(Press-News.org) There are "things hidden in plain sight" all around us. But art can help students see their world anew, unlocking discoveries in fields ranging from plant biology to biomedical imaging, according to University of Delaware professor John Jungck.
Jungck's sentiments were echoed by a panel of experts speaking on "Artful Science" on Feb. 15 at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) in Boston. Jungck organized the panel and also spoke at the event.
Canoeing on a lake near his home in northwestern Minnesota when he was a youngster, Jungck became enthralled by the patterns of the cloud formations he saw as the fog lifted.
Today, the respected biologist and mathematician, who is a AAAS Fellow, a Fulbright Scholar to Thailand, a Mina Shaughnessy Scholar and editor of Biology International, is still fascinated by the tremendous beauty he sees in nature's perfect patterns and how mathematics can help expose hidden information.
Jungck studies radiolaria, marine microbes that he refers to as "amoeba that live in glass houses." These organisms with glass-like skeletons have an awe-inspiring symmetry and geometry.
Jungck uses them in his teaching and research in mathematical biology, as well as 3D FractaL Tree, a software program he co-developed that allows students to build realistic three-dimensional computer models of trees from just a few measurements from actual trees.
The tree-building process not only helps students appreciate the aesthetics of nature, he says, but the mathematics of biological systems. Important lessons, indeed.
"The new forms of visualization available today show how the combination of art, biology and mathematics saves lives — would you rather have a brain biopsy to investigate a headache problem, or rely on magnetic resonance imaging that's dependent on math?" he asks.
Jungck joined the University of Delaware faculty this past September as a professor of biological sciences and as the director of interdisciplinary science learning laboratories in the new Interdisciplinary Science and Engineering Laboratory (ISE Lab), a 194,000 square-foot facility that will open during fall 2013.
The high-tech facility will bring together experts from a variety of disciplines to work on challenges in the energy and environmental arenas. Students will be taught in four problem-based learning instructional laboratories that feature lab spaces with adjoining classrooms for discussing research problems and immediately testing possible solutions.
Jungck is a big believer in interdisciplinary collaboration. His laboratory teams routinely have included biologists, mathematicians and artists, and he wants to involve policy specialists on future projects, as well.
Such an "interdisciplinary village" will be crucial to the future advances he envisions, such as a medical forecast channel to pinpoint globally when and where infectious diseases such as flu, SARS and West Nile virus are coming.
"You need all of these communities," he says. "They help foster imagination and allow you to see patterns that you otherwise wouldn't be able to see."
INFORMATION:
Artful science
Art and science do mix -- and can unlock new discoveries
2013-02-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Powerful people are looking out for their future selves
2013-02-20
Would you prefer $120 today or $154 in one year? Your answer may depend on how powerful you feel, according to new research in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Many people tend to forego the larger reward and opt for the $120 now, a phenomenon known as temporal discounting. But research conducted by Priyanka Joshi and Nathanael Fast of the University of Southern California Marshall School of Business suggests that people who feel powerful are more likely to wait for the bigger reward, in part because they feel a stronger connection ...
Engineering control theory helps create dynamic brain models
2013-02-20
BOSTON -- Models of the human brain, patterned on engineering control theory, may some day help researchers control such neurological diseases as epilepsy, Parkinson's and migraines, according to a Penn State researcher who is using mathematical models of neuron networks from which more complex brain models emerge.
"The dual concepts of observability and controlability have been considered one of the most important developments in mathematics of the 20th century," said Steven J. Schiff, the Brush Chair Professor of Engineering and director of the Penn State Center for ...
New approach alters malaria maps
2013-02-20
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. – Identifying areas of malarial infection risk depends more on daily temperature variation than on the average monthly temperatures, according to a team of researchers, who believe that their results may also apply to environmentally temperature-dependent organisms other than the malaria parasite.
"Temperature is a key driver of several of the essential mosquito and parasite life history traits that combine to determine transmission intensity, including mosquito development rate, biting rate, development rate and survival of the parasite within the ...
Mutant champions save imperiled species from almost-certain extinction
2013-02-20
Species facing widespread and rapid environmental changes can sometimes evolve quickly enough to dodge the extinction bullet. Populations of disease-causing bacteria evolve, for example, as doctors flood their "environment," the human body, with antibiotics. Insects, animals and plants can make evolutionary adaptations in response to pesticides, heavy metals and overfishing.
Previous studies have shown that the more gradual the change, the better the chances for "evolutionary rescue" – the process of mutations occurring fast enough to allow a population to avoid extinction ...
NASA saw Tropical Storm Haruna come together
2013-02-20
Tropical Storm Haruna came together on Feb. 19 in the Southern Indian Ocean and two NASA satellites provided visible and infrared imagery that helped forecasters see the system's organization.
A low pressure area called System 94S developed on Friday, Feb. 15 in the northern Mozambique Channel. Over the course of four days System 94S became more organized and by Feb. 19 it became Tropical Storm Haruna.
On Tuesday, Feb. 19, Tropical Storm Haruna had maximum sustained winds near 35 knots (40.2 mph/64.8 kph). Haruna was located in the Mozambique Channel, near 21.4 south ...
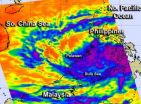
NASA satellite sees Tropical Depression 02W soak the Philippines
2013-02-20
The second tropical depression of the northwestern Pacific Ocean season formed on Feb. 19, and NASA's Aqua satellite showed the storm was soaking the central and southern Philippines.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Depression 02W (TD02W) as it was coming together and soaking provinces in Mindanao and the Palawan province of Luzon. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard Aqua captured an infrared image of the depression at 0541 UTC (12:41 a.m. EST). The AIRS image showed very cold cloud top temperatures, colder than -63F (-52C) ...
UC research examines interventions in treating African-Americans with substance abuse
2013-02-20
New research out of the University of Cincinnati reveals a relatively rare look into the success of substance abuse treatment programs for African-Americans. Researchers report that self-motivation could be an important consideration into deciding on the most effective treatment strategy. The study led by Ann Kathleen Burlew, a UC professor of psychology, and LaTrice Montgomery, a UC assistant professor of human services, is published online this week in Psychology of Addictive Behaviors.
Specifically among African-Americans, the study investigated the effectiveness of ...
It's not just amyloid: White matter hyperintensities and Alzheimer's disease
2013-02-20
New York, NY (February 19, 2013) — New findings by Columbia researchers suggest that along with amyloid deposits, white matter hyperintensities (WMHs) may be a second necessary factor for the development of Alzheimer's disease.
Most current approaches to Alzheimer's disease focus on the accumulation of amyloid plaque in the brain. The researchers at the Taub Institute for Research on Alzheimer's Disease and the Aging Brain, led by Adam M. Brickman, PhD, assistant professor of neuropsychology, examined the additional contribution of small-vessel cerebrovascular disease, ...
Increasing evidence links high glycemic index foods and dairy products to acne
2013-02-20
Philadelphia, PA, February 20, 2013 – A study published in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics has determined that there is increasing evidence of a connection between diet and acne, particularly from high glycemic load diets and dairy products, and that medical nutrition therapy (MNT) can play an important role in acne treatment.
More than 17 million Americans suffer from acne, mostly during their adolescent and young adult years. Acne influences quality of life, including social withdrawal, anxiety, and depression, making treatment essential. Since ...
Researchers find crime drama viewers more likely to aid sexual assault victims
2013-02-20
PULLMAN, Wash. – Viewers of primetime crime dramas, like NCIS, CSI or Law & Order, are more inclined than non-viewers to see themselves intervening on behalf of the victim of a sexual assault, according to recent research at Washington State University.
Published in the Journal of Health Communication, the study suggests prime-time television may be a successful medium for educating the public about sexual assault and encouraging positive responses, according to Stacey Hust, associate professor of communication with the Edward R. Murrow College of Communications and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Artful scienceArt and science do mix -- and can unlock new discoveries