(Press-News.org) Researchers have successfully piloted a process that enables natural resource managers to take action to conserve particular wildlife, plants and ecosystems as climate changes.
The Adaptation for Conservation Targets (ACT) framework is a practical approach to assessing how future changes in air and water temperatures, precipitation, stream flows, snowpack, and other environmental conditions might affect natural resources. ACT enables scientists and managers to work hand-in-hand to consider how management actions may need to be adjusted to address those impacts.
"As acceptance of the importance of climate change in influencing conservation and natural resource management increases, ACT can help practitioners connect the dots and integrate climate change into their decisions," said WCS Conservation Scientist, Dr. Molly Cross. "Most importantly, the ACT process allows practitioners to move beyond just talking about impacts to address the 'What do we do about it?' question."
The ACT framework was tested during a series of workshops at four southwestern United States landscapes (see map) that brought together 109 natural resource managers, scientists, and conservation practitioners from 44 local, state, tribal and federal agencies and organizations. The workshops were organized by the Southwest Climate Change Initiative, representing The Nature Conservancy (TNC), the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), Climate Assessment for the Southwest (CLIMAS), the Western Water Assessment, the U.S. Forest Service, and the National Center for Atmospheric Research.
One example comes from the Bear River basin in Utah, where workshop participants looked at how warmer air and water temperatures and decreased summer stream flow might affect native Bonneville cutthroat trout habitat and populations. The group strategized that restoring the ability of fish to move between the main stem of the Bear River and cooler tributaries, protecting cold-water habitat, and lowering the depth of outflow from reservoirs to reduce downstream water temperatures could help maintain or increase trout population numbers as climate changes.
Participants in another workshop considered the impacts of reduced snow-pack and greater variability in precipitation on stream flows in the Jemez Mountains of New Mexico. To maintain sufficient water in the system and support aquatic species and riparian vegetation, attendees identified options such as restoring beaver to streams, building artificial structures to increase the storage of water in floodplains, and thinning the density of trees in nearby forests to maximize snowpack retention.
"The ACT process helps workshop participants move beyond the paralysis many feel when tackling what is a new or even intimidating topic by creating a step-by-step process for considering climate change that draws on familiar conservation planning tools," Cross said. "By combining traditional conservation planning with an assessment of climate change impacts that considers multiple future scenarios, ACT helps practitioners lay out how conservation goals and actions may need to be modified to account for climate change."
The results will help land managers as well as people. "Climate change impacts livelihoods and threatens the water supplies of many of our communities," says Terry Sullivan, The Nature Conservancy's New Mexico state director. "We hope that this tool will be utilized to help make decisions which will lead to healthy and sustainable watersheds, and ultimately sustain water supplies for farms and cities."
ACT workshops have been used to launch climate change planning at 11 locations in the United States for more than 15 wildlife, plant, and ecosystem targets (for details see http://www.wcsnorthamerica.org/ConservationChallenges/ClimateChange/ClimateChangeAdaptationPlanning.aspx). Feedback given by workshop attendees indicates that the ACT approach was successful in increasing participants' capacity to address climate change in their conservation work.
"We need to see more practitioners applying approaches like ACT if biological diversity and ecosystem services are to be maintained in a rapidly changing world," Cross added.
###
Results from the workshops are published in the February 2013 volume of the journal Conservation Biology (available at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1523-1739.2012.01954.x/pdf). Authors include Molly Cross of WCS, Patrick McCarthy and David Gori of TNC, Gregg Garfin of the University of Arizona; and Carolyn Enquist of the U.S.A. National Phenology Network and The Wildlife Society.
The ACT planning process is described in detail in the September 2012 edition of Environmental Management (available at http://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007%2Fs00267-012-9893-7). Authors include:
Molly Cross, WCS;
Erika Zavaleta, University of California, Santa Cruz;
Dominique Bachelet, Conservation Biology Institute;
Marjorie Brooks, Southern Illinois University;
Carolyn Enquist, The Wildlife Society and the U.S.A. National Phenology Network;
Erica Fleischman, University of California, Davis;
Lisa Graumlich, University of Washington;
Craig Groves, TNC;
Lee Hannah, Conservation International;
Lara Hansen, EcoAdapt;
Greg Hayward, U.S. Forest Service;
Marni Koopman, Geos Institute;
Joshua Lawler, University of Washington;
Jay Malcolm, University of Toronto;
John Nordgren, Kresge Foundation;
Brian Petersen, Michigan State University;
Erika Rowland, WCS;
Daniel Scott, University of Waterloo;
Sarah Shafer, U.S. Geological Survey;
Rebecca Shaw, Environmental Defense Fund; and
Gary Tabor, Center for Large Landscape Conservation.
A game plan for climate change
Pilot project helps scientists, managers, and conservationists pro-actively prepare for a changing climate
2013-02-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Changing shape makes chemotherapy drugs better at targeting cancer cells
2013-02-28
(Santa Barbara, Calif. –) Bioengineering researchers at University of California, Santa Barbara have found that changing the shape of chemotherapy drug nanoparticles from spherical to rod-shaped made them up to 10,000 times more effective at specifically targeting and delivering anti-cancer drugs to breast cancer cells.
Their findings could have a game-changing impact on the effectiveness of anti-cancer therapies and reducing the side effects of chemotherapy, according to the researchers. Results of their study were published recently in Proceedings of the National Academy ...
Retailers should re-size maternity wear for women throughout their pregnancies, MU study finds
2013-02-28
COLUMBIA, Mo. — Fashion retailers have seen an increase in demand for maternity wear in recent years, as sales for maternity clothing have increased while overall women's apparel sales have declined. Currently, most retailers produce maternity wear using a standardized size chart that begins with women in their seventh month of pregnancy. Retailers produce garments for women who are earlier in their terms by adjusting the sizes smaller proportionally based on the standardized chart. In a recent study, University of Missouri researcher MyungHee Sohn, an assistant professor ...
Reading the human genome
2013-02-28
Researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have achieved a major advance in understanding how genetic information is transcribed from DNA to RNA by providing the first step-by-step look at the biomolecular machinery that reads the human genome.
"We've provided a series of snapshots that shows how the genome is read one gene at a time," says biophysicist Eva Nogales who led this research. "For the genetic code to be transcribed into messenger RNA, the DNA double helix has to be opened and the strand of gene ...
Workstation design improvements for drone operators may reduce costs & mishaps, researchers suggest
2013-02-28
The U.S. Department of Defense reports that drone accidents in which personnel or aircraft are damaged or destroyed occur 50 times more often than mishaps involving human-operated aircraft. The U.S. Marines and Army reported 43 mishaps that involved human factors issues associated with drone ground control workstations and technology during 2006−2007.
Human factors/ergonomics (HF/E) researchers Qaisar Waraich, Thomas Mazzuchi, Shahram Sarkani, and David F. Rico suggest that multimillion-dollar drone losses might be prevented if long-established and broadly applied ...
Protein balance key in preventing cancer
2013-02-28
PHILADELPHIA, PA (February 27, 2013)—Two proteins that scientists once thought carried out the same functions are actually antagonists of each other, and keeping them in balance is key to preventing diseases such as cancer, according to new findings published in the February 25 issue of Developmental Cell by scientists at Fox Chase Cancer Center. The results suggest that new compounds could fight cancer by targeting the pathways responsible for maintaining the proper balance between the proteins.
"It's our job now to understand how we can intervene therapeutically in ...
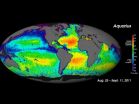
NASA's Aquarius sees salty shifts
2013-02-28
The colorful images chronicle the seasonal stirrings of our salty world: Pulses of freshwater gush from the Amazon River's mouth; an invisible seam divides the salty Arabian Sea from the fresher waters of the Bay of Bengal; a large patch of freshwater appears in the eastern tropical Pacific in the winter. These and other changes in ocean salinity patterns are revealed by the first full year of surface salinity data captured by NASA's Aquarius instrument.
"With a bit more than a year of data, we are seeing some surprising patterns, especially in the tropics," said Aquarius ...
GSA Today: Putting time in its place
2013-02-28
Boulder, Colorado, USA – In the March issue of GSA Today, seven scientists from six countries, led by Jan Zalasiewicz of the University of Leicester, propose a realignment of the terms "geochronology" and "chronostratigraphy" in an attempt to resolve the debate of whether units of the Geological Time Scale should have a single (time) or dual (time and time-rock) hierarchy.
In their system, which retains both parallel sets of units, with an option to adopt one or other when appropriate, geochronology refers to all methods of numerical dating and is used to express the ...
Fermi's motion produces a study in spirograph
2013-02-28
VIDEO:
The Vela pulsar outlines a fascinating pattern in this movie showing 51 months of position and exposure data from Fermi's Large Area Telescope (LAT). The pattern reflects numerous motions of...
Click here for more information.
NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope orbits our planet every 95 minutes, building up increasingly deeper views of the universe with every circuit. Its wide-eyed Large Area Telescope (LAT) sweeps across the entire sky every three hours, capturing ...
Rapid, point-of-care tests for syphilis: The future of diagnosis
2013-02-28
Montreal, February 27th – Syphilis is on the rise worldwide and there is an urgent need for reliable and rapid screening, particularly for people who live in areas where access to healthcare is limited. An international research team, led by scientists at the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI-MUHC) in Montreal, has demonstrated that rapid and point-of-care tests (POC) for syphilis are as accurate as conventional laboratory tests. The findings, which were published in PLoS ONE, call for a major change in approach to syphilis testing and recommend ...
Reading, writing, arithmetic, and aerobics -- Evaluating the new 'R' in academic performance
2013-02-28
Cincinnati, OH, February 28, 2013 -- Although the long-term consequences of childhood obesity are well documented, some school districts have reduced physical education classes to devote more time to the 3 Rs in education—reading, writing, and arithmetic. However, there is new evidence that leaving out an important fourth R—aerobics—could actually be counterproductive for increasing test scores. A new study scheduled for publication in The Journal of Pediatrics studied the associations between aerobic fitness, body mass index (BMI), and passing scores on standardized ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
[Press-News.org] A game plan for climate changePilot project helps scientists, managers, and conservationists pro-actively prepare for a changing climate