(Press-News.org) A recombinant Newcastle disease virus kills all kinds of prostate cancer cells, including hormone resistant cells, but leaves normal cells unscathed, according to a paper published online ahead of print in the Journal of Virology. A treatment for prostate cancer based on this virus would avoid the adverse side effects typically associated with hormonal treatment for prostate cancer, as well as those associated with cancer chemotherapies generally, says corresponding author Subbiah Elankumaran of Virginia Polytechnic Institute, Blacksburg. The modified virus is now ready to be tested in preclinical animal models, and possibly in phase I human clinical trials.
Newcastle disease virus kills chickens, but does not harm humans. It is an oncolytic virus that hones in on tumors, and has shown promising results in a number of human clinical trials for various forms of cancer. However, successful treatments have required multiple injections of large quantities of virus, because in such trials the virus probably failed to reach solid tumors in sufficient quantities, and spread poorly within the tumors.
The researchers addressed this problem by modifying the virus's fusion protein. Fusion protein fuses the virus envelope to the cell membrane, enabling the virus to enter the host cell. These proteins are activated by being cleaved by any of a number of different cellular proteases. They modified the fusion protein in their construct such that it can be cleaved only by prostate specific antigen (which is a protease). That minimizes off-target losses, because these "retargeted" viruses interact only with prostate cancer cells, thus reducing the amount of virus needed for treatment.
Retargeted Newcastle disease virus has major potential advantages over other cancer therapies, says Elankumaran. First, its specificity for prostate cancer cells means it would not attack normal cells, thereby avoiding the various unpleasant side effects of conventional chemotherapies. In previous clinical trials, even with extremely large doses of naturally occurring strains, "only mild flu-like symptoms were seen in cancer patients," says Elankumaran. Second, it would provide a new treatment for hormone-refractory patients, without the side effects of testosterone suppression that result from hormonal treatments.
About one man in six will be diagnosed with prostate cancer, and one in 36 will die of this disease. Men whose prostate cancer becomes refractory to hormone treatment have a median survival of about 40 months if they have bone metastases, and 68 months if they do not have bone metastases.
###
A copy of the manuscript can be found online at http://bit.ly/asmtip0213b. Formal publication of the article is scheduled for the first April 2013 issue of Journal of Virology.
(R. Shobana, S.K. Samal, and S. Elankumaran, 2013. Prostate-specific antigen-retargeted recombinant Newcastle disease virus for prostate cancer virotherapy. J. Virol. online ahead of print, 23 January 2013, doi:10.1128/JVI.02394-12)
Journal of Virology is a publication of the American Society for Microbiology (ASM). The ASM is the largest single life science society, composed of over 39,000 scientists and health professionals. Its mission is to advance the microbiological sciences as a vehicle for understanding life processes and to apply and communicate this knowledge for the improvement of health and environmental and economic well-being worldwide.
Virus shows promise as prostate cancer treatment
2013-02-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Higher levels of several toxic metals found in children with autism
2013-02-26
TEMPE, Ariiz. -- In a recently published study in the journal Biological Trace Element Research, Arizona State University researchers report that children with autism had higher levels of several toxic metals in their blood and urine compared to typical children. The study involved 55 children with autism ages 5 years compared to 44 controls of similar age and gender.
The autism group had significantly higher levels of lead in their red blood cells (+41 percent) and significantly higher urinary levels of lead (+74 percent), thallium (+77 percent), tin (+115 percent), ...
Study reveals stem cells in a human parasite
2013-02-26
CHAMPAIGN, lll. — From the point of view of its ultimate (human) host, the parasitic flatworm Schistosoma mansoni has a gruesome way of life. It hatches in feces-tainted water, grows into a larva in the body of a snail and then burrows through human skin to take up residence in the veins. Once there, it grows into an adult, mates and, if it's female, starts laying eggs. It can remain in the body for decades.
A new study offers insight into the cellular operations that give this flatworm its extraordinary staying power. The researchers, from the University of Illinois, ...
Global surveys show environmental concerns rank low among public concerns
2013-02-26
2/25/2013, Chicago, IL--A newly released international study reveals that the issue of climate change is not a priority for people in the United States and around the world.
The surveys showed that when asked to rank priority worries, people were five times more likely to point to the economy over the environment. Additionally, when asked about climate change, people identified the issue as more of a national problem than a personal concern.
Coordinated surveys, conducted by the International Social Survey Programme (ISSP) in 33 countries from 1993 through 2010, "are ...
Researchers explore PKC role in lung disease
2013-02-26
New research examines the role of PKC in airway smooth muscle contraction and raises the possibility that this enzyme could be a therapeutic target for treating asthma, COPD, and other lung diseases.
In the lungs, pathological increases in the contraction of the smooth muscle cells (SMCs) lining airway walls—a process that decreases airflow—contribute to the chain of events leading to asthma and COPD, two common lung diseases. Jose Perez-Zoghbi and colleagues from Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center designed a series of experiments to investigate the role of ...
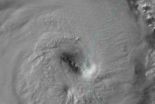
NASA sees Cyclone Rusty threatening Western Australia
2013-02-26
Tropical Cyclone Rusty formed on Feb. 24 and has already caused warnings up for the residents of northwestern West Australia, including Port Hedland. NASA's Terra satellite saw that outer bands of this quick-forming tropical cyclone were already affecting land.
The Australian Bureau of Meteorology (ABOM) has posted cyclone warnings and a yellow and blue alert for Western Australia as Rusty approaches for a landfall. A Cyclone Warning is in effect from Broome to Mardie, and adjacent inland areas of the Pilbara, including Marble Bar, Nullagine and Millstream. A Cyclone ...
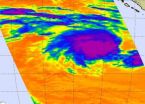
Infrared NASA data shows Cyclone Haruna being blown away
2013-02-26
Ex-cyclone Haruna is expected to dissipate in the Southern Indian Ocean under increasing wind shear in the next day or two. Infrared imagery from a NASA satellite shows that Haruna is being blown apart several hundred miles away from La Reunion Island.
Wind shear has been a problem for Haruna for days. A night-time image from the VIIRS instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite taken on Feb. 21 at 22:23 UTC showed the eye of Cyclone Haruna had elongated from northwest to southeast as a result of wind shear. For more information about the Suomi NPP satellite, visit: ...
NASA spots active Southern Indian Ocean's Tropical Storm 18S
2013-02-26
The eighteenth tropical cyclone of the Southern Indian Ocean season formed over the weekend of Feb. 23-24 along with Cyclone Rusty as Cyclone Haruna crossed southern Madagascar. NASA's Aqua satellite measured Tropical Storm 18S' cloud top temperatures and saw powerful thunderstorms around the storm's core.
Cyclone Rusty is nearing a landfall in northwestern West Australia, while Tropical Storm 18S is headed in a similar direction.
Tropical Storm 18S (TS18S) was born on Feb. 24 and achieved tropical storm strengthe with maximum sustained winds near 35 knots (40 mph). ...
PTSD symptoms common among ICU survivors
2013-02-26
One in three people who survived stays in an intensive care unit (ICU) and required use of a mechanical ventilator showed substantial post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms that lasted for up to two years, according to a new Johns Hopkins study of patients with acute lung injury.
Because acute lung injury (ALI) — a syndrome marked by excessive fluid in the lungs and frequent multi-organ failure — is considered an archetype for critical illness, the researchers suspect PTSD is common among other ICU survivors as well.
"We usually think of PTSD as something you ...
Potentially dangerous Mirena IUDs sparking U.S. lawsuits
2013-02-26
Potentially dangerous Mirena IUDs sparking U.S. lawsuits
Article provided by Bohrer Law Firm, L.L.C.
Visit us at http://www.bohrernationallawfirm.com
Millions of women in the United States and around the world are living with implanted Mirena intrauterine devices, commonly called Mirena IUDs, and some of these women have had nightmarish experiences from dangerous side effects of the devices. Approved by the U.S. government for birth control and to lessen abnormally heavy menstrual bleeding, reports of severe injuries and ectopic pregnancies (outside the uterus) ...
Book Marketing Announcements: The Authors Show Lineup For The Week Of February 25, 2013
2013-02-26
Don McCauley of the Free Publicity Focus Group and Danielle Hampson of eBroadcastMedia.com, founders of Book Marketing, announced today The Authors Show radio and TV weekly broadcast schedule.
Book Marketing, branded as 'The Authors Marketing Powerhouse', allows authors and publishers the opportunity to upload photos, bios, book covers, video and book videos. The site also offers discussion forums, segmented special interest groups and allows for event listings. Each author can develop a personalized page. In addition the site allows for integration with Facebook and ...