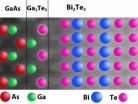
(Press-News.org) For years, researchers have developed thin films of bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) – which converts heat into electricity or electricity to cooling – on top of gallium arsenide (GaAs) to create cooling devices for electronics. But while they knew it could be done, it was not clear how – because the atomic structures of those unlikely pair of materials do not appear to be compatible. Now researchers from North Carolina State University and RTI International have solved the mystery, opening the door to new research in the field.
"We've used state-of-the-art technology to solve a mystery that has been around for years," says Dr. James LeBeau, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and co-author of a paper on the research. "And now that we know what is going on, we can pursue research to fine-tune the interface of these materials to develop more efficient mechanisms for converting electricity to cooling or heat into electricity. Ultimately, this could have applications in a wide range of electronic devices."
To study the phenomenon, the researchers had to create the nanometer-scale thin films on a GaAs substrate, or foundation. The GaAs is first placed in a vapor deposition chamber. Molecules containing bismuth and tellurium are then introduced into the chamber, where they react with each other and "grow" into a crystalline Bi2Te3 structure on the surface of the GaAs.
Using advanced "Super-X" X-ray spectroscopy technology in conjunction with an aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscope, the researchers were able to determine what was binding the Bi2Te3 to the GaAs – and it was not what they were expecting.
They found that when the tellurium molecules were introduced to the vapor deposition chamber, the tellurium reacted with the GaAs substrate to create a new surface layer of gallium telluride, which was only one molecule thick. The Bi2Te3 then formed a thin film on top of that new surface layer.
Because gallium telluride does not react with Bi2Te3, the research team knew chemical bonding could not be holding them together. Instead, the two layers are held together by the weaker force of van der Waals bonds – meaning the materials are held together by weak electrical forces.
"While these materials have been investigated previously by RTI and NC State, the state-of-the-art techniques applied by LeBeau and his team have revealed significant new insights into how the film grows," notes Dr. Rama Venkatasubramanian of RTI International, who is also a co-author of the paper.
INFORMATION:
The paper, "Atomic scale structure and chemistry of Bi2Te3/GaAs interfaces grown by metallorganic van der Waals epitaxy," is published online in Applied Physics Letters. Lead author of the paper is Houston Dycus, a Ph.D. student at NC State. Co-authors are Ryan White, a postdoctoral researcher at NC State; Drs. Jonathan Pierce and Rama Venkatasubramanian of RTI International; and LeBeau. The research was supported by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency.
Researchers solve riddle of what has been holding 2 unlikely materials together
2013-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Amplified greenhouse effect shifts north's growing seasons
2013-03-11
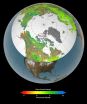
Vegetation growth at Earth's northern latitudes increasingly resembles lusher latitudes to the south, according to a NASA-funded study based on a 30-year record of land surface and newly improved satellite data sets.
An international team of university and NASA scientists examined the relationship between changes in surface temperature and vegetation growth from 45 degrees north latitude to the Arctic Ocean. Results show temperature and vegetation growth at northern latitudes now resemble those found 4 degrees to 6 degrees of latitude farther south as recently as 1982.
"Higher ...
Nerve damage may underlie widespread, unexplained chronic pain in children
2013-03-11
Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators have described what may be a newly identified disease that appears to explain some cases of widespread chronic pain and other symptoms in children and young adults. Their report that will appear in the April issue of the journal Pediatrics, and has received early online release, finds that most of a group of young patients seen at the MGH for chronic, unexplained pain had test results indicating small-fiber polyneuropathy, a condition not previously reported in children. The MGH investigators call this new syndrome juvenile-onset ...
Study: Antibiotics are unique assassins
2013-03-11
In recent years, a body of publications in the microbiology field has challenged all previous knowledge of how antibiotics kill bacteria. "A slew of papers came out studying this phenomenon, suggesting that there is a general mechanism of killing by antibiotics," said Kim Lewis, Northeastern University Distinguished Professor in the Department of Biology and director of Northeastern's Antimicrobial Discovery Center.
The standard thinking at the time was that the three main classes of bactericidal antibiotics each had a unique way of killing ...
The household carbon emission per capita in Northwestern China is only 2.05 tons CO2 per year
2013-03-11
The current international climate policy framework is mainly based on the national and regional level of macroscopic carbon emissions data, such as the regional per capita carbon emissions are often used as the indicator to measure the fairness of carbon emission rights. However, the per capita emissions based on regional macro data can not accurately reveal the low carbon emissions of the poor within the region, and cover up the emission differences among people intra-country and intra-region, the household carbon emission data based on field surveys could compensate for ...
Why people put themselves under the knife
2013-03-11
In a long-term study, Prof. Dr. Jürgen Margraf, Alexander von Humboldt Professor for Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy at the RUB, investigated the psychological effects of plastic surgery on approximately 550 patients in cooperation with colleagues from the University of Basel. Patients demonstrated more enjoyment of life, satisfaction and self-esteem after their physical appearance had been surgically altered. The results of the world's largest ever study on this issue are reported by the researchers in the journal "Clinical Psychological Science".
The aim of the ...
Environmental change impacts on migratory shorebirds differ for males and females
2013-03-11
Extensive shell fishing and sewerage discharge in river estuaries could have serious consequences for the rare Icelandic black-tailed godwits that feed there. But it is the males that are more likely to suffer, according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
Research published today in the journal Ecology and Evolution reveals very different winter feeding habits between the sexes.
Both males and females mainly consume bivalve molluscs, sea snails and marine worms, probing vigorously into soft estuary mud with their long beaks. But the study shows that ...
Coffee and tea during pregnancy affect fetal growth
2013-03-11
Drinking just two cups of coffee a day is associated with the risk of low birth weight. Researchers at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Sweden, have conducted a study on 59,000 women in collaboration with the Norwegian Institute of Public Health.
Expectant mothers who consume caffeine, usually by drinking coffee, are more likely to have babies with lower birth weight than anticipated, given their gestational age. Researchers at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, conducted a study on 59,000 pregnant Norwegian women in collaboration with the Norwegian ...
Evolution in the antibody factory
2013-03-11
This press release is available in German.
Immune system B cells play a crucial role in the defence of pathogens; when they detect such an intruder, they produce antibodies that help to combat the enemy. They concurrently and continuously improve these molecules to more precisely recognize the pathogens. A team of scientists with participation of the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research (HZI) has discovered that during this process the cells are able to advance their own evolution themselves by increasing the selection pressure through previously-produced antibodies. ...
Neck injuries linked to high costs for patients and spouses, reports study in Spine
2013-03-11
Philadelphia, Pa. (March 11, 2013) - Patients with neck injuries incur increased health and social costs—which also affect their spouses and may begin years before the initial injury, reports a study in the March 1 issue of Spine. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Some individuals and families seem more susceptible to experiencing socioeconomic consequences of neck injury, according to the new research by Dr Poul Jennum of University of Copenhagen and colleagues. Particularly for patients who develop chronic ...
NUS graphene researchers create 'superheated' water that can corrode diamonds
2013-03-11
A team of researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) led by Professor Loh Kian Ping, Head of the Department of Chemistry at the NUS Faculty of Science, has successfully altered the properties of water, making it corrosive enough to etch diamonds. This was achieved by attaching a layer of graphene on diamond and heated to high temperatures. Water molecules trapped between them become highly corrosive, as opposed to normal water.
This novel discovery, reported for the first time, has wide-ranging industrial applications, from environmentally-friendly degradation ...