Computers that mimic the function of the brain
2015-04-06
Researchers are always searching for improved technologies, but the most efficient computer possible already exists. It can learn and adapt without needing to be programmed or updated. It has nearly limitless memory, is difficult to crash, and works at extremely fast speeds. It's not a Mac or a PC; it's the human brain. And scientists around the world want to mimic its abilities.
Both academic and industrial laboratories are working to develop computers that operate more like the human brain. Instead of operating like a conventional, digital system, these new devices ...
Breastfeeding women and sex: Higher sex drive or relationship management?
2015-04-06
New mothers in the Philippines spend more time in the bedroom with their partner in the first few weeks after giving birth than they did before they became pregnant. This might be a type of survival strategy to keep the relationships with the fathers of their new babies alive and well, to ensure continued support for their offspring. So says Michelle Escasa-Dorne of the University of Colorado in the US, after studying how women from a society with a low divorce rate such as the Philippines adapt to being both mothers and lovers. The study appears in Springer's journal Human ...
Common antidepressant increased coronary atherosclerosis in animal model
2015-04-06
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - April 6, 2015 - A commonly prescribed antidepressant caused up to a six-fold increase in atherosclerosis plaque in the coronary arteries of non-human primates, according to a study by researchers at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center. Coronary artery atherosclerosis is the primary cause of heart attacks.
The study is published in the current online issue of the journal Psychosomatic Medicine.
"The medical community has known for years that depression is closely associated with heart disease, but we didn't know if treating it would reduce the heart ...
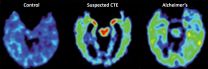
Characteristic pattern of protein deposits in brains of retired NFL players who suffered concussions
2015-04-06
A new UCLA study takes another step toward the early understanding of a degenerative brain condition called chronic traumatic encephalopathy, or CTE, which affects athletes in contact sports who are exposed to repetitive brain injuries. Using a new imaging tool, researchers found a strikingly similar pattern of abnormal protein deposits in the brains of retired NFL players who suffered from concussions.
The innovative imaging technique uses a chemical marker combined with positron emission tomography, or PET scan, and was initially tested in five retired NFL players ...
New research complicates seismic hazard for British Columbia, Alaska region
2015-04-06
SAN FRANCISCO--The Pacific and North America plate boundary off the coast of British Columbia and southeastern Alaska is a complex system of faults capable of producing very large earthquakes. The recent 2012 Mw 7.8 Haida Gwaii and 2013 Mw 7.5 Craig earthquakes released strain built up over years, but did not release strain along the Queen Charlotte Fault, which remains the likely source of a future large earthquake, according to reports published in a special issue of the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America (BSSA).
"The study of these two quakes revealed ...
Study identifies protein that triggers lupus-associated immune system activation
2015-04-06
Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators have identified an inflammatory molecule that appears to play an essential role in the autoimmune disorder systemic lupus erythematosus, commonly known as lupus. In their report being published online in Nature Immunology, the researchers describe finding that a protein that regulates certain cells in the innate immune system - the body's first line of defense against infection - activates a molecular pathway known to be associated with lupus and that the protein's activity is required for the development of lupus symptoms ...
Better sensors for medical imaging, contraband detection
2015-04-06
MIT researchers have developed a new, ultrasensitive magnetic-field detector that is 1,000 times more energy-efficient than its predecessors. It could lead to miniaturized, battery-powered devices for medical and materials imaging, contraband detection, and even geological exploration.
Magnetic-field detectors, or magnetometers, are already used for all those applications. But existing technologies have drawbacks: Some rely on gas-filled chambers; others work only in narrow frequency bands, limiting their utility.
Synthetic diamonds with nitrogen vacancies (NVs) -- ...
Researchers track protein 'hitchhiker' in fluorescent worms
2015-04-06
Dividing cells--whether they're in an embryo or an adult--rely on the right processes happening at the right time to turn out healthy.
Now, researchers at the University of Iowa have identified a mechanism that dividing cells in worms use to ensure their proper development, and they believe the same process could be going on in humans. The mechanism, unknown until now, describes one part of the cell, called the centrosome, as an "internal timekeeper"--like a train conductor. A crucial protein in charge of gene expression, beta-catenin, is described as a "hitchhiker"--it ...
Working up a sweat -- it could save your life
2015-04-06
Physical activity that makes you puff and sweat is key to avoiding an early death, a large Australian study of middle-aged and older adults has found.
The researchers followed 204,542 people for more than six years, and compared those who engaged in only moderate activity (such as gentle swimming, social tennis, or household chores) with those who included at least some vigorous activity (such as jogging, aerobics or competitive tennis).
They found that the risk of mortality for those who included some vigorous activity was 9 to 13 per cent lower, compared with those ...
We can fix the Great Barrier Reef
2015-04-06
Leading coral reef scientists say Australia could restore the Great Barrier Reef to its former glory through better policies that focus on science, protection and conservation.
In a paper published in the journal Nature Climate Change, the authors argue that all the stressors on the Reef need to be reduced for it to recover.
An Australian Government report into the state of the Great Barrier Reef found that its condition in 2014 was "poor and expected to further deteriorate in the future". In the past 40 years, the Reef has lost more than half of its coral cover and ...
Many nursing home residents die, don't walk after lower extremity revascularization
2015-04-06
Many nursing home residents who underwent lower extremity revascularization died, did not walk or had functional decline following the procedure, which is commonly used to treat leg pain caused by peripheral arterial disease, wounds that will not heal or worsening gangrene, according to an article published online by JAMA Internal Medicine.
Lower extremity revascularization is often performed so patients with peripheral arterial disease can maintain the ability to walk, which is a key component of functional independence. But outcomes among patients with high levels of ...
Neurologic function, temperature management in patients after cardiac arrest
2015-04-06
Quality of life was good and cognitive function was similar in patients with cardiac arrest who received targeted body-temperature management as a neuroprotective measure in intensive care units in Europe and Australia, according to an article published online by JAMA Neurology.
Brain injury is the primary cause of death for patients treated in intensive care units after suffering cardiac arrest (CA) outside of a hospital. Targeted temperature management (TTM) has been implemented as a neuroprotective treatment for comatose CA survivors because of reports of improved ...
Using pediatric cholesterol guidelines for teens, young adults would increase statin use
2015-04-06
Application of pediatric guidelines for lipid levels for persons 17 to 21 years of age who have elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels would result in statin treatment for more than 400,000 additional young people than the adult guidelines, according to an article published online by JAMA Pediatrics.
Adolescence is a common time for the emergence of risk factors for cardiovascular disease, including abnormal cholesterol levels. The 2011 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction in ...
Lower extremity revascularization not effective in majority of nursing home residents
2015-04-06
Only a few U.S. nursing home residents who undergo lower extremity revascularization procedures are alive and ambulatory a year after surgery, according to UCSF researchers, and most patients still alive gained little, if any, function.
The study appears in the April 6 issue of JAMA Internal Medicine.
"Our findings can inform conversations among physicians, patients and families about the risks and expected outcomes of surgery and whether the surgery is likely to allow patients to achieve their treatment goals," said senior author Emily Finlayson, MD, MS, associate ...
Western Canada to lose 70 percent of glaciers by 2100
2015-04-06
Seventy per cent of glacier ice in British Columbia and Alberta could disappear by the end of the 21st century, creating major problems for local ecosystems, power supplies, and water quality, according to a new study by University of British Columbia researchers.
The study found that while warming temperatures are threatening glaciers in Western Canada, not all glaciers are retreating at the same rate. The Rocky Mountains, in the drier interior, could lose up to 90 per cent of its glaciers. The wetter coastal mountains in northwestern B.C. are only expected to lose about ...
Pulling the strings of our genetic puppetmasters
2015-04-06
DURHAM, N.C. -- Duke researchers have developed a new method to precisely control when genes are turned on and active.
The new technology allows researchers to turn on specific gene promoters and enhancers -- pieces of the genome that control gene activity -- by chemically manipulating proteins that package DNA. This web of biomolecules that supports and controls gene activity is known as the epigenome.
The researchers say having the ability to steer the epigenome will help them explore the roles that particular promoters and enhancers play in cell fate or the risk ...
Aluminum battery from Stanford offers safe alternative to conventional batteries
2015-04-06
Stanford University scientists have invented the first high-performance aluminum battery that's fast-charging, long-lasting and inexpensive. Researchers say the new technology offers a safe alternative to many commercial batteries in wide use today.
"We have developed a rechargeable aluminum battery that may replace existing storage devices, such as alkaline batteries, which are bad for the environment, and lithium-ion batteries, which occasionally burst into flames," said Hongjie Dai, a professor of chemistry at Stanford. "Our new battery won't catch fire, even if you ...
New target for anticancer drugs: RNA
2015-04-06
Most of today's anticancer drugs target the DNA or proteins in tumor cells, but a new discovery by University of California, Berkeley, scientists unveils a whole new set of potential targets: the RNA intermediaries between DNA and proteins.
This RNA, called messenger RNA, is a blueprint for making proteins. Messenger RNA is created in the nucleus and shuttled out into the cell cytoplasm to hook up with protein-making machinery, the ribosome. Most scientists have assumed that these mRNA molecules are, aside from their unique sequences, generic, with few distinguishing ...
Women and men have different exclusion criteria for rtPA
2015-04-06
PROVIDENCE, R.I. - After analyzing stroke treatment records, researchers at Rhode Island Hospital in collaboration with researchers from the University of Cincinnati learned that women and men have different reasons for being excluded from receiving the common clot-dissolving drug, recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rtPA). Importantly, more women had very high blood pressures, which reduced their eligibility to be treated with the highly effective drug. The study was recently published in the American Heart Association's (AHA) journal, Stroke.
"Although men and ...
Women smokers concerned about weight are less likely to try to quit
2015-04-06
Women who believe smoking helps them manage their weight are less likely to try quitting in response to anti-smoking policies than other female smokers in the U.S.
The study, published online in the journal Tobacco Control, is the first to find that smokers who are concerned about their weight are less swayed by anti-smoking policies - such as bumps in cigarette prices, smoke-free laws or anti-tobacco messaging -- than other smokers are.
"We found that concerns about weight are a significant barrier to quitting," says lead author Ce Shang of the University of Illinois ...
For marketers, failing to align the emotions of your ads with TV programs may turn off consumers
2015-04-06
NEW YORK--A sad TV drama comes to conclusion, fading to black as music swells, and leaving the audience emotionally torn about the future of the main characters. Suddenly, the TV cuts to a peppy commercial and viewers are faced with the relentless cheer of an insurance spokesperson pitching their latest money saving product. This is a common occurrence in today's prime time-driven entertainment culture, but new research from Columbia Business School shows that this juxtaposition of emotions can leave TV viewers puzzled at the swing in content and emotion, so much so that ...
CU researchers: Brain activity boosts processes that promote neural connections
2015-04-06
AURORA, Colo. (April 6, 2015) - Brain activity affects the way the developing brain connects neurons and a study by researchers at the School of Medicine on the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and Children's Hospital Colorado suggests a new model for understanding that process.
In a study of zebrafish, scientists tested how brain activity affected the development of insulating sheaths on selected axons, which are slender nerve fibers that conduct electrical impulses between neurons. They found that, while the wrapping of axons was indiscriminate, the molecular ...
Winning women
2015-04-06
Political parties find that their fortunes improve when they put more women on the ballot, according to a study co-authored by an MIT economist.
The study analyzes changes to municipal election laws in Spain, which a decade ago began requiring political parties to have women fill at least 40 percent of the slots on their electoral lists. With other factors being equal, the research found, parties that increased their share of female candidates by 10 percentage points more than their opponents enjoyed a 4.2 percentage-point gain at the ballot box, or an outright switch ...
Antipsychotic use may increase the risk for diabetes in some children
2015-04-06
Philadelphia ? Today in JAMA Pediatrics, researchers from The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia's (CHOP) PolicyLab published the largest study to date documenting the significant risks to children's health associated with prescription antipsychotics, a powerful a class of medications used to treat mental and behavioral health disorders. The results suggest that initiating antipsychotics may elevate a child's risk not only for significant weight gain, but also for Type II diabetes by nearly 50 percent; moreover, among children who are also receiving antidepressants, the ...
Researchers create first metal-free catalyst for rechargeable zinc-air batteries
2015-04-06
Researchers from Case Western Reserve University and the University of North Texas have made what they believe is the first metal-free bifunctional electrocatalyst that performs as well or better than most metal and metal oxide electrodes in zinc-air batteries.
Zinc-air batteries are expected to be safer, lighter, cheaper and more powerful and durable than lithium-ion batteries common in mobile phones and laptops and increasingly used in hybrid and electric cars.
This carbon-based catalyst works efficiently in both the oxygen reduction reaction and oxygen evolution ...
[1] ... [3047]
[3048]
[3049]
[3050]
[3051]
[3052]
[3053]
[3054]
3055
[3056]
[3057]
[3058]
[3059]
[3060]
[3061]
[3062]
[3063]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.