(Press-News.org) PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Large chunks of an ancient tectonic plate that slid under North America millions of years ago are still present under parts of central California and Mexico, according to new research led by Brown University geophysicists.
Around 100 million years ago, the Farallon oceanic plate lay between the converging Pacific and North American plates, which eventually came together to form the San Andreas fault. As those plates converged, much of the Farallon was subducted underneath North America and eventually sank deep into the mantle. Off the west coast of North America, the Farallon plate fragmented, leaving a few small remnants at the surface that stopped subducting and became part of the Pacific plate.
But this new research suggests that large slabs from Farallon remain attached to these unsubducted fragments. The researchers used seismic tomography and other data to show that part of the Baja region and part of central California near the Sierra Nevada mountains sit atop "fossil" slabs of the Farallon plate.
"Many had assumed that these pieces would have broken off quite close to the surface," said Brown geophysicist Donald Forsyth, who led the research with Yun Wang, a former Brown graduate student now at the University of Alaska. "We're suggesting that they actually broke off fairly deep, leaving these large slabs behind."
The findings are published today (March 18, 2013) in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Geologists had known for years about a "high velocity anomaly" in seismic tomography data near the Sierra Nevada mountains in California. Seismic tomography measures the velocity of seismic waves deep underground. The speed of the waves provides information about the composition and temperature of the subsurface. Generally, slower waves mean softer and hotter material; faster waves mean stiffer and cooler material.
The anomaly in California, known as the Isabella anomaly, indicated that a large mass of relatively cool and dehydrated material is present at a depth of 100 to 200 kilometers below the surface. Just what that mass was wasn't known, but there were a few theories. It was often explained by a process called delamination. The crust beneath the eastern part of the mountains is thin and the mantle hot, indicating that part of the lithospheric plate under the mountains had delaminated—broken off. The anomaly, scientists thought, might be the signature of that sunken hunk of lithosphere, which would be cooler and dryer than the surrounding mantle.
But a few years ago, scientists detected a new anomaly under the Mexico's Baja Peninsula, due east of one of the known coastal remains of the Farallon plate. Because of its proximity to the Farallon fragment, Forsyth and Wang thought it was very likely that the anomaly represented an underground extension of the fragment.
A closer look at the region showed that there are high-magnesium andesite deposits on the surface near the eastern edge of the anomaly. These kinds of deposits are volcanic rocks usually associated with the melting of oceanic crust material. Their presence suggests that the eastern edge of the anomaly represents the spots where Farallon finally gave way and broke off, sending andesites to the surface as the crust at the end of the subducted plate melted.
That led Forsyth and his colleagues to suspect that perhaps the Isabella anomaly in California might also represent a slab still connected to an unsubducted fragment of the Farallon plate. So they re-examined the tomography data along the entire West Coast. They compared the Baja and Isabella anomalies to anomalies associated with known Farallon slabs underneath Washington and Oregon.
The study found that all of the anomalies are strongest at the same depth — right around 100 kilometers. And all of them line up nearly due east of known fragments from Farallon.
"The geometry was the kicker," Forsyth said. "The way they line up just makes sense."
The findings could force scientists to re-examine the tectonic history of western North America, Forsyth said. In particular, it forces a rethinking of the delamination of the Sierra Nevada, which had been used to explain the Isabella anomaly.
"However the Sierra Nevada was delaminated," Forsyth said, "it's probably not in the way that many people had been thinking."
His research colleague asnd co-author Brian Savage of the University of Rhode Island agrees. "This work has radically changed our understanding of the makeup of the west coast of North America," Savage said. "It will cause a thorough rethinking of the geological history of North America and undoubtedly many other continental margins."
INFORMATION:
The work was supported by the National Science Foundation. Other authors on the paper were Brown graduate student Christina Rau, Brown undergraduate Nina Carriero, Brandon Schmandt from the University of Oregon, and James Gaherty from Columbia University.
Slabs of ancient tectonic plate still lodged under California, researchers find
2013-03-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
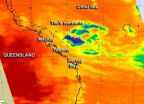
NASA sees remnants of Cyclone Tim fading near southeastern Queensland
2013-03-19
Infrared satellite imagery tells the temperature of the cloud tops within a tropical cyclone as well as the sea surface temperatures around the storms. A recent infrared image from NASA's Aqua satellite showed very little strength in the remnants of ex-cyclone Tim offshore from southeastern Queensland.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of Cyclone Tim on March 18 at 0355 UTC (March 17 at 11:55 p.m. EDT). The AIRS image showed that cloud top temperatures had warmed significantly since the previous ...
Uncontrolled hypertension could bring increased risk for Alzheimer's disease
2013-03-19
A study in the JAMA Neurology (formerly the Archives of Neurology) suggests that controlling or preventing risk factors such as hypertension earlier in life may limit or delay the brain changes associated with Alzheimer's disease and other age-related neurological deterioration.
Dr. Karen Rodrigue, assistant professor in the UT Dallas Center for Vital Longevity (CVL), was lead author on a study that looked at whether people with both hypertension and a common gene associated with risk of Alzheimer's disease (the APOE-4 gene carried by about 20 percent of the population) ...
Tourist-fed stingrays change their ways
2013-03-19
Stingrays living in one of the world's most famous and heavily visited ecotourism sites — Stingray City/Sandbar in the Cayman Islands — have profoundly changed their ways, raising questions about the impact of so-called "interactive ecotourism" on marine wildlife, reports a new study published March 18 in the journal PLOS ONE.
Researchers from Nova Southeastern University's Guy Harvey Research Institute in Hollywood, Fla., and the University of Rhode Island studied the southern stingray population of Stingray City — a sandbar in the Cayman Islands that draws nearly a ...
Discounts on purchases of healthy foods can improve diets, study finds
2013-03-19
Lowering the costs of healthy foods in supermarkets increases the amount of fruits, vegetables and whole grain foods that people eat, while also appearing to reduce consumption of nutritionally less-desirable foods, according to research from the RAND Corporation.
Researchers examined a program available to members of South Africa's largest private health insurance company that provides a rebate of 10 percent or 25 percent on purchases of healthy foods. The program, started in 2009, now has about 800 participating supermarkets and enrolls more than 260,000 households. ...
Cushioned heel running shoes may alter adolescent biomechanics, performance
2013-03-19
CHICAGO — Many of today's running shoes feature a heavy cushioned heel. New research presented today at the 2013 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) found that these shoes may alter an adolescent runner's biomechanics (the forces exerted by muscles and gravity on the skeletal structure) and diminish performance.
Researchers recruited 12 adolescent competitive athletes from local track teams, and asked them to run on a treadmill in large heel trainers, track flats and without any shoes (barefoot) at four different speeds. Biomechanics ...
Sexual function improves significantly after hip or knee replacement surgery
2013-03-19
CHICAGO — Osteoarthritis of the hip or knee, affecting millions of Americans each year, is known to limit sexual activity. New research presented today at the 2013 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) found that total hip (THR) or total knee replacement (TKR) surgery improves sexual function in 90 percent of patients.
In the study, 147 patients under age 70, scheduled for primary THR or TKR, agreed to participate in a study requiring the completion of questionnaires prior to surgery, at six months post surgery, and at one year post surgery. ...
Sports and recreation injuries drop 12 percent for children ages 5-14 during past decade
2013-03-19
CHICAGO — New research presented today at the at the 2013 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) found that overall, sports and recreation musculoskeletal injuries have declined 12.4 percent in the U.S. over the past 10 years for children ages 5 to 14 years. However, injuries sustained during football and soccer continues to rise.
In 2000, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) reported the top eight sports and recreational activities responsible for injuries in children ages 5 to 14, and estimated their annual cost at more than $33 ...
MRI may predict adverse tissue reaction in metal-on-metal hip replacement patients
2013-03-19
CHICAGO – Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can detect a failing, or potentially failing, metal-on-metal hip implant (MoM) early on, according to a new study presented today at the 2013 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS). Early detection can result in timely revision surgery, decreasing the risk for further tissue damage and pain.
Researchers reviewed the MRI images of 70 patients who ultimately underwent revision surgery for a failed MoM implant. The images were assessed for the presence of tissue damage, swelling and other characteristics. ...
Returning military personnel to duty following severe injury to the lower extremity
2013-03-19
CHICAGO – High-energy lower-extremity trauma (HELET) is common in modern warfare, often resulting in severe tissue damage, chronic pain, neurovascular injury and significant muscle loss, according to the new research presented today at the 2013 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS).
The Return to Run (RTR) program is an integrated orthotic and rehabilitation initiative designed to return high-level function to wounded warriors. It includes use of the new Intrepid Dynamic Exoskeletal Orthosis (IDEO), a custom-fit device made from carbon ...
Spine patients who quit smoking report diminished pain
2013-03-19
CHICAGO – Smoking is a known risk factor for back pain and disc disease. In a new study presented today at the 2013 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS), researchers reviewed smoking cessation rates and related pain in 6,779 patients undergoing treatment for spinal disorders with severe axial (spine) or radicular (leg) pain. Information on each patient's age, gender, weight, smoking history, assessment of pain, treatment type and co-morbid depression also were assessed.
Overall, 8.9 percent of patients over the age of 55 smoked compared ...