meditation help patients manage chronic pain and depression? In a newly published neurophysiological review, Brown University scientists propose that mindfulness practitioners gain enhanced control over sensory cortical alpha rhythms that help regulate how the brain processes and filters sensations, including pain, and memories such as depressive cognitions.
The proposal, based on published experimental results and a validated computer simulation of neural networks, derives its mechanistic framework ...
Wetland trees a significant overlooked source of methane, study finds
2013-02-13
Wetlands are a well-established and prolific source of atmospheric methane. Yet despite an abundance of seething swamps and flooded forests in the tropics, ground-based measurements of methane have fallen well short of the quantities detected in tropical air by satellites.
In 2011, Sunitha Pangala, a PhD student at The Open University, who is co-supervised by University of Bristol researcher Dr Ed Hornibrook, spent several weeks in a forested peat swamp in Borneo with colleague Sam Moore, assessing whether soil methane might be escaping to the atmosphere by an alternative ...
3 'Bigfoot' genomes sequenced in 5-year DNA study
2013-02-13
Dallas, Feb. 13--The multidisciplinary team of scientists, who on November 24, 2012 announced the results of their five-year long study of DNA samples from a novel hominin species, commonly known as "Bigfoot" or "Sasquatch," publishes their peer-reviewed findings today in the DeNovo Journal of Science (http://www.denovojournal.com). The study, which sequenced three whole Sasquatch nuclear genomes, shows that the legendary Sasquatch is extant in North America and is a human relative that arose approximately 13,000 years ago and is hypothesized to be a hybrid cross of modern ...
European satellite confirms UW numbers: Arctic Ocean is on thin ice
2013-02-13
The September 2012 record low in Arctic sea-ice extent was big news, but a missing piece of the puzzle was lurking below the ocean's surface. What volume of ice floats on Arctic waters? And how does that compare to previous summers? These are difficult but important questions, because how much ice actually remains suggests how vulnerable the ice pack will be to more warming.
New satellite observations confirm a University of Washington analysis that for the past three years has produced widely quoted estimates of Arctic sea-ice volume. Findings based on observations from ...
We're emotionally distant and that's just fine by me
2013-02-13
When it comes to having a lasting and fulfilling relationship, common wisdom says that feeling close to your romantic partner is paramount. But a new study finds that it's not how close you feel that matters most, it's whether you are as close as you want to be, even if that's really not close at all.
"Our study found that people who yearn for a more intimate partnership and people who crave more distance are equally at risk for having a problematic relationship," says the study's lead author, David M. Frost, PhD, of Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health. ...
Video study shows which fish clean up coral reefs, showing importance of biodiversity
2013-02-13
Using underwater video cameras to record fish feeding on South Pacific coral reefs, scientists have found that herbivorous fish can be picky eaters – a trait that could spell trouble for endangered reef systems.
In a study done at the Fiji Islands, the researchers learned that just four species of herbivorous fish were primarily responsible for removing common and potentially harmful seaweeds on reefs – and that each type of seaweed is eaten by a different fish species. The research demonstrates that particular species, and certain mixes of species, are potentially critical ...
Penn vet team uncovers a pathway that stimulates bone growth
2013-02-13
PHILADELPHIA — Researchers from the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine have discovered that a protein called Jagged-1 stimulates human stem cells to differentiate into bone-producing cells. This protein could help both human and animal patients heal from bone fractures faster and may form the basis of treatments for a rare metabolic condition called Alagille syndrome.
The study, published in the journal Stem Cells, was authored by three members of Penn Vet's departments of Clinical Studies-New Bolton Center and Animal Biology: postdoctoral researchers ...
FASEB joins President Obama in urging Congress to sustain investments in research and innovation
2013-02-13
FASEB also praised the President's emphasis on increasing investments in science and innovation. President Obama said, "Now is not the time to gut these job-creating investments in science and innovation. Now is the time to reach a level of research and development not seen since the height of the Space Race." In addition, the President noted that the automatic spending cuts known as sequestration would devastate priorities like education, energy, and medical research. "We will continue our advocacy efforts to urge Congress to sustain federal funding for the National Institutes ...
Opera's poisons and potions connect students with chemistry
2013-02-13
Opera audiences can feel the chemistry in romance-inspired classics like Mimi's aria from La Bohème, Cavaradossi's remembrance of his beloved while awaiting execution in Tosca and that young lady pining for her man with "O mio babbino caro" in the opera Gianni Schicchi. An article in ACS' Journal of Chemical Education, however, focuses on the real chemistry — of poisons and potions — that intertwines famous operatic plots.
João Paulo André points out that opera, in addition to being a form of theater, can be used as a teaching tool for chemistry students and the general ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
[Press-News.org] Carnegie Mellon brain imaging research shows how unconscious processing improves decision-makingFindings reveal that unconscious brain activity leads to better decisions