(Press-News.org) TORONTO, ON – A new study led by an international team of biologists has identified some of the brain chemicals that allow seals to sleep with half of their brain at a time.
The study was published this month in the Journal of Neuroscience and was headed by scientists at UCLA and the University of Toronto. It identified the chemical cues that allow the seal brain to remain half awake and asleep. Findings from this study may explain the biological mechanisms that enable the brain to remain alert during waking hours and go off-line during sleep.
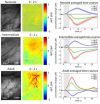
"Seals do something biologically amazing — they sleep with half their brain at a time. The left side of their brain can sleep while the right side stays awake. Seals sleep this way while they're in water, but they sleep like humans while on land. Our research may explain how this unique biological phenomenon happens" said Professor John Peever of the University of Toronto.
The study's first author, University of Toronto PhD student Jennifer Lapierre, made this discovery by measuring how different chemicals change in the sleeping and waking sides of the brain. She found that acetylcholine – an important brain chemical – was at low levels on the sleeping side of the brain but at high levels on the waking side. This finding suggests that acetylcholine may drive brain alertness on the side that is awake.
But, the study also showed that another important brain chemical – serotonin - was present at the equal levels on both sides of the brain whether the seals were awake or asleep. This was a surprising finding because scientist long thought that serotonin was a chemical that causes brain arousal.
These findings have possible human health implications because "about 40% of North Americans suffer from sleep problems and understanding which brain chemicals function to keep us awake or asleep is a major scientific advance. It could help solve the mystery of how and why we sleep" says the study's senior author Jerome Siegel of UCLA's Brain Research Institute.
###
An abstract of the study can be found online: http://www.csb.utoronto.ca/faculty/peever-john/symmetrical-serotonin-release-during-asymmetrical-slow-wave-sleep-implications-n
The online version of this release: http://media.utoronto.ca/media-releases/new-study-shows-how-seals-sleep-with-only-half-their-brain-at-a-time/
For more information, please contact:
Jerome Siegel, PhD
Chief, Neurobiology Research
Professor, Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences
Brain Research Institute, UCLA
jsiegel@ucla.edu
Tel: 818-891-7711 ext.7581
Mobile: 818-891-8612
John Peever, PhD
Associate Professor, Systems Neurobiology Laboratory
Dept. Cell & Systems Biology, University of Toronto
john.peever@utoronto.ca
Tel: 416-946-5564
Mobile: 647-207-7920 END
New study shows how seals sleep with only half their brain at a time
2013-02-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
We know when we're being lazy thinkers
2013-02-19
Are we intellectually lazy? Yes we are, but we do know when we take the easy way out, according to a new study by Wim De Neys and colleagues, from the CNRS in France. Contrary to what psychologists believe, we are aware that we occasionally answer easier questions rather than the more complex ones we were asked, and we are also less confident about our answers when we do. The work is published online in Springer's journal Psychonomic Bulletin & Review.
Research to date on human thinking suggests that our judgment is often biased because we are intellectually lazy, or ...
NYU's Shedlin publishes study on the health of Colombian refugees in Ecuador
2013-02-19
New York University College of Nursing's Professor Michele Shedlin, PhD, recently published a paper, "Sending-Country Violence and Receiving-Country Discrimination: Effects on the Health of Colombian Refugees in Ecuador," on-line in the Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health, February 2, 2013.
Studies of immigrant health have historically focused on individual-level risk factors more than environmental/structural factors as salient mediating variables. Shedlin's research addresses the need to reach a more complete understanding of the migration process and vulnerabilities ...
Study shows that diet of resistant starch helps the body resist colorectal cancer
2013-02-19
As the name suggests, you can't digest resistant starch so it ends up in the bowel in pretty much the same form it entered your mouth. As unlovely as that seems, once in the bowel this resistant starch does some important things, including decreasing bowel pH and transit time, and increasing the production of short-chain fatty acids. These effects promote the growth of good bugs while keeping bad bugs at bay. A University of Colorado Cancer Center review published in this month's issue of the journal Current Opinion in Gastroenterology shows that resistant starch also helps ...
Annals of Internal Medicine tip sheet for Feb. 19, 2013
2013-02-19
1. Acupuncture May be an Effective Alternative for Treating Seasonal Allergies
Patients receiving acupuncture treatments for seasonal allergic rhinitis reported statistically significant improvements in symptoms and decreased use of medication compared to patients having standard treatment or sham acupuncture, but the clinical significance of the observed improvements is uncertain. Allergic rhinitis (stuffy or runny nose caused by allergies) is an extremely common condition that affects approximately 20 percent of the U.S. population. Despite the availability of effective ...
Shedding new light on infant brain development
2013-02-19
New York, NY—February 18, 2013—A new study by Columbia Engineering researchers finds that the infant brain does not control its blood flow in the same way as the adult brain. The paper, which the scientists say could change the way researchers study brain development in infants and children, is published in the February 18 Early Online edition of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
"The control of blood flow in the brain is very important" says Elizabeth Hillman, associate professor of Biomedical Engineering and of Radiology, who led the research study ...
The role of goop: Research shows pollution doesn't change the rate of droplet formation
2013-02-19
When it comes to forming the droplets that make up clouds, a little oily and viscous organic material apparently doesn't matter that much. And that's good news for reducing the uncertainty of climate model predictions.
Understanding cloud formation is essential for accurate climate modeling, and understanding cloud formation begins with the droplets that make up clouds. Droplets form when water vapor is attracted to particles floating in the atmosphere. These particles include dust, sea salt from the ocean, microorganisms, soot, sulfur – and organic material that can ...
Study suggests women have higher risk of hip implant failure
2013-02-19
Women appear to have a higher risk of implant failure than men following total hip replacement after considering patient-, surgery-, surgeon-, volume- and implant-specific risk factors, according to a report published Online First by JAMA Internal Medicine, a JAMA Network publication.
Total hip replacement, also known as total hip arthroplasty (THA), is more often performed in women than men. Sex-specific risk factors and outcomes have been investigated in other major surgical procedures and, in theory, might be more important to study in THA because of anatomical differences ...
Study suggests reduced lung function in infancy associated with wheeze later
2013-02-19
A study in Australia suggests that reduced lung function in infancy was associated with wheezing beyond childhood at 18 years of age, according to a report published Online First by JAMA Pediatrics, a JAMA Network publication.
Abnormal airway function is characteristic of asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease, and other studies have suggested that reduced lung function is already apparent in childhood and tracks through adulthood. However, the relationship between the age of onset of airway dysfunction and wheeze, a symptom of obstructive airways disease, has ...
A solution to sinusitis from the sea
2013-02-19
A team of scientists and surgeons from Newcastle are developing a new nasal spray from a marine microbe to help clear chronic sinusitis.
They are using an enzyme isolated from a marine bacterium Bacillus licheniformis found on the surface of seaweed which the scientists at Newcastle University were originally researching for the purpose of cleaning the hulls of ships.
Publishing in PLOS ONE, they describe how in many cases of chronic sinusitis the bacteria form a biofilm, a slimy protective barrier which can protect them from sprays or antibiotics. In vitro experiments ...
Caffeine linked to low birth weight babies
2013-02-19
Maternal nutrition is important to a developing embryo and to the health of the child later in life. Supplementing the diet with specific vitamins is known to increase health of the foetus for example folic acid (vitamin B9) reduces the risk of spina bifida. However not everything an adult might consume is beneficial to a developing baby. New research published in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Medicine shows that caffeine is linked to low birth weight babies and that caffeine from coffee in linked to increasing length of pregnancy.
Along with nutrients and ...