(Press-News.org) Canola, cottonseed, and sunflower products can replace soybean meal in diets fed to pigs, but they contain less protein and energy. To determine if it makes economic sense to use them, producers need to know the concentrations and digestibility of the nutrients they contain. To help them make the decision, University of Illinois researchers examined amino acid digestibility for these products.
"Soybean is by far the biggest oilseed crop in the world," said Hans Stein, professor of animal sciences. "But canola, cottonseed, and sunflowers are grown in areas where soybeans can't grow. When the oil is taken out of the seed, meal is left over, as with soybean meal."
His team looked at amino acid digestibility in both intact canola seeds and canola meal, as well as in cottonseed meal, intact sunflower seeds, dehulled sunflower meal, and sunflower meal with hulls, on which there has been little recent digestibility research. The study included soybean meal for comparison.
Digestibility of amino acids in canola, cottonseed, and sunflower meal was lower than that of soybean meal. The main reason for their reduced digestibility was that these products have higher fiber content than does soybean meal. All of them except for the dehulled sunflower meal included hulls, whereas the soybean meal did not.
Also, Stein explained, "Soybeans do not contain as much oil as canola and sunflower. When you take more oil out, the seed hull becomes a bigger proportion of what you have left over – and that's where you have all the fiber. So, sunflower is over 50 percent oil, and canola is about 40 percent oil. Soybean is only 19 or 20 percent oil, so you concentrate the fiber more when you produce those meals."
Among the alternative meals, sunflower meal had the greatest values for digestibility of crude protein and the most amino acids. In cottonseed meal, values for most amino acids were the same as, or greater than, those in canola seeds or canola meal.
Canola meal and cottonseed meal contained the greatest concentrations of crude protein and indispensable amino acids after soybean meal. Stein said cottonseed is not used as much as it could be in pig production because it contains gossypol, an anti-nutritional factor that prevents pigs from utilizing lysine.
"But low gossypol varieties are available now, and it's been shown that if you add enough iron to the diet, it can bind the gossypol, which will then not bind the lysine," he explained. "So you can use some cottonseed in the diets and they'll do fine. Cottonseed meal has a relatively good digestibility compared with canola and sunflower meal, so more of it could be used than is used today."
Stein added that sunflower meal and canola meal need to be significantly less expensive than soybean meal before they are an economical alternative because they have reduced amino acid digestibility and a lower concentration of amino acids and energy than soybean meal.
The researchers have not determined inclusion rates for canola, cottonseed, and sunflower products. Stein said that this may be the subject of future research.
###
The study, "Amino acid digestibility in canola, cottonseed, and sunflower products fed to finishing pigs," was published in Journal of Animal Science and was co-authored with Caroline González-Vega, a Ph.D. candidate in the Stein Monogastric Nutrition Laboratory at Illinois. It is available at http://www.journalofanimalscience.org/content/90/12/4391.full. END
Replacing soybean meal in pig diets
2013-02-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
After the human genome project: The human microbiome project
2013-02-28
Bethesda, MD—Earth Day may be more than a month away, but another, more personal, ecosystem has been shown to also be worth protecting—within our bodies are communities of microbes that affect the behavior of human cells hosting them. These communities, called the "microbiome," are so crucial to our health that some consider it to be a complex "second genome." Understanding the interaction of these microbes among one another and their human hosts has the potential to yield insights into numerous diseases and complex human disorders from obesity to susceptibility to infection. ...
Physical activity does not protect against in situ breast cancer
2013-02-28
A European study published in the 'Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention' journal has analysed the association between physical activities and in situ or non-invasive breast cancer, or, in other words, cancer that has not yet invaded cells within or outside of the breast.
Headed by researchers from ten European countries including Spain, the work carried out under the framework of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) concludes that physical activity has no relation with the risk of developing this type of non-invasive cancer. ...
Eating junk food while pregnant may make your child a junk food addict
2013-02-28
Bethesda, MD—Here's another reason why a healthy diet during pregnancy is critical to the future health of your children: New research published in the March 2013 issue of The FASEB Journal, suggests that pregnant mothers who consume junk food actually cause changes in the development of the opioid signaling pathway in the brains of their unborn children. This change results in the babies being less sensitive to opioids, which are released upon consumption of foods that are high in fat and sugar. In turn, these children, born with a higher "tolerance" to junk food need ...
Global tipping point not backed by science: Study
2013-02-28
A group of international ecological scientists led by the University of Adelaide have rejected a doomsday-like scenario of sudden, irreversible change to the Earth's ecology.
In a paper published today in the journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution, the scientists from Australia, US and UK argue that global-scale ecological tipping points are unlikely and that ecological change over large areas seem to follow a more gradual, smooth pattern.
This opposes recent efforts to define 'planetary tipping points' ‒ critical levels of biodiversity loss or land-use change ...
The giant cockroach genus Pseudophoraspis expands to the north with 3 new species
2013-02-28
Cockroaches (Blattodea) are an insect order remarkable in their biodiversity and distribution, with more than 4500 species known and great geographical reach. Cockroach fossils date back around 400 million years, which testifies to their great adaptability and endurance that puts them among the planet's great survivors.
The cockroach genus Pseudophoraspism has has been reported from China for the first time thanks to the discovery of three new species: Pseudophoraspis clavellata, Pseudophoraspis recurvata and Pseudophoraspis incurvata, alongside the first regional record ...
Metal ions regulate terpenoid metabolism in insects
2013-02-28
This press release is available in German.
Max Planck scientists in Jena, Germany, have discovered an unusual regulation of enzymes that catalyze chain elongation in an important secondary metabolism, the terpenoid pathway. In the horseradish leaf beetle Phaedon cochleariae a single enzyme can trigger the production of two completely different substances depending on whether it is regulated by cobalt, manganese or magnesium ions: iridoids, which are defensive substances the larvae use to repel predators, or juvenile hormones, which control insect's development. Insects ...
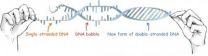
Study led by NUS researchers proves the existence of 3 overstretched DNA structures
2013-02-28
A team of researchers led by Associate Professor Yan Jie from the Department of Physics at the National University of Singapore (NUS) Faculty of Science has identified three new distinct overstretched deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) structures caused by mechanical stretching. This discovery provides a clear answer to a long-running debate among scientists over the nature of DNA overstretching.
Debate on Possible DNA Structural Transitions
Recent single-molecule studies revealed that mechanical stretching could induce transitions to elongated DNA structures. Three possible ...
Atoms with quantum memory
2013-02-28
This press release is available in German.
Ice cubes in a cocktail glass melt until an equilibrium state is reached in which the ice cubes are gone. After that, the geometric shape of the ice cubes is completely lost. The liquid does not contain any memory of their shape, the ordered ice crystal has turned into disordered water molecules. Ultra cold Bose-Einstein condensates behave differently; these highly ordered clouds of ultra cold particles also approach a disordered equilibrium state, but they retain some "memory" about their initial state for a remarkably long ...
Mayo Clinic finds steroids may shorten hospital stay for pneumonia patients
2013-02-28
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Patients with pneumonia may spend fewer days in the hospital if they are given steroids along with antibiotics and supportive care. That's the finding of a Mayo Clinic analysis of eight randomized-controlled clinical trials involving more than 1,100 patients. The results appear in the March issue of the Journal of Hospital Medicine.
"Given that the average hospital stay for community-acquired pneumonia can range from nine to 23 days, the prospect of speeding recovery, even by a day or two, is helpful," says co-author M. Rizwan Sohail, M.D., a Mayo infectious ...
'Crazy-busy' Canadians under pressure on the job
2013-02-28
Having more control in the workplace can have negative consequences for individuals but it depends on the form of job control, according to new research out of the University of Toronto.
Sociologist Scott Schieman measured a range of work conditions using data from a national survey of 6,004 Canadian workers. To measure levels of job pressure, he asked study participants questions such as: "How often do you feel overwhelmed by how much you had to do at work?" "How often do you have to work on too many tasks at the same time?" and "How often do the demands of your job ...