(Press-News.org) An international CSIRO-led team of astronomers has developed a new way to weigh the planets in our Solar System – using radio signals from the small spinning stars called pulsars."This is first time anyone has weighed entire planetary systems – planets with their moons and rings," said team leader Dr David Champion from Germany's Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie.
"And we've provided an independent check on previous results, which is great for planetary science."
Measurements of planet masses made this new way could feed into data needed for future space missions.
Until now, astronomers have weighed planets by measuring the orbits of their moons or of spacecraft flying past them. That's because mass creates gravity, and a planet's gravitational pull determines the orbit of anything that goes around it – both the size of the orbit and how long it takes to complete.
The new method is based on corrections astronomers make to signals from pulsars – small spinning stars that deliver regular 'blips' of radio waves.
The Earth is travelling around the Sun, and this movement affects exactly when pulsar signals arrive here.
To remove this effect, astronomers calculate when the pulses would have arrived at the Solar System's centre of mass, or barycentre, around which all the planets orbit.
Because the arrangement of the planets around the Sun changes all the time, the barycentre moves around too.
To work out its position, astronomers use both a table (called an ephemeris) of where all the planets are at a given time, and the values for their masses that have already been measured.
CSIRO Astronomy and Space Science (CASS) researcher, Dr Dick Manchester, says that if these figures are slightly wrong, and the position of the barycentre is slightly wrong, then a regular, repeating pattern of timing errors appears in the pulsar data.
"For instance, if the mass of Jupiter and its moons is wrong, we see a pattern of timing errors that repeats over 12 years, the time Jupiter takes to orbit the Sun," Dr Manchester said.
"But if the mass of Jupiter and its moons is corrected, the timing errors disappear. This is the feedback process that the astronomers have used to determine the planets' masses."
Data from a set of four pulsars have been used to weigh Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn with their moons and rings. Most of these data were recorded by CSIRO's Parkes radio telescope in eastern Australia, with some contributed by the Arecibo telescope in Puerto Rico and the Effelsberg telescope in Germany.
The masses were consistent with those measured by spacecraft. The mass of the Jovian system, 9.547921(2) x 10-4 times the mass of the Sun, is significantly more accurate than the mass determined from the Pioneer and Voyager spacecraft, and consistent with, but less accurate than, the value from the Galileo spacecraft.
The new measurement technique is sensitive to a mass difference of two hundred thousand million million tonnes – just 0.003 per cent of the mass of the Earth, and one ten-millionth of Jupiter's mass.
CASS scientist Dr George Hobbs says that, in the short term, spacecraft will continue to make the most accurate measurements for individual planets.
"But the pulsar technique will be the best for planets not being visited by spacecraft, and for measuring the combined masses of planets and their moons," Dr Hobbs said,
Repeating the measurements would improve the values even more. If astronomers observed a set of 20 pulsars over seven years they'd weigh Jupiter more accurately than spacecraft have. Doing the same for Saturn would take 13 years.
The head of the 'Fundamental Physics in Radio Astronomy' research group at the Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Professor Michael Kramer, says astronomers need this accurate timing because they are using pulsars to hunt for gravitational waves predicted by Einstein's general theory of relativity.
"Finding these waves depends on spotting minute changes in the timing of pulsar signals, and so all other sources of timing error must be accounted for, including the traces of Solar System planets," Professor Kramer said
INFORMATION: END
WASHINGTON, D.C., (Oct. 21, 2010) -- Over the past decade, Christine Mahoney and a team of scientists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in Maryland have been working to stop the threat of terrorist-based attacks in the form of explosives or explosive-based devices, by providing a sound measurement and standard infrastructure.
"Our program encompasses many different aspects of explosives research, from development of measurement standards for trace explosives detection at airports, to the development and application of new metrology for the direct ...
Measuring three biomarkers in a single blood sample may improve physicians' ability to identify patients at high risk of developing chronic kidney disease (CKD), according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.
"Our results identify biomarkers that can improve CKD risk prediction," comments Caroline S. Fox, MD, MPH of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute's Framingham Heart Study, Framingham, Mass.
The study included more than 2,300 participants in the Framingham Offspring Study, a long-term follow-up ...
NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) and its sophisticated suite of instruments have determined that hydrogen, mercury and other volatile substances are present in permanently shaded soils on the Moon, according to a paper published today in Science.
The Lunar Crater Remote Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS), which launched with LRO, was intentionally crashed onto the Moon's surface Oct. 9, 2009, while LRO instruments watched. About 90 seconds after LCROSS hit the Moon, LRO flew past the debris plume raised by the impact, while the Lyman Alpha Mapping Project ...
AMES, Iowa – The flu virus uses a shuttle mechanism to relay protons through a channel in a process necessary for the virus to infect a host cell, according to a research project led by Mei Hong of Iowa State University and the Ames Laboratory.
The findings are published in the Oct. 22 issue of the journal Science.
Hong, an Iowa State professor of chemistry and an associate of the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory, said her research team used solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to determine the structure and workings of the proton channel ...
Beating the flu is already tough, but it has become even harder in recent years – the influenza A virus has mutated so that two antiviral drugs don't slow it down anymore.
Reporting their findings in the journal Science, researchers from Florida State and Brigham Young move closer to understanding why not, and how future treatments can defeat the nasty bug no matter how it changes.
The two drugs, amantadine and rimantadine, are no longer recommended by the CDC for use against flu.
They used to work by blocking a hole in the influenza A virus called the "M2 channel," ...
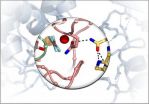
(Embargoed) Scientists at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine have reported the exact molecular structure and mechanisms of a major cell signaling pathway that serves a broad range of functions in humans.
Up to half of drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration directly or indirectly target G protein-coupled receptors. These receptors, which are proteins that live in the outer membranes of cells, take molecular signals from outside the cell and convert them into responses within – and those responses help control behaviors as ...
Research led by Klaus Stark and Christian Hengstenberg of the University of Regensburg identified a common variant of the cardiovascular heat shock protein gene, HSPB7, which was found to increase risk for dilated cardiomyopathy by almost 50%. Their paper appears on October 28 in the open-access journal PLoS Genetics.
Per year, about 6 in 100,000 individuals develop dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), with a higher prevalence in men. This disease is characterized by an enlarged, weakened heart, subsequently affecting the pumping capacity and often leading to chronic heart failure. ...
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- Most marathon runners know they need to consume carbohydrates before and during a race, but many don't have a good fueling strategy. Now, one dedicated marathoner -- an MD/PhD student in the Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology -- has taken a more rigorous approach to calculating just how much carbohydrate a runner needs to fuel him or herself through 26.2 miles, and what pace that runner can reasonably expect to sustain.
The result is a new model, described in the Oct. 21 issue of the journal PLoS Computational Biology, which allows ...
VIDEO:
Peter Schultz and graduate student Brendan Hermalyn analyzed data from bits of the Moon’s surface kicked up by a NASA-engineered collision. They found unexpected complexity -- and traces of silver....
Click here for more information.
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Scientists led by Brown University are offering the first detailed explanation of the crater formed when a NASA rocket slammed into the Moon last fall and information about the composition of the ...
STANFORD, Calif. — In a study to be published online Oct. 21 in PLoS Genetics, researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have implicated the lack of a protein important in hooking our skin cells together in the most common variety of skin cancer. Depletion of this protein, called Perp, could be an early indicator of skin cancer development, and could be useful for staging and establishing prognoses.
These findings' significance may extend beyond skin cancer, as Perp is found in the linings of many of our internal organs, where it plays the same role it ...