(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Rochester and the University of Ottawa have applied a recently developed technique to directly measure for the first time the polarization states of light. Their work both overcomes some important challenges of Heisenberg's famous Uncertainty Principle and also is applicable to qubits, the building blocks of quantum information theory.
They report their results in a paper published this week in Nature Photonics.
The direct measurement technique was first developed in 2011 by scientists at the National Research Council, Canada, to measure the wavefunction – a way of determining the state of a quantum system.
Such direct measurements of the wavefunction had long seemed impossible because of a key tenet of the uncertainty principle – the idea that certain properties of a quantum system could be known only poorly if certain other related properties were known with precision. The ability to make these measurements directly challenges the idea that full understanding of a quantum system could never come from direct observation.
The Rochester/Ottawa researchers, led by Robert Boyd, who has appointments at both universities, measured the polarization states of light - the directions in which the electric and magnetic fields of the light oscillate. Their key result, like that of the team that pioneered direct measurement, is that it is possible to measure key related variables, known as "conjugate" variables, of a quantum particle or state directly. The polarization states of light can be used to encode information, which is why they can be the basis of qubits in quantum information applications.
"The ability to perform direct measurement of the quantum wavefunction has important future implications for quantum information science," explained Boyd, Canada Excellence Research Chair in Quantum Nonlinear Optics at the University of Ottawa and Professor of Optics and Physics at the University of Rochester. "Ongoing work in our group involves applying this technique to other systems, for example, measuring the form of a "mixed" (as opposed to a pure) quantum state."
Previously, a technique called quantum tomography has allowed researchers to measure the information contained in these quantum states, but only indirectly. Quantum tomography requires intensive post-processing of the data, and this is a time-consuming process that is not required in the direct measurement technique. Thus, in principle, the new technique provides the same information as quantum tomography but in significantly less time.
"The key to characterizing any quantum system is gathering information about conjugate variables," said co-author Jonathan Leach, who is now a lecturer at Heriot-Watt University, UK. "The reason it wasn't thought possible to measure two conjugate variables directly was because measuring one would destroy the wavefunction before the other one could be measured."
The direct measurement technique employs a "trick" to measure the first property in such a way that the system is not disturbed significantly and information about the second property can still be obtained. This careful measurement relies on the "weak measurement" of the first property followed by a "strong measurement" of the second property.
First described 25 years ago, weak measurement requires that the coupling between the system and what is used to measure it be, as its name suggests, "weak", which means that the system is barely disturbed in the measurement process. The downside of this type of measurement is that a single measurement only provides a small amount of information, and to get an accurate readout, the process has to be repeated multiple times and the average taken.
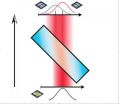
Boyd and his colleagues used the position and momentum of the light as the indicator of the polarization state. To couple the polarization to the spatial degree of freedom they used birefringent crystals: when light goes through such a crystal, there is a spatial separation introduced for different polarizations. For example, if light is made of a combination of horizontally and vertically polarized component, the positions of the individual components will spread out when it goes through the crystal according to its polarization. The thickness of the crystal can control the strength of the measurement, weak or strong, and determine the degree of separation, correspondingly small or large.
In this experiment, Boyd and his colleagues passed polarized light through two crystals of differing thicknesses: the first, a very thin crystal that "weakly" measures the horizontal and vertical polarization state; the second, a much thicker crystal that "strongly" measures the diagonal and anti-diagonal polarization state. As the first measurement was performed weakly, the system is not significantly disturbed, and therefore, information gained from the second measurement was still valid. This process is repeated several times to build up accurate statistics. Putting all of this together gives a full, direct characterization of the polarization states of the light.
INFORMATION:
The other authors of the paper are Jeff Z. Salvail, Megan Agnew and Allan S. Johnson, all of whom were undergraduates at Ottawa when the research was carried out, and Ottawa graduate student Eliot Bolduc.
This work was supported by the Canada Excellence Research Chairs (CERC) Program and Boyd also acknowledges support from the DARPA InPho program.
About the University of Rochester
The University of Rochester is one of the nation's leading private universities. Located in Rochester, N.Y., the University gives students exceptional opportunities for interdisciplinary study and close collaboration with faculty through its unique cluster-based curriculum. Its College, School of Arts and Sciences, and Hajim School of Engineering and Applied Sciences are complemented by its Eastman School of Music, Simon School of Business, Warner School of Education, Laboratory for Laser Energetics, School of Medicine and Dentistry, School of Nursing, Eastman Institute for Oral Health, and the Memorial Art Gallery.
Getting around the Uncertainty Principle
Physicists make first direct measurements of polarization states of light
2013-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cancer vaccines self-sabotage, channel immune attack to injection site
2013-03-04
HOUSTON – Cancer vaccines that attempt to stimulate an immune system assault fail because the killer T cells aimed at tumors instead find the vaccination site a more inviting target, scientists at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center report in Nature Medicine.
A common substance used in many cancer vaccines to boost immune attack betrays the cause by facilitating a buildup of T cells at the vaccination site, which then summon more T cells to help with the perceived threat.
"Vaccines stimulate production of T cells primed to attack the target cancer, and ...
2 new genes linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and related disorders
2013-03-04
A study led by St. Jude Children's Research Hospital has discovered mutations in two genes that lead to the death of nerve cells in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig's disease, and related degenerative diseases.
The same mutation occurred in both genes and led to the abnormal build-up of the proteins inside cells. These proteins play an essential role in normal RNA functioning and have also been linked to cancer, including the Ewing sarcoma, the second most common type of bone cancer in children and adolescents. The finding is the latest in ...
Study maps human metabolism in health and disease
2013-03-04
Scientists have produced an instruction manual for the human genome that provides a framework to better understand the relationship between an individual's genetic make-up and their lifestyle.
The international team of researchers say their study – published in Nature Biotechnology – provides the best model yet to explain why individuals react differently to environmental factors such as diet or medication.
"This research is the second important stage of our understanding of the human genome," said study author Professor Pedro Mendes, from The University of Manchester's ...
Researchers describe first 'functional HIV cure' in an infant
2013-03-04
A team of researchers from Johns Hopkins Children's Center, the University of Mississippi Medical Center and the University of Massachusetts Medical School describe the first case of a so-called "functional cure" in an HIV-infected infant. The finding, the investigators say, may help pave the way to eliminating HIV infection in children.
A report on the case is scheduled for presentation at a press conference on Sunday, March 3, at the 20th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) in Atlanta. Johns Hopkins Children's Center virologist Deborah Persaud, ...
International consortium builds 'Google Map' of human metabolism
2013-03-04
Building on earlier pioneering work by researchers at the University of California, San Diego, an international consortium of university researchers has produced the most comprehensive virtual reconstruction of human metabolism to date. Scientists could use the model, known as Recon 2, to identify causes of and new treatments for diseases like cancer, diabetes and even psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Each person's metabolism, which represents the conversion of food sources into energy and the assembly of molecules, is determined by genetics, environment and ...
Man-made material pushes the bounds of superconductivity
2013-03-04
MADISON — A multi-university team of researchers has artificially engineered a unique multilayer material that could lead to breakthroughs in both superconductivity research and in real-world applications.
The researchers can tailor the material, which seamlessly alternates between metal and oxide layers, to achieve extraordinary superconducting properties — in particular, the ability to transport much more electrical current than non-engineered materials.
The team includes experts from the University of Wisconsin-Madison, Florida State University and the University ...
International consortium discovers seven new genomic regions associated with AMD
2013-03-04
(Boston) – An international group of researchers has discovered seven new regions of the human genome—called loci—that are associated with increased risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of blindness. The AMD Gene Consortium, a network of international investigators representing 18 research groups, also confirmed 12 loci identified in previous studies. The study, which is published online in Nature Genetics and represents the most comprehensive genome-wide analysis of genetic variations associated with AMD, was supported by the National Eye Institute ...
Genetic risk factors for common eye disorder come into focus
2013-03-04
An international group of investigators has identified seven new genetic regions associated with age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a common cause of blindness in older individuals. The findings, reported online March 3 in Nature Genetics, could point to new biological pathways and therapeutic targets for AMD.
The AMD Gene Consortium, a network of 18 research groups supported by the National Eye Institute, also confirmed 12 genetic loci identified in previous studies. The study represents the most comprehensive genome-wide analysis of genetic variations associated ...
ADHD takes a toll well into adulthood
2013-03-04
BOSTON, Mass, March 4, 2013—The first large, population-based study to follow children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) into adulthood shows that ADHD often doesn't "go away," and that children with ADHD are more likely to have other psychiatric disorders as adults. Although numbers were small, they also appear more likely to commit suicide and are often incarcerated as adults.
"Only 37.5 percent of the children we contacted as adults were free of these really worrisome outcomes," says William Barbaresi, MD, of Boston Children's Hospital, lead investigator ...
Life saving treatment for fire ant allergy under used
2013-03-04
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, ILL. (March 4, 2013) – Two million Americans are allergic to insect stings, an allergy which sends more than 500,000 people to the emergency room annually. Yet, according to a study published today in the March issue of Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, the scientific journal of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAA), while fire ant allergy sufferers know allergy shots can save their life, more than 60 percent do not adhere to treatment guidelines.
For optimal protection against fire ant stings, allergists recommend allergy ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
[Press-News.org] Getting around the Uncertainty PrinciplePhysicists make first direct measurements of polarization states of light