(Press-News.org) A team of astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has taken an important step closer to finding the birth certificate of a star that's been around for a very long time.
"We have found that this is the oldest known star with a well-determined age," said Howard Bond of Pennsylvania State University in University Park, Pa., and the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Md.
The star could be as old as 14.5 billion years (plus or minus 0.8 billion years), which at first glance would make it older than the universe's calculated age of about 13.8 billion years, an obvious dilemma.
But earlier estimates from observations dating back to 2000 placed the star as old as 16 billion years. And this age range presented a potential dilemma for cosmologists. "Maybe the cosmology is wrong, stellar physics is wrong, or the star's distance is wrong," Bond said. "So we set out to refine the distance."
The new Hubble age estimates reduce the range of measurement uncertainty, so that the star's age overlaps with the universe's age — as independently determined by the rate of expansion of space, an analysis of the microwave background from the big bang, and measurements of radioactive decay.
This "Methuselah star," cataloged as HD 140283, has been known about for more than a century because of its fast motion across the sky. The high rate of motion is evidence that the star is simply a visitor to our stellar neighborhood. Its orbit carries it down through the plane of our galaxy from the ancient halo of stars that encircle the Milky Way, and will eventually slingshot back to the galactic halo.
This conclusion was bolstered by the 1950s astronomers who were able to measure a deficiency of heavier elements in the star as compared to other stars in our galactic neighborhood. The halo stars are among the first inhabitants of our galaxy and collectively represent an older population from the stars, like our sun, that formed later in the disk. This means that the star formed at a very early time before the universe was largely "polluted" with heavier elements forged inside stars through nucleosynthesis. (The Methuselah star has an anemic 1/250th as much of the heavy element content of our sun and other stars in our solar neighborhood.)
The star, which is at the very first stages of expanding into a red giant, can be seen with binoculars as a 7th-magnitude object in the constellation Libra.
Hubble's observational prowess was used to refine the distance to the star, which comes out to be 190.1 light-years. Bond and his team performed this measurement by using trigonometric parallax, where an apparent shift in the position of a star is caused by a change in the observer's position. The results are published in the February 13 issue of the Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The parallax of nearby stars can be measured by observing them from opposite points in Earth's orbit around the sun. The star's true distance from Earth can then be precisely calculated through straightforward triangulation.
Once the true distance is known, an exact value for the star's intrinsic brightness can be calculated. Knowing a star's intrinsic brightness is a fundamental prerequisite to estimating its age.
Before the Hubble observation, the European Space Agency's Hipparcos satellite made a precise measurement of the star's parallax, but with an age measurement uncertainty of 2 billion years. One of Hubble's three Fine Guidance Sensors measured the position of the Methuselah star. It turns out that the star's parallax came out to be virtually identical to the Hipparcos measurements. But Hubble's precision is five times better that than of Hipparcos. Bond's team managed to shrink the uncertainty so that the age estimate was five times more precise.
With a better handle on the star's brightness Bond's team refined the star's age by applying contemporary theories about the star's burn rate, chemical abundances, and internal structure. New ideas are that leftover helium diffuses deeper into the core and so the star has less hydrogen to burn via nuclear fusion. This means it uses fuel faster and that correspondingly lowers the age.
Also, the star has a higher than predicted oxygen-to-iron ratio, and this too lowers the age. Bond thinks that further oxygen measurement could reduce the star's age even more, because the star would have formed at a slightly later time when the universe was richer in oxygen abundance. Lowering the upper age limit would make the star unequivocally younger than the universe.
"Put all of those ingredients together and you get an age of 14.5 billion years, with a residual uncertainty that makes the star's age compatible with the age of the universe," said Bond. "This is the best star in the sky to do precision age calculations by virtue of its closeness and brightness."
This Methuselah star has seen many changes over its long life. It was likely born in a primeval dwarf galaxy. The dwarf galaxy eventually was gravitationally shredded and sucked in by the emerging Milky Way over 12 billion years ago.
The star retains its elongated orbit from that cannibalism event. Therefore, it's just passing through the solar neighborhood at a rocket-like speed of 800,000 miles per hour. It takes just 1,500 years to traverse a piece of sky with the angular width of the full Moon. The star's proper motion angular rate is so fast (0.13 milliarcseconds an hour) that Hubble could actually photograph its movement in literally a few hours.
INFORMATION:
The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Md., conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington.
For images, illustrations, and more information about HD 140283, visit:
http://hubblesite.org/news/2013/08
http://www.nasa.gov/hubble
Hubble finds birth certificate of oldest known star
2013-03-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Small physician practices that care for children unprepared to become medical homes
2013-03-08
Ann Arbor, Mich. — Primary care practices around the country are being encouraged and even paid to become "medical homes," but small practices might be at a significant disadvantage in this race to improve health care for children, according to a new study by child health experts at C.S. Mott Children's Hospital.
Efforts around the country to improve health care for children have increasingly focused on the medical home as a model to make primary care practices more accessible, comprehensive, and focused on quality improvement. Since 2008, practices could become officially ...
Biologists produce rainbow-colored algae
2013-03-08
What can green algae do for science if they weren't, well, green?
That's the question biologists at UC San Diego sought to answer when they engineered a green alga used commonly in laboratories, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, into a rainbow of different colors by producing six different colored fluorescent proteins in the algae cells.
While fluorescent green, red, blue and yellow may be all the rage this year for running shoes and other kinds of sporting gear, fluorescent algae hasn't been a style trend yet in scientific laboratories. But in announcing their achievement in ...
Stocking Florida bass in Texas reservoirs may alter stream systems connected to stocked reservoirs
2013-03-08
WACO, Texas (March 7, 2013) - A genetic analysis by Baylor University biologists suggests that the stocking of Florida bass in Texas reservoirs impacts bass populations far beyond the actual stocking location.
The native largemouth bass has a long and nearly continuous stocking history in Texas. However, the Florida bass is widely considered a better sport fish because it grows to a greater size. Subsequently, stocking efforts in Texas reservoirs have transitioned from largemouth bass to Florida bass.
The Baylor researchers analyzed the genetic composition of 69 largemouth ...
Net advantage
2013-03-08
Malaria, the leading cause of death among children in Africa, could be eliminated if three-fourths of the population used insecticide-treated bed nets, according to a new study from the National Institute for Mathematical and Biological Synthesis (NIMBioS).
The study, which uses a mathematical model, found that use of insecticide-treated bed nets or ITNs positively affected the infection's reproduction number, or R, which is the primary epidemiological number used to determine the degree which a disease can spread through a population. The model concludes that if 75 percent ...
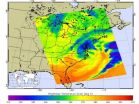
NASA provides satellite views of Nor'easter on March 7, 2013
2013-03-08
VIDEO:
This animation of NOAA GOES-13 satellite imagery from March 5-7, 2013, shows the progression of a cold front from the west associated with a low pressure system that brought snow...
Click here for more information.
The merging of two low pressure areas into a large Nor'easter on March 6 brought winter weather advisories and warnings to the Mid-Atlantic. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared and near infrared image of the storm's power, and NASA created an animation ...
Pan-STARRS finds a 'lost' supernova
2013-03-08
The star Eta Carinae is ready to blow. 170 years ago, this 100-solar-mass object belched out several suns' worth of gas in an eruption that made it the second-brightest star after Sirius. That was just a precursor to the main event, since it will eventually go supernova.
Supernova explosions of massive stars are common in spiral galaxies like the Milky Way, where new stars are forming all the time. They are almost never seen in elliptical galaxies where star formation has nearly ceased. As a result, astronomers were surprised to find a young-looking supernova in an old ...
Earth is warmer today than during 70 to 80 percent of the past 11,300 years
2013-03-08
With data from 73 ice and sediment core monitoring sites around the world, scientists have reconstructed Earth's temperature history back to the end of the last Ice Age.
The analysis reveals that the planet today is warmer than it's been during 70 to 80 percent of the last 11,300 years.
Results of the study, by researchers at Oregon State University (OSU) and Harvard University, are published this week in a paper in the journal Science.
Lead paper author Shaun Marcott of OSU says that previous research on past global temperature change has largely focused on the ...
UTHealth research: Low incidence of venous insufficiency in MS
2013-03-08
HOUSTON – (March 7, 2013) – Results of a study using several imaging methods showed that CCSVI (chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency) occurs at a low rate in both people with multiple sclerosis (MS) and non-MS volunteers, contrary to some previous studies. The research by an interdisciplinary team at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) was published in a recent early online edition of the Annals of Neurology.
"Our results in this phase of the study suggest that findings in the major veins that drain the brain consistent with CCSVI ...
'Climate-smart strategies' proposed for spectacular US-Canadian landscape
2013-03-08
A new report from the Wildlife Conservation Society Canada (WCS Canada) creates a conservation strategy that will promote wildlife resiliency in the Southern Canadian Rockies to the future impacts of climate change and road use. The report's "safe passages and safe havens" were informed in part by an assessment of six iconic species—bull trout, westslope cutthroat trout, grizzly bears, wolverines, mountain goats and bighorn sheep—five of which were ranked as highly vulnerable to projected changes.
Nestled between Glacier National Park in Montana and Banff National ...
How to thrive in battery acid and among toxic metals
2013-03-08
In the movie Alien, the title character is an extraterrestrial creature that can survive brutal heat and resist the effects of toxins.
In real life, organisms with similar traits exist, such as the "extremophile" red alga Galdieria sulphuraria.
In hot springs in Yellowstone National Park, Galdieria uses energy from the sun to produce sugars through photosynthesis.
In the darkness of old mineshafts in drainage as caustic as battery acid, it feeds on bacteria and survives high concentrations of arsenic and heavy metals.
How has a one-celled alga acquired such ...