(Press-News.org) Critically endangered leatherback sea turtle populations in the western Pacific Ocean may be losing their last foothold of survival on the beaches of Indonesia, according to a paper published today in the scientific journal Ecosphere by an international group of scientists.
Researchers from the State University of Papua Indonesia, NOAA Fisheries Service, University of Alabama at Birmingham and World Wildlife Fund Indonesia released a report today documenting the continued decline of leatherback sea turtle nesting in the western Pacific Ocean.
"At least 75 percent of all Leatherback turtles in the western Pacific Ocean hatch from eggs laid on a few beaches in an area known as Bird's Head Peninsula in Papua Barat-Indonesia," said Peter Dutton of NOAA's Southwest Fisheries Science Center and one of the researchers who co-authored the paper. "Our analysis indicates the number of leatherback turtle nests on this beach has declined 78 percent over the last 27 years."
Leatherbacks are the largest of all marine turtles and the largest living reptile in the world weighing up to 2000 pounds and over six feet in length. Female leatherbacks lay clutches of approximately 100 eggs and typically nest several times during a nesting season. After about two months, the hatchlings emerge from the nest and enter the ocean where they mature and may migrate as far away as California to feed on jellyfish; a distance of about 6,000 miles.
Scientists believe there are a number of reasons why the leatherback turtle populations have continued to decline over the past three decades. Extensive harvesting of eggs, predation of nests by feral pigs and other predators, and the accidental capture in commercial fisheries are the primary factors involved.
Ricardo Tapilatu, lead author on the Ecosphere paper, and co-authors Manjula Tiwari and Dutton, began assessing and developing a nesting beach census and management plan over a decade ago as part of an international partnership to halt the species decline.
"The turtles nesting at Papua Barat, Papua New Guinea, and other islands in our region depend on food resources in waters managed by many other nations for their survival," said Tapilatu. "It is important to protect leatherbacks in these foraging areas so that our nesting beach conservation efforts can be effective".
"The international effort has attempted to develop a science-based nesting beach management plan by evaluating and addressing the factors that affect hatching success such as high sand temperatures, erosion, feral pig predation, and relocating nests to maximize hatchling output," said Manjula Tiwari, a researcher at NOAA's Southwest Fisheries Science Center, in La Jolla, California.
The conservation value of nesting beach protection has also been recognized by groups like the International Seafood Sustainability Foundation (ISSF) that have raised funds from industry-affiliated members including tuna canners and processors, to help support UNIPA's nest protection program with the local communities on Bird's Head Peninsula.
"NOAA Fisheries Service is committed to doing our part in the international effort to recover the leatherback turtle through advancing science, implementing our recovery plans and management efforts such as the establishment of critical habitat off California," said Cisco Werner, Director of the Southwest Fisheries Science Center. "Reducing threats on the nesting beaches and at leatherback foraging areas will require continued international cooperation and action if we hope to save Pacific leatherbacks from extinction."
###
Article available here: http://www.esajournals.org/doi/pdf/10.1890/ES12-00348.1 END
Bridal registries might be efficient – sparing the gift-giver from hours of shopping and the recipient from having to return unwanted items. But that convenience may come at a cost: Where once the mom held great sway over selecting the intimate items that shaped the new household, now Target, Macy's and other retailers have taken over that role.
"Decades ago, the main role of the mother of the bride was creating the new home for the union of two families," says Tonya Williams Bradford, assistant professor of marketing at the University of Notre Dame. "By turning to bridal ...
People think of wind as an energy source with few limits, offering an unending power source with distinct capacity advantages over sources that deplete, such as fossil fuel.
Yet, new research in mesoscale atmospheric modeling by UNC Charlotte's Amanda S. Adams and Harvard University's David W. Keith, published Monday in the journal Environmental Research Letters, suggests that the power capacity of large-scale wind farms may have been significantly overestimated.
With large-scale wind farms, as many as hundreds of turbines mounted on tall towers and connected to the ...
Though it's most often associated with disorders like diabetes, Harvard researchers have shown how the signaling pathway of insulin and insulin-like peptides plays another critical role in the body – helping to regulate learning and memory.
In addition to showing that the insulin-like peptides play a critical role in regulating the activity of neurons involved in learning and memory, a team of researchers led by Yun Zhang, Associate Professor of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, show that the interaction between the molecules can fine-tune how, or even if, learning ...
Low birth weights are more prevalent among Brazilians with African ancestry and may be attributed to less use of prenatal care facilities and where those ethnic groups live, according to a new study.
The study from researchers at the University of Iowa and health analysts in South America also suggests that infants of African ancestry, alone or mixed, were more likely to be born prematurely than those born of European-only stock. The findings could help policymakers decide how best to bridge the difference in infant health among non-European-ancestry races in South America's ...
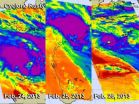
An infrared look at Tropical Storm 18S by NASA's Aqua satellite revealed wind shear continues to take its toll on the storm and keeps pushing its main precipitation away from the center of the storm.
Wind shear is a major factor that can keep a tropical cyclone "down" or unable to consolidate and intensify because it keeps pounding the circulation of winds head on. Strong wind shear has been battering Tropical Cyclone 18S for a couple of days and is expected to continue the next couple of days.
On Feb. 26 at 1500 UTC (10 a.m. EST) Tropical Storm 18S was located about ...
Cyclone Rusty has been moving very slow over the last two days on its approach to landfall near Port Hedland in Western Australia, and NASA satellites have observed the storm's increase in power. NASA's TRMM and Aqua satellites provided rainfall, cloud height and temperature data that showed Cyclone Rusty intensified as it neared land.
Rusty is a large storm and its slow movement means more rainfall, more flooding potential, increasingly rough surf and a longer period of tropical-storm-force winds along the Pilbara coast.
The Australian Bureau of Meteorology (ABOM) ...
In January 2012, the United States Department of Agriculture passed a series of regulations designed to make school lunches more nutritious, which included requiring schools to increase whole grain offerings and making students select either a fruit or vegetable with their purchased lunch. However, children cannot be forced to eat these healthier lunches. In a new study scheduled for publication in The Journal of Pediatrics, researchers determined that small, inexpensive changes to school cafeterias influenced the choice and consumption of healthier foods.
Andrew S. ...
WASHINGTON, DC, February 21, 2013 — Same-sex cohabitors report worse health than people of the same socioeconomic status who are in heterosexual marriages, according to a new study, which may provide fuel for gay marriage proponents.
"Past research has shown that married people are generally healthier than unmarried people," said Hui Liu, lead author of the study and an assistant professor of sociology at Michigan State University. "Although our study did not specifically test the health consequences of legalizing same-sex marriage, it's very plausible that legalization ...
New research shows the dramatic gap in household wealth that now exists along racial lines in the United States cannot solely be attributed to personal ambition and behavioral choices, but rather reflects policies and institutional practices that create different opportunities for whites and African-Americans.
So powerful are these government policies and institutional practices that for typical families, a $1 increase in average income over the 25-year study period generates just $0.69 in additional wealth for an African-American household compared with $5.19 for a white ...
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Same-sex couples that live together report worse health than people of the same socioeconomic status who are in heterosexual marriages, according to a national study that could have implications for the gay marriage debate.
Research has shown that married people are healthier than the unmarried. Yet, while gay marriage is gaining support in Michigan and around the country, most same-sex cohabiters do not have the option of legally marrying their partners, noted Hui Liu, Michigan State University sociologist and lead investigator on the study.
While ...