(Press-News.org) Amsterdam, March 14, 2013 - Bumblebees are much more unstable when they hover than when they fly fast, according to new research published this month in the Journal of Theoretical Biology.
The authors of the paper, Na Xu and Mao Sun from Beijing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics in China, used a mathematical model to analyze the way bumblebees fly at different speeds, showing that the bumblebee is unstable when it hovers and flies slowly, and becomes neutral or weakly stable at medium and high flight speeds.
The instability at hovering and low speed is mainly caused by a sideways wind made by the movement of the wings – a 'positive roll moment'. As the bee flies faster, the wings bend towards the back of the body, reducing the effect of the sideways wind and increasing the stability of its flight.
According to the authors the results could be useful in the development of small flying machines like robotic insects.
"Dynamic flight stability is of great importance in the study of biomechanics of insect flight," said Mao Sun. "It is the basis for studying flight control, because the inherent stability of a flying system represents the dynamic properties of the basic system. It also plays a major role in the development of insect-like micro-air vehicles."
In recent years, with the understanding of the aerodynamic force mechanisms of insect flight, researchers have been devoting more effort to the area of flight dynamics.
The study further refutes the persistent misconception that, according to physics, bumblebees shouldn't be able to fly. The fallacy can be traced back to Le Vol Des Insects (Hermann and Cle, Paris, 1934) by French entomologist August Magnan – on page 8 he mentions bumblebees, stating, "First prompted by what is done in aviation, I applied the laws of air resistance to insects, and I arrived, with Mr. Sainte-Laguë, at this conclusion that their flight is impossible."
This new research looks at bumblebee flight using the same methods as used in quantum mechanics. By using average measurements – such as wing size and shape, body mass, and upwards and downwards forces – the researchers made the stability analysis of the flapping flight of an insect mathematically the same as that of a rigid airplane. By using the mathematical model rather than studying live bees, the researchers could be more accurate in their analysis of mechanical flight.
"The computational approach allows simulation of the inherent stability of a flapping motion in the absence of active control, which is very difficult, even impossible, to achieve in experiments using real insects," Sun further explained.
Xu and Sun used a model of a bumblebee with wings approximately the same size and shape as a real bee's – flat plates with rounded edges, and with a thickness of three percent of the length of one wing. The outline they used of the body was also approximately the same as that of a bumblebee.
Previous research has looked at the hovering flight dynamics of different insects, including the dronefly, fruit fly and bumblebee. However, in hovering flight, there is no consideration of forwards movement, and the forces created by the wings cancel each other out. This study details that both vertical and horizontal movement need to be taken into consideration to determine how stable the flight is overall.
The results show a significant difference in stability measurements between bumblebees and droneflies – something the researchers think is connected to the size and shape of the insects' wings. They plan to conduct further research in this area to compare the stability of flight at different speeds of bumblebees and droneflies.
###
This article is "Lateral dynamic flight stability of a model bumblebee in hovering and forward flight",
by Na Xu, Mao Sun – Beijing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, China (doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2012.11.033). The article appears in Journal of Theoretical Biology, 319 (2013) 102, 21 February 2013, published by Elsevier.
Notes for Editors
Full text of the article is available to credentialed journalists upon request, contact newsroom@elsevier.com. Journalists wishing to interview the authors may contact Lucy Goodchild +31 20 485 2467, l.goodchild@elsevier.com
About Journal of Theoretical Biology
The Journal of Theoretical Biology is the leading forum for theoretical papers that give insight into biological processes. It covers a very wide range of topics and is of interest to biologists in many areas of research. The Journal of Theoretical Biology is published by Elsevier. http://www.journals.elsevier.com/journal-of-theoretical-biology
About Elsevier
Elsevier is a world-leading publisher of scientific, technical and medical information products and services. The company works in partnership with the global science and health communities to publish more than 2,000 journals, including The Lancet and Cell, and close
to 20,000 book titles, including major reference works from Mosby and Saunders. Elsevier's online solutions include SciVerse ScienceDirect, SciVerse Scopus, Reaxys, MD Consult and Nursing Consult, which enhance the productivity of
science and health professionals, and the SciVal suite and MEDai's Pinpoint Review, which help research and health care institutions deliver better outcomes more cost-effectively.
A global business headquartered in Amsterdam, Elsevier employs 7,000 people worldwide. The company is part of Reed Elsevier Group PLC, a world-leading publisher and information provider, which is jointly owned by Reed Elsevier PLC and Reed Elsevier NV. The ticker symbols are REN (Euronext Amsterdam), REL (London Stock Exchange), RUK and ENL (New York Stock Exchange).
Smoking significantly increases individuals' risk of developing serious forms of urothelial carcinoma and a higher likelihood of dying from the disease, particularly for women. That is the conclusion of a recent study published in BJU International. While the biological mechanisms underlying this gender difference are unknown, the findings indicate that clinicians and society in general should focus on smoking prevention and cessation to safeguard against deadly cancers of the bladder, ureters, and renal pelvis, especially in females.
To evaluate the gender-specific effects ...
This press release is available in Spanish.
A U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientist is giving guidance to growers in Montana and the Dakotas on how grazing sheep when fields are left fallow will affect soil quality.
Grazing sheep and other livestock was once common in the region before fertilizers were introduced in the 1950s. While fertilizers increased yields, they also have increased nitrogen runoff and leaching, made soils more acidic, and contributed to greenhouse gas emissions, according to Upendra Sainju, a soil scientist with the Agricultural Research ...
Researchers from the University of Granada and the Carlos III University of Madrid have patented a new method to measure the flow of motorized traffic that a specific street carries each day, by measuring solely the levels of atmospheric noise. This pioneer system, unique in the world, is an alternative, or a complement, to other methods currently used to measure traffic flow, such as image counting or magnetic discharge levels.
This method, designed by the University of Granada, allows a differentiation between the flow of cars, LGVs, HGVs and motorbikes/scooters along ...
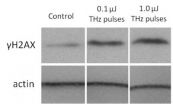
Terahertz (THz) radiation, a slice of the electromagnetic spectrum that occupies the middle ground between microwaves and infrared light, is rapidly finding important uses in medical diagnostics, security, and scientific research. As scientists and engineers find evermore practical uses for this form of radiation, questions persist about its potential human health risks.
New research performed on lab-grown human skin suggests that short but powerful bursts of THz radiation may both cause DNA damage and increase the production of proteins that help the body fight cancer. ...
The beetle family Cerambycidae, also known as long-horned beetles or longicorns, is characterized by emblematic extremely long antennae, which are usually longer than the total body length of the animal. The family is rather rich in diversity with more than 20 000 species known, distributed worldwide. Some representatives of these bizarre-shaped beetles, are also known as serious pests with their wood-feeding larvae causing extensive damage to living trees or untreated lumber. The beetles from this family are mainly associated with leaf litter habitats, where the specimens ...
New Rochelle, NY, March 14, 2013—A woman's health status before pregnancy is critical for the health and wellbeing of the fetus and mother-to-be. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has set Healthy People 2020 national objectives for women of reproductive age, and young women are making important gains toward achieving some of those health goals, while some trends are less encouraging, as reported in a study published in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on ...
(WASHINGTON)-Transplants of blood-forming stem cells from umbilical cord blood may be an effective alternative to transplants of matched donor bone marrow stem cells to treat children with a rare, debilitating disease known as Hurler's syndrome (HS), according to results of a study published online today in Blood, the Journal of the American Society of Hematology (ASH).
HS is an inherited metabolic disease characterized by the lack of a critical metabolic enzyme (lysosomal α-L-iduronidase) that breaks down long chains of sugar molecules in the body. In the absence ...
TORONTO, ON – Both daughters and sons from divorced families are significantly more likely to initiate smoking in comparison to their peers from intact families, shows a new analysis of 19,000 Americans.
This University of Toronto study, published online this month in the journal Public Health, shows that men who experienced parental divorce before they turned 18 had 48-per-cent higher odds of ever smoking 100 or more cigarettes than men whose parents did not divorce. Women from divorced families were also at risk, with 39-per-cent higher odds of smoking in comparison ...
TORONTO, ON — Researchers from the University of Toronto and SickKids Research Institute announced today that they have successfully mapped the genes in the fungus that causes Dutch Elm Disease.
The researchers believe this is the first time the 30 million DNA letters for the fungus Ophiostoma ulmi have been mapped. The findings, published in this week's online journal BMC Genomics, could help scientists figure out how to prevent the fungus from destroying elm trees in the future.
"Essentially, Dutch Elm Disease is caused by a fungus that prevents the normal distribution ...
A virus that most people have probably never heard of, yet most of us carry, is the number 1 infectious cause of congenital birth defects. One in 750 children are born with, or develop, permanent disabilities such as hearing loss or brain damage as a result of CMV (cytomegalovirus) infection in the womb. Major research efforts are underway to combat this invidious disease.
Researchers from Cardiff University and the La Jolla Institute, California, have discovered a previously unknown cellular mechanism that could prove critical in creating a CMV vaccine.
"CMV is ...