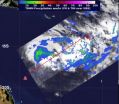
(Press-News.org) NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite noticed areas of heavy rainfall in low pressure System 92P hours before it became the nineteenth tropical cyclone of the Southern Pacific Ocean.
NASA's TRMM satellite captured a look at the rainfall rates within low pressure System 92P on March 7 at 0023 UTC (March 6 at 7:23 p.m. EST), just hours before it became Tropical Cyclone 19P (TC 19P). TRMM data indicated that heavy rain was falling at a rate of 2 inches/50 mm per hour around the center of circulation, and that some of the thunderstorms were powerful as they topped heights of 9.3 miles (15 kilometers). Bands of thunderstorms around the storm expanded, strengthened and wrapped tighter around the storm's center today, March 7, according to the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC).
On March 7 at 1200 UTC (7 a.m. EST) the intensifying tropical storm had maximum sustained winds near 35 knots (40 mph/64 kph). TC 19P was centered near 15.4 south latitude and 156.9 east longitude about 660 nautical miles (759.5 miles/1,222 km) northwest of Noumea, New Caledonia. TC19P was moving to the east-northeast at 11 knots (12.6 mph/20.3 kph).
JTWC forecasters expect TC 19P to strengthen and curve to the southeast, affecting New Caledonia by March 11.
INFORMATION:
NASA's TRMM satellite sees Tropical Cyclone 19P form
2013-03-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Trauma simulation technique makes better journalists
2013-03-08
This press release is available in French.
Montreal, March 7, 2013 – Just hours after the tragic shooting of 27 victims at Sandy Hook Elementary School, Twitter was overloaded with messages slamming reporters for interviewing children involved in the tragedy. While some of the journalists probably knew better but wanted the story at all costs, others were rookie reporters facing ethical decisions for the first time and unaware of the impact these interviews might have on the young survivors.
Past studies have documented that new journalists can cause a number of ...
Hubble finds birth certificate of oldest known star
2013-03-08
A team of astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has taken an important step closer to finding the birth certificate of a star that's been around for a very long time.
"We have found that this is the oldest known star with a well-determined age," said Howard Bond of Pennsylvania State University in University Park, Pa., and the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Md.
The star could be as old as 14.5 billion years (plus or minus 0.8 billion years), which at first glance would make it older than the universe's calculated age of about 13.8 billion ...
Small physician practices that care for children unprepared to become medical homes
2013-03-08
Ann Arbor, Mich. — Primary care practices around the country are being encouraged and even paid to become "medical homes," but small practices might be at a significant disadvantage in this race to improve health care for children, according to a new study by child health experts at C.S. Mott Children's Hospital.
Efforts around the country to improve health care for children have increasingly focused on the medical home as a model to make primary care practices more accessible, comprehensive, and focused on quality improvement. Since 2008, practices could become officially ...
Biologists produce rainbow-colored algae
2013-03-08
What can green algae do for science if they weren't, well, green?
That's the question biologists at UC San Diego sought to answer when they engineered a green alga used commonly in laboratories, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, into a rainbow of different colors by producing six different colored fluorescent proteins in the algae cells.
While fluorescent green, red, blue and yellow may be all the rage this year for running shoes and other kinds of sporting gear, fluorescent algae hasn't been a style trend yet in scientific laboratories. But in announcing their achievement in ...
Stocking Florida bass in Texas reservoirs may alter stream systems connected to stocked reservoirs
2013-03-08
WACO, Texas (March 7, 2013) - A genetic analysis by Baylor University biologists suggests that the stocking of Florida bass in Texas reservoirs impacts bass populations far beyond the actual stocking location.
The native largemouth bass has a long and nearly continuous stocking history in Texas. However, the Florida bass is widely considered a better sport fish because it grows to a greater size. Subsequently, stocking efforts in Texas reservoirs have transitioned from largemouth bass to Florida bass.
The Baylor researchers analyzed the genetic composition of 69 largemouth ...
Net advantage
2013-03-08
Malaria, the leading cause of death among children in Africa, could be eliminated if three-fourths of the population used insecticide-treated bed nets, according to a new study from the National Institute for Mathematical and Biological Synthesis (NIMBioS).
The study, which uses a mathematical model, found that use of insecticide-treated bed nets or ITNs positively affected the infection's reproduction number, or R, which is the primary epidemiological number used to determine the degree which a disease can spread through a population. The model concludes that if 75 percent ...
NASA provides satellite views of Nor'easter on March 7, 2013
2013-03-08
VIDEO:
This animation of NOAA GOES-13 satellite imagery from March 5-7, 2013, shows the progression of a cold front from the west associated with a low pressure system that brought snow...
Click here for more information.
The merging of two low pressure areas into a large Nor'easter on March 6 brought winter weather advisories and warnings to the Mid-Atlantic. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared and near infrared image of the storm's power, and NASA created an animation ...
Pan-STARRS finds a 'lost' supernova
2013-03-08
The star Eta Carinae is ready to blow. 170 years ago, this 100-solar-mass object belched out several suns' worth of gas in an eruption that made it the second-brightest star after Sirius. That was just a precursor to the main event, since it will eventually go supernova.
Supernova explosions of massive stars are common in spiral galaxies like the Milky Way, where new stars are forming all the time. They are almost never seen in elliptical galaxies where star formation has nearly ceased. As a result, astronomers were surprised to find a young-looking supernova in an old ...
Earth is warmer today than during 70 to 80 percent of the past 11,300 years
2013-03-08
With data from 73 ice and sediment core monitoring sites around the world, scientists have reconstructed Earth's temperature history back to the end of the last Ice Age.
The analysis reveals that the planet today is warmer than it's been during 70 to 80 percent of the last 11,300 years.
Results of the study, by researchers at Oregon State University (OSU) and Harvard University, are published this week in a paper in the journal Science.
Lead paper author Shaun Marcott of OSU says that previous research on past global temperature change has largely focused on the ...
UTHealth research: Low incidence of venous insufficiency in MS
2013-03-08
HOUSTON – (March 7, 2013) – Results of a study using several imaging methods showed that CCSVI (chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency) occurs at a low rate in both people with multiple sclerosis (MS) and non-MS volunteers, contrary to some previous studies. The research by an interdisciplinary team at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) was published in a recent early online edition of the Annals of Neurology.
"Our results in this phase of the study suggest that findings in the major veins that drain the brain consistent with CCSVI ...