(Press-News.org) Despite years of research, the genetic factors behind many human diseases and characteristics remain unknown. The inability to find the complete genetic causes of family traits such as height or the risk of type 2 diabetes has been called the "missing heritability" problem.
A new study by Princeton University researchers, however, suggests that missing heritability may not be missing after all — at least not in yeast cells, which the researchers used as a model for studying the problem. Published in the journal Nature, the results suggest that heritability in humans may be hidden due only to the limitations of modern research tools, but could be discovered if scientists know where (and how) to look.
[Images can be seen at http://www.princeton.edu/main/news/archive/S36/13/86G93. To obtain high-res images, contact Princeton science writer Morgan Kelly, (609) 258-5729, mgnkelly@princeton.edu]
"The message of our study is that if you look hard enough you will find the missing heritability," said the senior researcher, Leonid Kruglyak, Princeton's William R. Harman '63 and Mary-Love Harman Professor in Genomics and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator. Kruglyak worked with first author Joshua Bloom, a Princeton graduate student; Wesley Loo, a 2010 Princeton graduate now a graduate student at Harvard University; Thuy-Lan Lite, Class of 2012, who is working at the National Institutes of Health for a year before starting graduate school; and Ian Ehrenreich, a past Princeton postdoctoral researcher now at the University of Southern California.
"We don't think there is some fundamental limitation — such as that there are things we don't understand about how genes behave — that is holding us back," Kruglyak said. "Instead, we should be able to detect the heritability in humans if we use the right tools."
Passed down from parent to child, genes determine not only eye color and other physical characteristics but also the risk of diseases. Some inherited diseases are caused by a mutation in a single gene. These single-gene disorders have well-defined patterns of inheritance that can be used to predict the chances that an individual will inherit the disease.
However, many diseases and physical traits arise due to multiple genes, multiple locations within genes, and even the regions of DNA between genes. Across the genome — which is an individual's total genetic content — small variations in DNA code can, when added together, increase or decrease the likelihood that a person will develop a disease or characteristic.
Height, for example, results from variations in DNA at multiple locations on the genome. Researchers have detected about 180 locations in the human genome where small alterations in the DNA code can have an influence on how tall or short a person is. Nonetheless, these locations account for only 13 percent of the expected contribution genetic code has on a person's height.
Type 2 diabetes also has missing heritability: About 40 identified genome locations are associated with the risk of developing the condition, but those account for only 10 percent of the estimated genetic influence. Finding the missing heritability for diseases like type 2 diabetes, Crohn's disease and schizophrenia could help inform prevention and treatment strategies.
In the present study, the researchers scanned the genomes of yeast cells for DNA variations — which can be thought of as spelling errors in the four-letter DNA code — and then matched those variations with qualities or characteristics inherited from the cells' parents. This type of study, known as a genome-wide association study (GWAS), is a common tool for searching for diseases and traits associated with variations in the genome. The researchers detected numerous DNA variations that, when added together, accounted for almost all of the offsprings' inherited characteristics, indicating that there was very little missing heritability in yeast.
Although the search for heritability was successful in yeast, finding missing heritability in humans is far more complicated, Kruglyak said. For example, interactions between genes can contribute to heritable traits, but such interactions are difficult to detect with genome-wide association studies (GWAS), which are the primary means by which geneticists look for DNA variations associated with diseases or traits. In addition, environmental factors such as nutrition also can influence gene activity, and these influences can be elusive to the genome-wide study. GWAS also may be inadequate at detecting common DNA spelling errors that have only small effects, or it may fail to find DNA variations that have a large effect but are rare.
The study sheds light on the role of nature (genetic factors) versus nurture (environmental factors) in determining traits and disease risk, according to Bert Vogelstein, director of the Ludwig Center at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator.
"The nature versus nurture argument has been brewing for decades, both among scientists and the lay public, and 'missing heritability' has been problematic for the 'nature' component," said Vogelstein, who was not involved in the Princeton study.
"This beautiful study demonstrates that the genetic basis for heritability (nature) can be precisely defined if extensive, well-controlled experiments can be performed," Vogelstein said. "Though the results were obtained in a model organism, I would be surprised if they didn't apply, at least in part, to higher organisms, including humans."
Kruglyak said that one approach to finding the missing heritability in humans might be to apply genome-wide scans to large families, rather than focusing on large populations as is currently done. Family studies take advantage of the fact that the same genetic variations will be more common in families — and thus easier to detect. However, the disadvantage of family studies is that the detected genetic variations may not be widespread in the population.
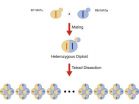
For the study in yeast, the team examined the offspring of two yeast cells, one that is commonly used in laboratory studies and the other in wine making. Although yeast usually reproduce asexually, under certain conditions, such as lack of food, two yeast cells will mate and produce offspring that, like human children, receive roughly half their genetic material from each parent. "Our study involves thousands of 'kids' from a single set of parents," Kruglyak said.
The team first sequenced the genomes of the two parent cells and then conducted scans for DNA variations in the genomes of 1,008 offspring. Yeast do not inherit height or disease risk from their parents, but they can inherit the ability to survive in adverse conditions. The researchers tested the parents and their offspring for the ability to grow under various conditions, including different temperatures, acidity levels, food sources, antibiotics, metal compounds, and in drugs such as caffeine.
The researchers then looked for associations between the DNA variations inherited from the parents and growth ability, and determined that the DNA variations accounted for nearly all of the resilience noted in the offspring.
INFORMATION:
The paper, "Finding the sources of missing heritability in a yeast cross," was published in Nature on Feb. 3, 2013. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants R37 MH59520 and R01 GM102308; a James S. McDonnell Centennial Fellowship (L.K.); the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (L.K.); a National Science Foundation (NSF) fellowship (J.S.B.); an NIH postdoctoral fellowship F32 HG51762 (I.M.E.); and NIH grant P50 GM071508 to the Center for Quantitative Biology at the Lewis-Sigler Institute of Princeton University.
Genomic detectives crack the case of the missing heritability
2013-02-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers find appointed justices outperform elected counterparts
2013-02-22
State supreme court justices who don't face voters are generally more effective than their elected counterparts, according to research led by Princeton University political scientists.
The research combines data about almost 6,000 state supreme court rulings nationwide between 1995 and 1998 with a new theoretical model to reach the conclusions that appointed justices generally bring a higher quality of information to the decision-making process, are more likely to change their preconceived opinions about a case, and are less likely to make errors than elected justices.
"Judges ...
1 week and counting: Don't cut the research that fuels the US economy
2013-02-22
WASHINGTON, DC – With only one week left before sequestration is to take effect, America's research community sustained its call for an end to the across-the-board cuts to discretionary spending that will severely restrict the nation's ability to invest in the basic scientific research that drives innovation and produces economic growth. Sequestration will reduce federal funding for scientific research by nearly $95 billion over the next nine years, which will result in a reduction of U.S. GDP by at least $203 billion. The net impact will be 200,000 fewer jobs per year ...
Israel rocket attacks increase miscarriage likelihood -- Ben-Gurion U. research study
2013-02-22
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, February 21, 2013 -- Rocket attacks in Sderot, Israel significantly increase the likelihood of miscarriages, according to a new study by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) researchers.
The study, published in the January issue of Psychosomatic Medicine Journal of Bio-behavioral Medicine, compared 1,341 pregnancies of women (exposed group) who resided in Sderot, an area exposed to frequent rocket fire, with 2,143 pregnancies of women who lived in Kiryat Gat (unexposed group), which is out of range of missiles. Among women residing in the exposed ...
Forecast is for more snow in polar regions, less for the rest of us
2013-02-22
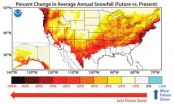
A new climate model predicts an increase in snowfall for the Earth's polar regions and highest altitudes, but an overall drop in snowfall for the globe, as carbon dioxide levels rise over the next century.
The decline in snowfall could spell trouble for regions such as the western United States that rely on snowmelt as a source of fresh water.
The projections are the result of a new climate model developed at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory (GFDL) and analyzed by scientists at GFDL and Princeton University. ...
The lifetime journeys of manure-based microbes
2013-02-22
This press release is available in Spanish.
Studies at the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) are shedding some light on the microbes that dwell in cattle manure—what they are, where they thrive, where they struggle, and where they can end up.
This research, which is being conducted by Agricultural Research Service (ARS) scientists at the agency's Agroecosystems Management Research Unit in Lincoln, Neb., supports the USDA priority of ensuring food safety. ARS is USDA's chief intramural scientific research agency.
In one project, ARS microbiologist Lisa Durso ...
Catheters linked with high risk of infections, heart problems, and death in dialysis patients
2013-02-22
Highlights
Dialysis patients using catheters to access the blood have the highest risks for death, infections, and cardiovascular events compared with patients using other types of vascular access.
Higher quality studies are needed to determine the true safety of different types of vascular access used for hemodialysis.
Worldwide, more than 1.5 million people are treated with hemodialysis.
Washington, DC (February 21, 2013) — Dialysis patients using catheters to access the blood have the highest risks for death, infections, and cardiovascular events compared with ...
Certain mutations affect kidney disease risk and prognosis
2013-02-22
Highlights
Certain mutations and combinations of mutations in immune-related genes affect individuals' risk of developing a rare but serious kidney condition.
These mutations also affect patient prognosis following different treatments.About half of patients with the condition, called atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, develop kidney failure.
Washington, DC (February 21, 2013) — Certain gene mutations affect individuals' risk of developing a serious kidney condition, as well as their prognosis after being diagnosed with the disease, according to a study appearing in ...
Penn researchers develop protein 'passport' that help nanoparticles get past immune system
2013-02-22
VIDEO:
Penn's Dennis Discher explains how his lab designed a protein that acts a "passport " for the body's immune system. Nanoparticles equipped with this passport last longer in the bloodstream than...
Click here for more information.
PHILADELPHIA — The body's immune system exists to identify and destroy foreign objects, whether they are bacteria, viruses, flecks of dirt or splinters. Unfortunately, nanoparticles designed to deliver drugs, and implanted devices ...
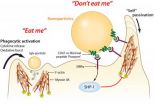
Stem cell 'homing' signal may help treat heart failure patients
2013-02-22
In the first human study of its kind, researchers activated heart failure patients' stem cells with gene therapy to improve their symptoms, heart function and quality of life, according to a study in the American Heart Association journal Circulation Research.
Researchers delivered a gene that encodes a factor called SDF-1 to activate stem cells like a "homing" signal.
The study is unique because researchers introduced the "homing" factor to draw stem cells to the site of injury and enhance the body's stem cell-based repair process. Generally, researchers extract and ...
Floral signs go electric
2013-02-22
Flowers' methods of communicating are at least as sophisticated as any devised by an advertising agency, according to a new study, published today in Science Express by researchers from the University of Bristol. The research shows for the first time that pollinators such as bumblebees are able to find and distinguish electric signals given out by flowers. However, for any advert to be successful, it has to reach, and be perceived by, its target audience.
Flowers often produce bright colours, patterns and enticing fragrance to attract their pollinators. Researchers ...