(Press-News.org) Scientists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Maryland, College Park, have built a practical, high-efficiency nanostructured electron source. Described in the journal Nanotechnology*, this new, patent-pending technology could lead to improved microwave communications and radar, and more notably to new and improved X-ray imaging systems for security and health-care applications.
While thermionic electron sources such as the hot filaments inside cathode ray tubes have largely been replaced by LEDs and liquid crystals for display screens and televisions, they are still used to produce microwaves for radar and X-rays for medical imaging. Thermionic sources use an electric current to boil electrons off the surface of a wire filament, similar to the way an incandescent light bulb uses an electric current to heat a wire filament until it glows.
And like an incandescent light bulb, thermionic sources are generally not very energy efficient. It takes a lot of power to boil off the electrons, which spew in every direction. Those that aren't lost have to be captured and focused using a complicated system of electric and magnetic fields. Field emission electron sources require much less power and produce a much more directional and easily controllable stream of electrons.
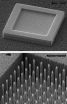
To build their field emission source, the NIST team took a tough material—silicon carbide—and used a room-temperature chemical process to make it highly porous like a sponge. They then patterned it into microscopic emitting structures in the shape of pointed rods or sharp-edged fins. When an electric field is applied, these novel field emitters can produce an electron flow comparable to a thermionic source but without all the disadvantages—and with many advantages.
According to co-inventor Fred Sharifi, the new field emitters have inherently fast response times compared with thermionic sources, and the absence of heat makes it easier to create arrays of sources. Moreover, the porous nanostructure of the emitters makes them very reliable. Even if the emitter surface wears away during use—a common problem—the newly exposed material continues to work just as well.
Sharifi says that the NIST field emitters hold the potential to enhance the resolution and quality of X-ray images and allow for new modes of detection.
"X-ray images are based on the density of the material being examined, which limits their ability to see certain types of materials, including some types of explosives," says Sharifi. "Our field emitter will let us see not just that something is there, but, because we can build large arrays and place them at different angles, we can identify the material in question by looking at how the X-rays coming from different directions scatter from the object."
The technology is available for licensing through NIST's Technology Partnerships Office.
INFORMATION:
*M. Kang, H. Lezec and F. Sharifi. Stable field emission from nanoporous silicon carbide. Nanotechnology. 24 (2013) 065201.
New player in electron field emitter technology makes for better imaging and communications
2013-03-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NIST quantum refrigerator offers extreme cooling and convenience
2013-03-09
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have demonstrated a solid-state refrigerator that uses quantum physics in micro- and nanostructures to cool a much larger object to extremely low temperatures.
What's more, the prototype NIST refrigerator, which measures a few inches in outer dimensions, enables researchers to place any suitable object in the cooling zone and later remove and replace it, similar to an all-purpose kitchen refrigerator. The cooling power is the equivalent of a window-mounted air conditioner cooling a building the size ...
New NIST time code to boost reception for radio-controlled clocks
2013-03-09
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is changing the way it broadcasts time signals that synchronize radio-controlled "atomic" clocks and watches to official U.S. time in ways that will enable new radio-controlled timepieces to be significantly more robust and reliable.
This new time broadcast protocol will not only improve the performance of new radio-controlled clocks and watches, but will encourage the development of new timekeeping products that were not practical with the old broadcast system because of local interference or other limitations. ...
Study shows confidence builds better exercise habits for cancer survivors
2013-03-09
HOUSTON - Endometrial cancer survivors are more likely to complete physical activity, and for longer durations, when their daily self-efficacy is higher, according to a study published online in the journal Health Psychology – a publication of the American Psychology Association.
"Sedentary behavior is associated with increased cancer risk, including endometrial cancer," said Karen Basen-Engquist, Ph.D., professor in the Department of Behavioral Science at MD Anderson and lead investigator on the study. "When cancer survivors exercise, it not only improves their physical ...
NIST panel expands recommendations for use of electronic health records in pediatrics
2013-03-09
To speed development and adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) for pediatrics, a group of experts from industry, academia and government convened by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has focused its attention on three key audiences—records-system vendors and developers, small-group pediatric medical practices and children's hospitals.
In a paper* in The Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety, the panel of medical, human factors engineering and software-usability experts detail how specific recommendations from a recent guide ...
Why a hereditary anemia is caused by genetic mutation in mechanically sensitive ion channel
2013-03-09
BUFFALO, N.Y. – A genetic mutation that alters the kinetics of an ion channel in red blood cells has been identified as the cause behind a hereditary anemia, according to a paper (http://bit.ly/13LgCzc) published this month in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences by University at Buffalo scientists and colleagues.
The research team was led by Frederick Sachs, PhD, SUNY Distinguished Professor in the UB Department of Physiology and Biophysics, who discovered in the 1980s that some ion channels are mechanosensitive, that is, they convert mechanical stress ...
Temp-controlled 'nanopores' may allow detailed blood analysis
2013-03-09
Tiny biomolecular chambers called nanopores that can be selectively heated may help doctors diagnose disease more effectively if recent research by a team at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Wheaton College, and Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU) proves effective. Though the findings* may be years away from application in the clinic, they may one day improve doctors' ability to search the bloodstream quickly for indicators of disease—a longstanding goal of medical research.
The team has pioneered work on the use of nanopores—tiny chambers ...
Some biologists shun new media
2013-03-09
Although biologists think that "new media" such as blogs and online social networks have an important influence on public opinion and political decisions, they aren't much inclined to use them themselves to stay informed about developments in science. Rather, they prefer traditional outlets such as newspapers and television. That seems, at least, to be the implication of a study published in the April issue of BioScience.
The study, by Joachim Allgaier of the Jülich Research Center in Germany and four coauthors, examined the opinions of 257 neuroscientists working in ...
UTHealth researchers say more rapid test for Group B strep successful
2013-03-09
HOUSTON – (March 8, 2013) – A more rapid laboratory test for pregnant women to detect potentially deadly Group B strep (GBS) has been successful at identifying GBS colonization in six and a half hours, according to the results of a study from The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth).
The more rapid test could be helpful for the 13 percent of patients who experience pre-term labor before they are screened for GBS, which usually occurs between 35 and 37 weeks of gestation. The current standard test takes 48 hours. Antibiotics can be administered ...
NASA satellite sees Sandra strengthening at sea
2013-03-09
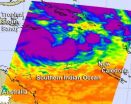
Cyclone 19P in the Southern Pacific Ocean was renamed Sandra today, March 8, as NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data on the storm that indicated it would continue to strengthen. Residents of New Caledonia should prepare for impacts from Sandra early next week.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of Cyclone Sandra's cloud top temperatures on March 8 at 1717 UTC (12:17 p.m. EST). Strong thunderstorms around Sandra's center and in a band east of the center appeared as cold as -63 Fahrenheit ...
University of Illinois researchers develop AFM-IR for nanometer scale chemical identification
2013-03-09
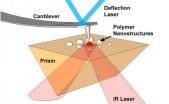
For more than 20 years, researchers have been using atomic force microscopy (AFM) to measure and characterize materials at the nanometer scale. However AFM-based measurements of chemistry and chemical properties of materials were generally not possible, until now.
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign report that they have measured the chemical properties of polymer nanostructures as small as 15 nm, using a novel technique called atomic force microscope infrared spectroscopy (AFM-IR). The article, "Atomic force microscope infrared spectroscopy ...