(Press-News.org) After the molybdenite chip, we now have molybdenite flash memory, a significant step forward in the use of this new material in electronics applications. The news is even more impressive because scientists from EPFL's Laboratory of Nanometer Electronics and Structures (LANES) came up with a truly original idea: they combined the advantages of this semiconducting material with those of another amazing material – graphene. The results of their research have recently been published in the journal ACS Nano.
Two years ago, the LANES team revealed the promising electronic properties of molybdenite (MoS2), a mineral that is very abundant in nature. Several months later, they demonstrated the possibility of building an efficient molybdenite chip. Today, they've gone further still by using it to develop a flash memory prototype – that is, a cell that can not only store data but also maintain it in the absence of electricity. This is the kind of memory used in digital devices such as cameras, phones, laptop computers, printers, and USB keys.
An ideal "energy band"
"For our memory model, we combined the unique electronic properties of MoS2 with graphene's amazing conductivity," explains Andras Kis, author of the study and director of LANES.
Molybdenite and graphene have many things in common. Both are expected to surpass the physical limitations of our current silicon chips and electronic transistors. Their two-dimensional chemical structure – the fact that they're made up of a layer only a single atom thick – gives them huge potential for miniaturization and mechanical flexibility.
Although graphene is a better conductor, molybdenite has advantageous semi-conducting properties. MoS2 has an ideal "energy band" in its electronic structure that graphene does not. This allows it to switch very easily from an "on" to an "off" state, and thus to use less electricity. Used together, the two materials can thus combine their unique advantages.
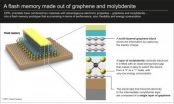
Like a sandwich
The transistor prototype developed by LANES was designed using "field effect" geometry, a bit like a sandwich. In the middle, instead of silicon, a thin layer of MoS2 channels electrons. Underneath, the electrodes transmitting electricity to the MoS2 layer are made out of graphene. And on top, the scientists also included an element made up of several layers of graphene; this captures electric charge and thus stores memory.
"Combining these two materials enabled us to make great progress in miniaturization, and also using these transistors we can make flexible nanoelectronic devices," explains Kis. The prototype stores a bit of memory, just a like a traditional cell. But according to the scientist, because molybdenite is thinner than silicon and thus more sensitive to charge, it offers great potential for more efficient data storage.
INFORMATION:
Fantastic flash memory combines graphene and molybdenite
2013-03-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Are survivors of childhood leukemia and lymphoma at greater risk of chronic fatigue as adults?
2013-03-20
New Rochelle, NY, Mar 19, 2013—Chronic fatigue, a persistent lack of energy that does not improve with rest, is at least three times more prevalent among adult survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphoma experienced during childhood or adolescence than in the general adult population, according to an article in Journal of Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology (JAYAO), (http://www.liebertpub.com/JAYAO) a multidisciplinary peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. (http://www.liebertpub.com) JAYAO is the Official Journal of the Society for ...
Biennial mammograms best after 50, even for women with dense breasts
2013-03-20
Screening for breast cancer every two years appears just as beneficial as yearly mammograms for women ages 50 to 74, with significantly fewer "false positives" – even for women whose breasts are dense or who use hormone therapy for menopause.
That is the finding of a new national study involving more than 900,000 women.
The study was published on March 18 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The same team of researchers from UC San Francisco and Seattle-based Group Health Research Institute recently reported similar results for older women ages 66 to 89 years old.
By contrast, ...
Record simulations conducted on Lawrence Livermore supercomputer
2013-03-20
LIVERMORE, Calif. -- Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory have performed record simulations using all 1,572,864 cores of Sequoia, the largest supercomputer in the world. Sequoia, based on IBM BlueGene/Q architecture, is the first machine to exceed one million computational cores. It also is No. 2 on the list of the world's fastest supercomputers, operating at 16.3 petaflops (16.3 quadrillion floating point operations per second).
The simulations are the largest particle-in-cell (PIC) code simulations by number of cores ever performed. PIC simulations ...
To make health systems more effective, physicians say time is now for clinician-led innovation
2013-03-20
(Boston) –Physician experts in health system issues propose a timely alternative process for harnessing and supporting physician-led innovations to rapidly address front-line health care delivery problems and improve health. Published as a Viewpoint article in the March 20th issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), the authors propose health systems adopt a strategy widely accepted in U.S. industries of "user-led" innovation.
User-led innovation is predicated on the idea that important enhancements to products and services are often made by users ...
University of Maryland researchers identify fish protein that may inhibit cancer metastasis
2013-03-20
BALTIMORE – March 19, 2013. Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine have identified a peptide, or protein, derived from Pacific cod that may inhibit prostate cancer and possibly other cancers from spreading, according to preclinical research published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
"The use of natural dietary products with anti-tumor activity is an important and emerging field of research," says senior author Hafiz Ahmed, Ph.D., assistant professor of biochemistry and molecular biology at the University of Maryland ...
Transportation study reveals potential for deep cuts to petroleum use and carbon emissions
2013-03-20
The U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and Argonne National Laboratory (ANL) today announced the release of the Transportation Energy Futures (TEF) study, an assessment of avenues to reach deep cuts in petroleum use and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the transportation sector.
"Transportation is an engine of our economic strength, but it also represents a key challenge for the future of U.S. energy use," NREL Senior Analyst Austin Brown said. "Transportation accounts for 71 percent of total U.S. petroleum consumption and 33 ...
Highlights from the March GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy special issue on colorectal cancer
2013-03-20
OAK BROOK, Ill. – March 19, 2013 – In recognition of National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month, GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy has published a special issue for March on colorectal cancer. The issue includes a practical guide for approaching and managing serrated colon polyps, one of the most common types of polyps, and a study on reducing postpolypectomy bleeding with prophylactic clip closure. GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy is the monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE).
"The cutting edge of serrated ...
Nurses can play key role in reducing deaths from world's most common diseases
2013-03-20
Nurses and midwives can play a critical role in lessening people's risk of cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory disease and diabetes, according to a groundbreaking new report issued by the World Health Organization and co-authored by a UCLA nursing professor.
These four non-communicable disease types account for a combined 60 percent of all deaths worldwide.
"The global burden of non-communicable diseases is already high and continues to grow in all regions of the world," said Linda Sarna, a professor at the UCLA School of Nursing and co-author ...
US company identified as manufacture of lead paint in Africa
2013-03-20
SAN FRANCISCO, CA (March 19, 2013) - House paint containing dangerous
concentrations of lead is being sold in Cameroon by an American company – and the
company is refusing to remove the paint from store shelves.
"There is an immediate need for regulations to restrict the lead content of paint in
Cameroon to protect public health," said Perry Gottesfeld, Executive Director of
Occupational Knowledge International (OK International) and co-author of a new
research study about this lead hazard.
"The levels of lead are extraordinarily high, and these products have been ...
Study could aid development of new drugs to treat gout
2013-03-20
MAYWOOD, Ill. – Findings from a Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine study could lead to the development of new drugs to treat gout.
The study, led by Liang Qiao, MD, and his colleagues and collaborators, was published March 19 in the journal Nature Communications.
Gout is caused by a buildup of uric acid around joints, typically the big toe, knee or ankles. The immune system revs up to attack uric acid salt crystals, and this immune response causes painful inflammation.
The innate immune response is mainly activated by calcium that enters a macrophage ...