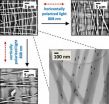
(Press-News.org) Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a way to melt or "weld" specific portions of polymers by embedding aligned nanoparticles within the materials. Their technique, which melts fibers along a chosen direction within a material, may lead to stronger, more resilient nanofibers and materials.
Physicists Jason Bochinski and Laura Clarke, with materials scientist Joe Tracy, placed specifically aligned gold nanorods within a solid material. Gold nanorods absorb light at different wavelengths, depending upon the size and orientation of the nanorod, and then they convert that absorbed light directly into heat. In this case, the nanorods were designed to respond to light wavelengths of 520 nanometers (nm) in a horizontal alignment and 800 nm when vertically aligned. Human beings can see light at 520 nm (it looks green), while 808 nm is in the near infrared spectrum, invisible to our eyes.
When the different wavelengths of light were applied to the material, they melted the fibers along the chosen directions, while leaving surrounding fibers largely intact.
"Being able to heat materials spatially in this way gives us the ability to manipulate very specific portions of these materials, because nanorods localize heat – that is, the heat they produce only affects the nanorod and its immediate surroundings," Tracy says.
According to Bochinski, the work also has implications for optimizing materials that have already been manufactured: "We can use heat at the nanoscale to change mechanical characteristics of objects postproduction without affecting their physical properties, which means more efficiency and less waste."
The researchers' findings appear in Particle & Particle Systems Characterization. The work was funded by grants from the National Science Foundation and Sigma Xi. Graduate students Wei-Chen Wu and Somsubhra Maity and former undergraduate student Krystian Kozek contributed to the work.
INFORMATION:
Note to editors: An abstract of the paper follows.
"Anisotropic Thermal Processing of Polymer Nanocomposites via the Photothermal Effect of Gold Nanorods"
Authors: Jason Bochinski, Laura Clarke, Joe Tracy, Somsubrha Maity, Krystian Kozek and Wei-Chen Wu, North Carolina State University
Published: Particle & Particle Systems Characterization
Abstract:
By embedding metal nanoparticles within polymeric materials, selective thermal polymer processing can be accomplished via irradiation with light resonant with the nanoparticle surface plasmon resonance due to the photothermal effect of the nanoparticles which efficiently transforms light
into heat. The wavelength and polarization sensitivity of photothermal heating from embedded gold nanorods is used to selectively process a collection of polymeric nanofibers, completely melting those fibers lying along a chosen direction while leaving the remaining material largely unheated and unaffected. Fluorescence-based temperature and viscosity sensing was employed to confirm the presence of heating and melting in selected fibers and its absence in counter-aligned fibers. Such tunable specificity in processing a subset of a sample, while the remainder is unchanged, cannot easily be achieved through conventional heating techniques.
Researchers 'nanoweld' by applying light to aligned nanorods in solid materials
2013-02-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists make older adults less forgetful in memory tests
2013-02-22
Toronto, Canada – Scientists at Baycrest Health Sciences' Rotman Research Institute (RRI) and the University of Toronto's Psychology Department have found compelling evidence that older adults can eliminate forgetfulness and perform as well as younger adults on memory tests.
Scientists used a distraction learning strategy to help older adults overcome age-related forgetting and boost their performance to that of younger adults. Distraction learning sounds like an oxymoron, but a growing body of science is showing that older brains are adept at processing irrelevant and ...
Immigration among Latin-American countries fails to improve income
2013-02-22
Although immigration to the United States from Latin American countries, particularly Mexico, has captured much public attention, immigrants who move between countries in Latin America have more difficulty than those moving to the United States.
Donald Bogue, professor emeritus in sociology and a distinguished scholar of demography, has found that unlike immigrants to the United States, immigrants between nations in Latin America frequently do not improve their lives by moving.
A popular theory on immigration contends that immigrants are self-selected achievers who ...
Why some soldiers develop PTSD while others don't
2013-02-22
Pre-war vulnerability is just as important as combat-related trauma in predicting whether veterans' symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) will be long-lasting, according to new research published in Clinical Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Researcher Bruce Dohrenwend and colleagues at Columbia's Mailman School of Public Health and the New York State Psychiatric Institute found that traumatic experiences during combat predicted the onset of the full complement of symptoms, known as the PTSD "syndrome," in Vietnam ...
Why sourdough bread resists mold
2013-02-22
Sourdough bread resists mold, unlike conventionally leavened bread. Now Michael Gaenzle and colleagues of the University of Alberta, Edmonton, show why. During sourdough production, bacteria convert the linoleic acid in bread flour to a compound that has powerful antifungal activity. The research, which could improve the taste of bread, is published online ahead of print in the journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
The major benefits from the research are twofold: better tasting bread, says Gaenzle, because "preservatives can be eliminated from the recipes, ...
Student loans help women more than men in reaching graduation
2013-02-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Student loans provide more help to women than they do for men in encouraging graduation from college, a new nationwide study reveals.
Findings showed that, on average, taking out loans actually makes graduation more likely for all students. But at a certain point – which is about $2,000 lower for men than for women – debt has diminishing returns and becomes less effective at boosting chances of graduation.
One reason loans help women more may be tied to job prospects for college dropouts – which are much better for men than for women.
"At least early ...
For embolism patients, clot-busting drug is worth risk
2013-02-22
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- When doctors encounter a patient with a massive pulmonary embolism, they face a difficult choice: Is it wise to administer a drug that could save the patient's life, even though many people suffer life-threatening bleeding as a result?
Based on new findings published in the American Journal of Medicine, Michigan State University researchers are answering that question in no uncertain terms.
"The message to doctors is clear: Take the chance," said Paul D. Stein, a professor in MSU's Department of Osteopathic Medical Specialties. "It doesn't matter ...
Smarter lunchrooms make lunch choices child's play
2013-02-22
Cincinnati, OH, February 22, 2013 -- In January 2012, the United States Department of Agriculture passed a series of regulations designed to make school lunches more nutritious, which included requiring schools to increase whole grain offerings and making students select either a fruit or vegetable with their purchased lunch. However, children cannot be forced to eat these healthier lunches. In a new study scheduled for publication in The Journal of Pediatrics, researchers determined that small, inexpensive changes to school cafeterias influenced the choice and consumption ...
Ignition interlock device program in Virginia
2013-02-22
Ignition interlock device program in Virginia
Article provided by Montagna & Montagna, P.C.
Visit us at http://www.montagnalaw.com
The Virginia legislature recently updated state law to require ignition interlock devices to be installed into vehicles of convicted first time DUI offenders who have a blood alcohol level above .08. The offenders must have these devices installed in order to receive a restricted driver's license.
Previously, judges had more discretion in cases of first time DUI offenders. It is hoped that the mandated installation of the devices ...
Teen drivers do better with fewer teen passengers
2013-02-22
Teen drivers do better with fewer teen passengers
Article provided by Cohen & Feeley
Visit us at http://www.cohenfeeley.com
Recent findings by the AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety highlight the need for a watchful approach when licensing teenaged drivers. Analyzing fatal crashes in the United States between 2005 and 2010, AAA looked at the effect of having passengers age 13 to 19 with 16- and 17-year-old drivers.
During this five-year period 9,578 drivers in this age group were involved in fatal car accidents. Of these, 3,994 had at least one teenage passenger ...
Division of marital property crucial issue in most divorces
2013-02-22
Division of marital property crucial issue in most divorces
Article provided by Law Offices of Catherine A. Schwartz
Visit us at http://www.cschwartzlaw.com
Most of us know someone who has gone through a divorce. In many cases, it is often a highly-contested matter, leaving each of the spouses emotionally drained. It can take time before they are ready to enter into another relationship.
But as the time passes, individuals may find someone new. They may fall in love all over again, and decide to get married. However, these individuals need to protect themselves ...