(Press-News.org) Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have demonstrated a solid-state refrigerator that uses quantum physics in micro- and nanostructures to cool a much larger object to extremely low temperatures.
What's more, the prototype NIST refrigerator, which measures a few inches in outer dimensions, enables researchers to place any suitable object in the cooling zone and later remove and replace it, similar to an all-purpose kitchen refrigerator. The cooling power is the equivalent of a window-mounted air conditioner cooling a building the size of the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C.
"It's one of the most flabbergasting results I've seen," project leader Joel Ullom says. "We used quantum mechanics in a nanostructure to cool a block of copper. The copper is about a million times heavier than the refrigerating elements. This is a rare example of a nano- or microelectromechanical machine that can manipulate the macroscopic world."
The technology may offer a compact, convenient means of chilling advanced sensors below standard cryogenic temperatures—300 milliKelvin (mK), typically achieved by use of liquid helium—to enhance their performance in quantum information systems, telescope cameras, and searches for mysterious dark matter and dark energy.
As described in Applied Physics Letters,* the NIST refrigerator's cooling elements, consisting of 48 tiny sandwiches of specific materials, chilled a plate of copper, 2.5 centimeters on a side and 3 millimeters thick, from 290 mK to 256 mK. The cooling process took about 18 hours. NIST researchers expect that minor improvements will enable faster and further cooling to about 100 mK.
The cooling elements are sandwiches of a normal metal, a 1-nanometer-thick insulating layer, and a superconducting metal. When a voltage is applied, the hottest electrons "tunnel" from the normal metal through the insulator to the superconductor. The temperature in the normal metal drops dramatically and drains electronic and vibrational energy from the object being cooled.
NIST researchers previously demonstrated this basic cooling method** but are now able to cool larger objects that can be easily attached and removed. Researchers developed a micromachining process to attach the cooling elements to the copper plate, which is designed to be a stage on which other objects can be attached and cooled. Additional advances include better thermal isolation of the stage, which is suspended by strong, cold-tolerant cords.
Cooling to temperatures below 300 mK currently requires complex, large and costly apparatus. NIST researchers want to build simple, compact alternatives to make it easier to cool NIST's advanced sensors. Researchers plan to boost the cooling power of the prototype refrigerator by adding more and higher-efficiency superconducting junctions and building a more rigid support structure.
INFORMATION:
This work is supported by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
* P.J. Lowell, G.C. O'Neil, J.M. Underwood and J.N. Ullom. Macroscale refrigeration by nanoscale electron transport. Applied Physics Letters. 102, 082601 (2013); Published online 26 Feb. 26, 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4793515.
** See 2005 NIST Tech Beat article, "Chip-scale Refrigerators Cool Bulk Objects," at http://www.nist.gov/pml/div686/chip_scale_042105.cfm.
NIST quantum refrigerator offers extreme cooling and convenience
2013-03-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New NIST time code to boost reception for radio-controlled clocks
2013-03-09
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is changing the way it broadcasts time signals that synchronize radio-controlled "atomic" clocks and watches to official U.S. time in ways that will enable new radio-controlled timepieces to be significantly more robust and reliable.
This new time broadcast protocol will not only improve the performance of new radio-controlled clocks and watches, but will encourage the development of new timekeeping products that were not practical with the old broadcast system because of local interference or other limitations. ...
Study shows confidence builds better exercise habits for cancer survivors
2013-03-09
HOUSTON - Endometrial cancer survivors are more likely to complete physical activity, and for longer durations, when their daily self-efficacy is higher, according to a study published online in the journal Health Psychology – a publication of the American Psychology Association.
"Sedentary behavior is associated with increased cancer risk, including endometrial cancer," said Karen Basen-Engquist, Ph.D., professor in the Department of Behavioral Science at MD Anderson and lead investigator on the study. "When cancer survivors exercise, it not only improves their physical ...
NIST panel expands recommendations for use of electronic health records in pediatrics
2013-03-09
To speed development and adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) for pediatrics, a group of experts from industry, academia and government convened by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has focused its attention on three key audiences—records-system vendors and developers, small-group pediatric medical practices and children's hospitals.
In a paper* in The Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety, the panel of medical, human factors engineering and software-usability experts detail how specific recommendations from a recent guide ...
Why a hereditary anemia is caused by genetic mutation in mechanically sensitive ion channel
2013-03-09
BUFFALO, N.Y. – A genetic mutation that alters the kinetics of an ion channel in red blood cells has been identified as the cause behind a hereditary anemia, according to a paper (http://bit.ly/13LgCzc) published this month in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences by University at Buffalo scientists and colleagues.
The research team was led by Frederick Sachs, PhD, SUNY Distinguished Professor in the UB Department of Physiology and Biophysics, who discovered in the 1980s that some ion channels are mechanosensitive, that is, they convert mechanical stress ...
Temp-controlled 'nanopores' may allow detailed blood analysis
2013-03-09
Tiny biomolecular chambers called nanopores that can be selectively heated may help doctors diagnose disease more effectively if recent research by a team at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Wheaton College, and Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU) proves effective. Though the findings* may be years away from application in the clinic, they may one day improve doctors' ability to search the bloodstream quickly for indicators of disease—a longstanding goal of medical research.
The team has pioneered work on the use of nanopores—tiny chambers ...
Some biologists shun new media
2013-03-09
Although biologists think that "new media" such as blogs and online social networks have an important influence on public opinion and political decisions, they aren't much inclined to use them themselves to stay informed about developments in science. Rather, they prefer traditional outlets such as newspapers and television. That seems, at least, to be the implication of a study published in the April issue of BioScience.
The study, by Joachim Allgaier of the Jülich Research Center in Germany and four coauthors, examined the opinions of 257 neuroscientists working in ...
UTHealth researchers say more rapid test for Group B strep successful
2013-03-09
HOUSTON – (March 8, 2013) – A more rapid laboratory test for pregnant women to detect potentially deadly Group B strep (GBS) has been successful at identifying GBS colonization in six and a half hours, according to the results of a study from The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth).
The more rapid test could be helpful for the 13 percent of patients who experience pre-term labor before they are screened for GBS, which usually occurs between 35 and 37 weeks of gestation. The current standard test takes 48 hours. Antibiotics can be administered ...
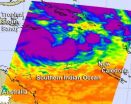
NASA satellite sees Sandra strengthening at sea
2013-03-09
Cyclone 19P in the Southern Pacific Ocean was renamed Sandra today, March 8, as NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data on the storm that indicated it would continue to strengthen. Residents of New Caledonia should prepare for impacts from Sandra early next week.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of Cyclone Sandra's cloud top temperatures on March 8 at 1717 UTC (12:17 p.m. EST). Strong thunderstorms around Sandra's center and in a band east of the center appeared as cold as -63 Fahrenheit ...
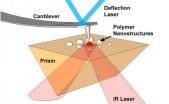
University of Illinois researchers develop AFM-IR for nanometer scale chemical identification
2013-03-09
For more than 20 years, researchers have been using atomic force microscopy (AFM) to measure and characterize materials at the nanometer scale. However AFM-based measurements of chemistry and chemical properties of materials were generally not possible, until now.
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign report that they have measured the chemical properties of polymer nanostructures as small as 15 nm, using a novel technique called atomic force microscope infrared spectroscopy (AFM-IR). The article, "Atomic force microscope infrared spectroscopy ...
Quantum computing moves forward
2013-03-09
New technologies that exploit quantum behavior for computing and other applications are closer than ever to being realized due to recent advances, according to a review article published this week in the journal Science.
A silicon chip levitates individual atoms used in quantum information processing. Photo: Curt Suplee and Emily Edwards, Joint Quantum Institute and University of Maryland. Credit: Science.
These advances could enable the creation of immensely powerful computers as well as other applications, such as highly sensitive ...