(Press-News.org) A University of Central Florida chemist has come up with a unique way to kill certain cancer cells – give them acid reflux.
Chemistry professor Kevin Belfield used a special salt to make cancer cells more acidic – similar to the way greasy foods cause acid reflux in some people. He used a light-activated, acid-generating molecule to make the cells more acidic when exposed to specific wavelengths of light, which in turn kills the bad cells. The surrounding healthy cells stay intact.
The technique is a simple way around a problem that has frustrated researchers for years. For photodynamic therapy (the special laser-light treatment) to work, cancer cells loaded with photosensitizers need oxygen to trigger the fatal reaction. But by their very nature, most cancer cells lack oxygen. Nonetheless, scientists were intent on making the photodynamic system work because it offers a way to target cancer cells deep within human tissue without causing a lot of collateral damage.
Instead of focusing on oxygen, Belfield flipped the problem around and found another way to poison the bad cells, while protecting the healthy ones.
"It's the first time we've found a way around the oxygen problem," Belfield said. "This work is truly ground breaking. It should eventually provide a therapeutic means to treat certain types of cancers with minimal side effects. It should also be a very useful tool for cell biologists and biomedical researchers. It could even find a place in treating other diseases such as neurodegenerative diseases."
His work was recently published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society. (http://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/ja3122312)
Belfield and his team at UCF used human colorectal carcinoma cells for the study, which was funded by the National Science Foundation and the National Institutes for Health. More research is needed to determine that there are no serious side affects in humans and whether the technique will work on a variety of cancers, but Belfield is optimistic.
"Predicting commercialization is difficult at best," he said. "But we are well situated to forge ahead".
So how did Belfield come up with such an "outside the box" approach? His other non-medical related research was the inspiration.
Belfield has developed a three-dimensional, optical data-storage system, which involves the use of acid generators. About six years ago he wondered if his approach could have applications in medical therapy.
"It took about five years to get someone in my research group interested to take on the unorthodox project," Belfield said. "But it seems to have paid off."
Other contributors to the research are Xiling Yue, Ciceron O. Yanez and Sheng Yao, researchers and students at UCF students focusing on chemistry or photonics.
Belfield is one of the pioneers in two-photon absorbing materials, two-photon photochemistry, and two-photon photophysics. His research spans a number of disciplines including organic, polymer, and physical chemistry, as well as optics, optical microscopy, and bioimaging. His research has potential applications in everything from the way people store data on DVDs to fighting cancer.
INFORMATION:
50 Years of Achievement: The University of Central Florida, the nation's second-largest university with nearly 60,000 students, is celebrating its 50th anniversary in 2013. UCF has grown in size, quality, diversity and reputation, and today the university offers more than 200 degree programs at its main campus in Orlando and more than a dozen other locations. Known as America's leading partnership university, UCF is an economic engine attracting and supporting industries vital to the region's success now and into the future. For more information, visit http://today.ucf.edu.
Killing cancer cells with acid reflux
2013-03-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pancakes with a side of math
2013-03-07
Philadelphia, PA—For many of us, maple syrup is an essential part of breakfast—a staple accompaniment to pancakes and waffles—but rarely do we think about the complicated and little-understood physiological aspects of syrup production. Each spring, maple growers in temperate regions around the world collect sap from sugar maple trees, which is one of the first steps in producing this delicious condiment.
However, the mechanisms behind sap exudation—processes that trigger pressure differences causing sap to flow— in maple trees are a topic of much debate. In a paper ...
HIV therapy just got easier: Fewer drugs may be needed for treatment-experienced patients
2013-03-07
VIDEO:
Karen Tashima, MD, director of the HIV Clinical Trials Program at The Miriam Hospital, led a study to look at new treatment regimens for patients with drug-resistant HIV.
...
Click here for more information.
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – A new multi-site study reveals patients with drug-resistant HIV can safely achieve viral suppression – the primary goal of HIV therapy – without incorporating the traditional class of HIV medications into their treatment regimen. Karen Tashima, M.D., ...
Majority of Albertans support assisted suicide: UAlberta study
2013-03-07
(Edmonton) An overwhelming majority of Albertans believe dying adults should have the right to request to end their life, according to new research from the University of Alberta.
U of A researcher Donna Wilson led the team that studied the views of 1,203 Albertans on assisted suicide, currently illegal in Canada. A majority—77.4 per cent—felt dying adults should have the right to end their life early.
"Increasingly, there are countries or states where they are allowing assisted suicide or euthanasia. Like many of those countries, Canada will have to grapple with this ...
UTHealth researchers find industrial chemicals in food samples
2013-03-07
HOUSTON – (March 6, 2013) – Researchers at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) have discovered phthalates, industrial chemicals, in common foods purchased in the United States. Phthalates can be found in a variety of products and food packaging material, child-care articles and medical devices.
"Although it's not completely understood how phthalates get into our food, packaging may be a contributor to the levels of the toxin in food," said lead investigator Arnold Schecter, M.D., M.P.H., professor of environmental health at The University ...
A new cryptic spider species from Africa
2013-03-07
The species from the genus Copa are very common spiders found in the leaf litter of various habitats. Being predominantly ground-living, they occur widely in savanna woodlands but also occasionally in forests, where they are well camouflaged. They usually share the litter microhabitats with several other species of the family Corinnidae. The spiders from this cryptic, ground-dwelling genus in the continental Afrotropical Region are revised in a study published in the open access journal Zookeys.
The number of continental species in the Afrotropical Region has been reduced ...
How to predict the progress of technology
2013-03-07
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Researchers at MIT and the Santa Fe Institute have found that some widely used formulas for predicting how rapidly technology will advance — notably, Moore's Law and Wright's Law — offer superior approximations of the pace of technological progress. The new research is the first to directly compare the different approaches in a quantitative way, using an extensive database of past performance from many different industries.
Some of the results were surprising, says Jessika Trancik, an assistant professor of engineering systems at MIT. The findings could ...
Iowa State engineers developing ideas, technologies to save the Earth from asteroids
2013-03-07
AMES, Iowa – Bong Wie has heard the snickers.
You want to protect the Earth from asteroids? Where were you when the dinosaurs needed you? You want to be like Bruce Willis in that asteroid movie?
Wie has a serious reply: After five years of science and engineering work, Wie and his small team have a publication list of 40-plus technical papers, $600,000 of NASA research support and a proposal for a $500 million test launch of an asteroid intercept system. Plus, Wie has just been invited to show off his research as part of NASA's Technology Day on the Hill in Washington, ...
INRS overcomes a hurdle in the development of terahertz lasers
2013-03-07
This press release is available in French.
Dr. Roberto Morandotti and his team at the INRS Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications Research Centre have developed a device that is critical to the use of terahertz (THz) sources for a variety of applications. Their electromagnetic non-reciprocal isolator is the subject of a recent article in Nature Communications, showing just how important this new development is. Until now, no isolator existed that was effective in the THz region of the spectrum, a situation that held back the development of certain technologies. The new ...
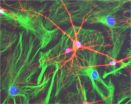
Star-shaped glial cells act as the brain's 'motherboard'
2013-03-07
The transistors and wires that power our electronic devices need to be mounted on a base material known as a "motherboard." Our human brain is not so different — neurons, the cells that transmit electrical and chemical signals, are connected to one another through synapses, similar to transistors and wires, and they need a base material too.
But the cells serving that function in the brain may have other functions as well. PhD student Maurizio De Pittà of Tel Aviv University's Schools of Physics and Astronomy and Electrical Engineering says that astrocytes, the star-shaped ...
Ketchup turns somersaults
2013-03-07
This press release is available in German.
The unusual behavior of complex fluids is part of our daily life: cake dough climbs up the stirring bar, ketchup becomes liquid when you shake it. Also technology uses such phenomena: if we add a small amount of long-chained polymer molecules, a pipeline can transport more oil. The polymers reduce the flow resistance. But up to now the origin of these effects was unclear. The engineers had to rely on estimates and lengthy trials.
A team of physicists led by Professor Andreas Bausch, Chair of Cellular Biophysics at TUM now ...