(Press-News.org) Though it's most often associated with disorders like diabetes, Harvard researchers have shown how the signaling pathway of insulin and insulin-like peptides plays another critical role in the body – helping to regulate learning and memory.
In addition to showing that the insulin-like peptides play a critical role in regulating the activity of neurons involved in learning and memory, a team of researchers led by Yun Zhang, Associate Professor of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, show that the interaction between the molecules can fine-tune how, or even if, learning takes place. Their work is described in a February 6 paper in Neuron.
"People think of insulin and diabetes, but many metabolic syndromes are associated with some types of cognitive defects and behavioral disorders, like depression or dementia," Zhang said. "That suggests that insulin and insulin-like peptides may play an important role in neural function, but it's been very difficult to nail down the underlying mechanism, because these peptides do not have to function through synapses that connect different neurons in the brain"
To get at that mechanism, Zhang and colleagues turned to an organism whose genome and nervous system are well described and highly accessible by genetics – C. elegans.
Using genetic tools, researchers altered the small, transparent worms by removing their ability to create individual insulin-like compounds. These new "mutant" worms were then tested to see whether they would learn to avoid eating a particular type of bacteria that is known to infect the worms. Tests showed that while some worms did learn to steer clear of the bacteria, others didn't – suggesting that removing a specific insulin-like compound halted the worms' ability to learn.
Researchers were surprised to find, however, that it wasn't just removing the molecules that could make the animals lose the ability to learn – some peptide was found to inhibit learning.
"We hadn't predicted that we would find both positive and negative regulators from these peptides," Zhang said. "Why does the animal need this bidirectional regulation of learning? One possibility is that learning depends on context. There are certain things you want to learn – for example, the worms in these experiments wanted to learn that they shouldn't eat this type of infectious bacteria. That's a positive regulation of the learning. But if they needed to eat, even if it is a bad food, to survive, they would need a way to suppress this type of learning."
Even more surprising for Zhang and her colleagues was evidence that the various insulin-like molecules could regulate each other.
"Many animals, including the humans, have multiple insulin-like molecules and it appears that these molecules can act like a network," she said. "Each of them may play a slightly different role in the nervous system, and they function together to coordinate the signaling related to learning and memory. By changing the way the molecules interact, the brain can fine tune learning in a host of different ways."
Going forward, Zhang said she hopes to characterize more of the insulin-like peptides as a way of better understanding how the various molecules interact, and how they act on the neural circuits for learning and memory.
Understanding how such pathways work could one day help in the development of treatment for a host of cognitive disorders, including dementia.
"The signaling pathways for insulin and insulin-like peptides are highly conserved in mammals, including the humans," Zhang said. "There is even some preliminary evidence that insulin treatment, in some cases, can improve cognitive function. That's one reason we believe that if we understand this mechanism, it will help us better understand how insulin pathways are working in the human brain."
### END
Linking insulin to learning
Researchers show how insulin-like molecules play critical role in learning and memory
2013-02-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
African-ancestry babies get less prenatal care in Brazil
2013-02-27
Low birth weights are more prevalent among Brazilians with African ancestry and may be attributed to less use of prenatal care facilities and where those ethnic groups live, according to a new study.
The study from researchers at the University of Iowa and health analysts in South America also suggests that infants of African ancestry, alone or mixed, were more likely to be born prematurely than those born of European-only stock. The findings could help policymakers decide how best to bridge the difference in infant health among non-European-ancestry races in South America's ...
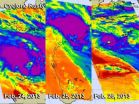
NASA infrared data shows Tropical Cyclone 18S still battling wind shear
2013-02-27
An infrared look at Tropical Storm 18S by NASA's Aqua satellite revealed wind shear continues to take its toll on the storm and keeps pushing its main precipitation away from the center of the storm.
Wind shear is a major factor that can keep a tropical cyclone "down" or unable to consolidate and intensify because it keeps pounding the circulation of winds head on. Strong wind shear has been battering Tropical Cyclone 18S for a couple of days and is expected to continue the next couple of days.
On Feb. 26 at 1500 UTC (10 a.m. EST) Tropical Storm 18S was located about ...
NASA satellites see slow-moving Cyclone Rusty before landfall
2013-02-27
Cyclone Rusty has been moving very slow over the last two days on its approach to landfall near Port Hedland in Western Australia, and NASA satellites have observed the storm's increase in power. NASA's TRMM and Aqua satellites provided rainfall, cloud height and temperature data that showed Cyclone Rusty intensified as it neared land.
Rusty is a large storm and its slow movement means more rainfall, more flooding potential, increasingly rough surf and a longer period of tropical-storm-force winds along the Pilbara coast.
The Australian Bureau of Meteorology (ABOM) ...
Libertarian paternalism and school lunches: Guiding healthier behavior while preserving choices
2013-02-27
In January 2012, the United States Department of Agriculture passed a series of regulations designed to make school lunches more nutritious, which included requiring schools to increase whole grain offerings and making students select either a fruit or vegetable with their purchased lunch. However, children cannot be forced to eat these healthier lunches. In a new study scheduled for publication in The Journal of Pediatrics, researchers determined that small, inexpensive changes to school cafeterias influenced the choice and consumption of healthier foods.
Andrew S. ...
Study: Same-sex cohabitors less healthy than those in heterosexual marriages
2013-02-27
WASHINGTON, DC, February 21, 2013 — Same-sex cohabitors report worse health than people of the same socioeconomic status who are in heterosexual marriages, according to a new study, which may provide fuel for gay marriage proponents.
"Past research has shown that married people are generally healthier than unmarried people," said Hui Liu, lead author of the study and an assistant professor of sociology at Michigan State University. "Although our study did not specifically test the health consequences of legalizing same-sex marriage, it's very plausible that legalization ...
Brandeis University study finds public policy, institutional barriers are pushing racial wealth gap
2013-02-27
New research shows the dramatic gap in household wealth that now exists along racial lines in the United States cannot solely be attributed to personal ambition and behavioral choices, but rather reflects policies and institutional practices that create different opportunities for whites and African-Americans.
So powerful are these government policies and institutional practices that for typical families, a $1 increase in average income over the 25-year study period generates just $0.69 in additional wealth for an African-American household compared with $5.19 for a white ...
Studying the health of same-sex couples
2013-02-27
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Same-sex couples that live together report worse health than people of the same socioeconomic status who are in heterosexual marriages, according to a national study that could have implications for the gay marriage debate.
Research has shown that married people are healthier than the unmarried. Yet, while gay marriage is gaining support in Michigan and around the country, most same-sex cohabiters do not have the option of legally marrying their partners, noted Hui Liu, Michigan State University sociologist and lead investigator on the study.
While ...
Mental health-substance use services in hospitals up after parity law, finds new report
2013-02-27
WASHINGTON, DC —The Paul Wellstone and Pete Domenici Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act of 2008 ("Parity Act") increased access to mental health and substance use services in hospitals, yet consumers continued to pay more out-of-pocket for substance use admissions than for other types of hospital admissions, finds a new Health Care Cost Institute (HCCI) report.
The report is one of the first of its kind to look at hospital spending, utilization, prices, and out-of-pocket payments for mental health and substance use admissions for those younger than age 65 ...
New fabrication technique could provide breakthrough for solar energy systems
2013-02-27
A novel fabrication technique developed by a University of Connecticut engineering professor could provide the breakthrough technology scientists have been looking for to vastly improve the efficiency of today's solar energy systems.
For years, scientists have studied the potential benefits of a new branch of solar energy technology that relies on nanosized antenna arrays theoretically capable of harvesting more than 70 percent of the sun's electromagnetic radiation and simultaneously converting it into usable electric power.
But while nanosized antennas that also serve ...
IU discovery on animal memory opens doors to research on memory impairment diseases
2013-02-27
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- If you ask a rat whether it knows how it came to acquire a certain coveted piece of chocolate, Indiana University neuroscientists conclude, the answer is a resounding, "Yes." A study newly published in the journal Current Biology offers the first evidence of source memory in a nonhuman animal.
The findings have "fascinating implications," said principal investigator Jonathon Crystal, both in evolutionary terms and for future research into the biological underpinnings of memory, as well as the treatment of diseases marked by memory failure such as ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
Adults with concurrent hearing and vision loss report barriers and challenges in navigating complex, everyday environments
Breast cancer stage at diagnosis differs sharply across rural US regions
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
[Press-News.org] Linking insulin to learningResearchers show how insulin-like molecules play critical role in learning and memory