(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR—In evolutionary biology, there is a deeply rooted supposition that you can't go home again: Once an organism has evolved specialized traits, it can't return to the lifestyle of its ancestors.
There's even a name for this pervasive idea. Dollo's law states that evolution is unidirectional and irreversible. But this "law" is not universally accepted and is the topic of heated debate among biologists.
Now a research team led by two University of Michigan biologists has used a large-scale genetic study of the lowly house dust mite to uncover an example of reversible evolution that appears to violate Dollo's law.
The study shows that tiny free-living house dust mites, which thrive in the mattresses, sofas and carpets of even the cleanest homes, evolved from parasites, which in turn evolved from free-living organisms millions of years ago.
"All our analyses conclusively demonstrated that house dust mites have abandoned a parasitic lifestyle, secondarily becoming free-living, and then speciated in several habitats, including human habitations," according to Pavel Klimov and Barry OConnor of the U-M Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology.
Their paper, "Is permanent parasitism reversible?—Critical evidence from early evolution of house dust mites," is scheduled to be published online March 8 in the journal Systematic Biology.
Mites are arachnids related to spiders (both have eight legs) and are among the most diverse animals on Earth. House dust mites, members of the family Pyroglyphidae, are the most common cause of allergic symptoms in humans, affecting up to 1.2 billion people worldwide.
Despite their huge impact on human health, the evolutionary relationships between these speck-sized creatures are poorly understood. According to Klimov and OConnor, there are 62 different published hypotheses arguing about whether today's free-living dust mites originated from a free-living ancestor or from a parasite—an organism that lives on or in a host species and damages its host.
In their study, Klimov and OConnor evaluated all 62 hypotheses. Their project used large-scale DNA sequencing, the construction of detailed evolutionary trees called phylogenies, and sophisticated statistical analyses to test the hypotheses about the ancestral ecology of house dust mites.
On the phylogenetic tree they produced, house dust mites appear within a large lineage of parasitic mites, the Psoroptidia. These mites are full-time parasites of birds and mammals that never leave the bodies of their hosts. The U-M analysis shows that the immediate parasitic ancestors of house dust mites include skin mites, such as the psoroptic mange mites of livestock and the dog and cat ear mite.
"This result was so surprising that we decided to contact our colleagues to obtain their feedback prior to sending these data for publication," said Klimov, the first author of the paper and an assistant research scientist in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology.
The result was so surprising largely because it runs counter to the entrenched idea that highly specialized parasites cannot return to the free-living lifestyle of their ancestors.
"Parasites can quickly evolve highly sophisticated mechanisms for host exploitation and can lose their ability to function away from the host body," Klimov said. "They often experience degradation or loss of many genes because their functions are no longer required in a rich environment where hosts provide both living space and nutrients. Many researchers in the field perceive such specialization as evolutionarily irreversible."
The U-M findings also have human-health implications, said OConnor, a professor in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and a curator of insects and arachnids at the U-M Museum of Zoology.
"Our study is an example of how asking a purely academic question may result in broad practical applications," he said. "Knowing phylogenetic relationships of house dust mites may provide insights into allergenic properties of their immune-response-triggering proteins and the evolution of genes encoding allergens."
The project started in 2006 with a grant from the National Science Foundation. The first step was to obtain specimens of many free-living and parasitic mites—no simple task given that some mite species are associated with rare mammal or bird species around the world.
The research team relied on a network of 64 biologists in 19 countries to obtain specimens. In addition, Klimov and OConnor conducted field trips to North and South America, Europe, Asia and Africa. On one occasion, it took two years to obtain samples of an important species parasitizing African birds.
A total of around 700 mite species were collected for the study. For the genetic analysis, the same five nuclear genes were sequenced in each species.
How might the ecological shift from parasite to free-living state have occurred?
There is little doubt that early free-living dust mites were nest inhabitants—the nests of birds and mammals are the principal habitat of all modern free-living species in the family Pyroglyphidae. Klimov and OConnor propose that a combination of several characteristics of their parasitic ancestors played an important role in allowing them to abandon permanent parasitism: tolerance of low humidity, development of powerful digestive enzymes that allowed them to feed on skin and keratinous (containing the protein keratin, which is found in human hair and fingernails) materials, and low host specificity with frequent shifts to unrelated hosts.
These features, which occur in almost all parasitic mites, were likely important precursors that enabled mite populations to thrive in host nests despite low humidity and scarce, low-quality food resources, according to Klimov and OConnor. For example, powerful enzymes allowed these mites to consume hard-to-digest feather and skin flakes composed of keratin.
With the advent of human civilization, nest-inhabiting pyroglyphids could have shifted to human dwellings from the nests of birds and rodents living in or around human homes. Once the mites moved indoors, the potent digestive enzymes and other immune-response-triggering molecules they carry made them a major source of human allergies.
###
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation and also benefited, in part, from specimens collected by the Field Museum's Emerging Pathogens Project, funded by the Davee Foundation and the Dr. Ralph and Marian Falk Medical Research Trust. The molecular work was conducted in the Genomic Diversity Laboratory of the U-M Museum of Zoology.
Pavel Klimov: http://www.lsa.umich.edu/eeb/directory/research_scientists/pklimov/default.asp
Barry OConnor: http://www.lsa.umich.edu/eeb/directory/faculty/bmoc
Genetic study of house dust mites demonstrates reversible evolution
2013-03-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New fish species described from the streams of Manyas Lake basin, Turkey
2013-03-08
The newly described species Alburnoides manyasensis, belongs the large carp family Cyprinidae that includes freshwater fishes such as he carps, the minnows, and their relatives. This is the largest fish family, and more notably the largest family of vertebrate animals, with the remarkable numbers of over 2,400 species. Cyprinids are highly important food fish because they make the largest part of biomass in most water types except for fast-flowing rivers.
The genus Alburnoides is widely distributed in Turkey in rivers and streams of basins of the Marmara, Black and ...
Mom's sensitivity helps language development in children with hearing loss
2013-03-08
CORAL GABLES, FL (March 8, 2013) -- University of Miami (UM) Psychologist Alexandra L. Quittner leads one of the largest, most nationally representative studies of the effects of parenting on very young, deaf children who have received cochlear implants. The findings indicate that mothers who are most sensitive in their interactions with their children receiving cochlear implants have kids that develop language faster, almost "catching up" to their hearing peers. The report is published in the Journal of Pediatrics.
"I was surprised that maternal sensitivity had such ...
BRAF inhibitor treatment causes melanoma cells to shift how they produce energy
2013-03-08
A multi-institutional study has revealed that BRAF-positive metastatic malignant melanomas develop resistance to treatment with drugs targeting the BRAF/MEK growth pathway through a major change in metabolism. The findings, which will be published in Cancer Cell and have been released online, suggest a strategy to improve the effectiveness of currently available targeted therapies.
"We were surprised to find that melanoma cells treated with the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib dramatically change the way they produce energy to stay alive," says David E. Fisher, MD, PhD, chief ...
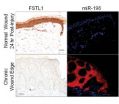
A*STAR scientists discover 'switch' critical to wound healing
2013-03-08
Patients with diseases such as diabetes suffer from painful wounds that take a long time to heal making them more susceptible to infections that could even lead to amputations. A*STAR's discovery paves the way for therapeutics to improve healing of such chronic wounds, which are a significant burden to patients.
1. Scientists from A*STAR's Institute of Medical Biology (IMB) have identified a molecular "switch" that controls the migration of skin cells necessary for wounds to close and heal. This is especially significant for diabetics and other patients who suffer from ...
Stanford scientists calculate the carbon footprint of grid-scale battery technologies
2013-03-08
Americans take electrical power for granted whenever they flip on a light switch. But the growing use of solar and wind power in the United States makes the on-demand delivery of electricity more challenging.
A key problem is that the U.S. electrical grid has virtually no storage capacity, so grid operators can't stockpile surplus clean energy and deliver it at night, or when the wind isn't blowing.
To provide more flexibility in managing the grid, researchers have begun developing new batteries and other large-scale storage devices. But the fossil fuel required to ...
Home toxic home
2013-03-08
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Most organisms would die in the volcanic sulfur pools of Yellowstone and Mount Etna. Robust simple algae call it home, and their secrets to survival could advance human medicine and bioremediation.
Mike Garavito, Michigan State University professor of biochemistry and molecular biology was part of a research team that revealed how primitive red algae use horizontal gene transfer, in essence stealing useful genes from other organisms to evolve and thrive in harsh environments.
Their study, published in the current issue of Science, shows that the ...
Anti-aging drug breakthrough
2013-03-08
Drugs that combat ageing may be available within five years, following landmark work led by an Australian researcher.
The work, published in the March 8 issue of Science, finally proves that a single anti-ageing enzyme in the body can be targeted, with the potential to prevent age-related diseases and extend lifespans.
The paper shows all of the 117 drugs tested work on the single enzyme through a common mechanism. This means that a whole new class of anti-ageing drugs is now viable, which could ultimately prevent cancer, Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes.
"Ultimately, ...
Virus and genes involved in causation of schizophrenia
2013-03-08
Viruses and genes interact in a way that may increase the risk of developing schizophrenia significantly. This happens already in the developing foetus.
An international team of scientists led by Aarhus University, Denmark, has made this discovery. As the first in the world, they scanned the entire genome of hundreds of sick and healthy people to see if there is an interaction between genes and a very common virus - cytomegalovirus - and to see whether the interaction influences the risk of developing schizophrenia.
And it does.
Women that have been infected by the virus ...
Specialised germanium surface as universal protein adapter
2013-03-08
Researchers at the Ruhr Universität Bochum have developed a new method for attaching proteins to the surface of germanium crystals – for the first time also membrane proteins. This enables time-resolved tracking of the interactions between molecules using infrared spectroscopy in a way that is accurate down to atomic resolution. The method is applied in the EU project "Kinetics for Drug Discovery, K4DD", in which scientists explore the interplay of drugs and their interaction partners. With the new technology, the researchers can also study so-called G-protein-coupled receptors, ...
Maternal obesity increases the risk of frequent wheezing in offspring
2013-03-08
The fact that excess weight during pregnancy has negative consequences is not new information. A new study now concludes that the children of mothers obese before falling pregnant are four times more likely to have frequent wheezing, which is one of the symptoms of asthma, compared to the children of mothers weighing a normal weight.
Researchers from the Centre for Research in Environmental Epidemiology (CREAL) assessed whether obesity in mothers increases the risk of their children having frequent wheezing, a symptom associated with susceptibility to asthma during infancy ...