With breast cancer treatment, you do get what you pay for
2015-04-06
Despite concerns about the increasing costs of treating illnesses like breast cancer, higher treatment costs are linked to better survival rates, according to a study by Yale School of Medicine researchers in the Cancer Outcomes Public Policy and Effectiveness Research (COPPER) Center at Yale School of Medicine and Yale Cancer Center.
The study appears in the April issue of Health Affairs.
"Our findings indicate that in some instances, newer and costlier approaches may be leading to improved outcomes in breast cancer patients," said senior author Cary P. Gross, M.D., ...
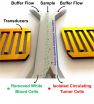
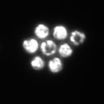
Sound separates cancer cells from blood samples
2015-04-06
Separating circulating cancer cells from blood cells for diagnostic, prognostic and treatment purposes may become much easier using an acoustic separation method and an inexpensive, disposable chip, according to a team of engineers.
"Looking for circulating tumor cells in a blood sample is like looking for a needle in a haystack," said Tony Jun Huang, professor of engineering science and mechanics. "Typically, the CTCs are about one in every one billion blood cells in the sample."
Existing methods of separation use tumor-specific antibodies to bind with the cancer ...
Lead hokes the age
2015-04-06
06.04.2015: Rocks do not loose their memory during Earth history but their true ages might be distorted: even under ultra high-temperature metamorphic conditions exceeding 1200°C zircon maintains its lead content accumulated during radioactive decay of uranium and thorium.
Giga year old zircon crystals still contain lead in form of nanometre size spheres of pure lead. However, the inhomogeneous spatial distribution of the lead spheres might falsify ages determined from high-resolution Pb isotope measurement with ion probe.
Zircon is an ideal mineral for age determination ...
Under the microscope, strong-swimming swamp bacteria spontaneously organize into crystals
2015-04-06
Insects form swarms, fish school, birds flock together. Likewise, one species of bacteria forms dynamic, living crystals, says new research from Rockefeller University. Biophysicists have revealed that fast-swimming, sulfur-eating microbes known as Thiovulum majus can organize themselves into a two-dimensional lattice composed of rotating cells, the first known example of bacteria spontaneously forming such a pattern.
"The regular, repeated arrangement of the microbial cells shares the geometry of atoms within a mineral crystal, but the dynamics are fundamentally different; ...
Study suggests new role for gene in suppressing cancer
2015-04-06
Scientists at The University of Manchester have discovered that a previously known gene also helps cells divide normally and that its absence can cause tumours.
The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) has previously been shown to have a role in cell development, immune response and metabolism. It is found in almost every cell in the body. Many widely used drugs, including prednisolone, act through this protein.
The research from Manchester, to be published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), showed a new role for GR after the scientists ...
Neighborhood stigma affects online transactions, NYU researchers find
2015-04-06
The stigma associated with particular neighborhoods has a direct impact on economic transactions, a team of New York University sociologists has found.
Their study, which appears in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, shows that when sellers are seen as being from an economically disadvantaged neighborhood, they receive fewer responses to advertisements placed in online marketplaces.
"Advertisements identifying the seller as a resident of a lower-income neighborhood received significantly fewer responses than advertisements identifying the ...
Sea sponge anchors are natural models of strength
2015-04-06
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Life may seem precarious for the sea sponge known as Venus' flower basket. Tiny, hair-like appendages made essentially of glass are all that hold the creatures to their seafloor homes. But fear not for these creatures of the deep. Those tiny lifelines, called basalia spicules, are fine-tuned for strength, according to new research led by Brown University engineers.
In a paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers show that the secret to spicules' strength lies in their remarkable internal ...
Study: Near-death brain signaling accelerates demise of the heart
2015-04-06
ANN ARBOR, Mich. - What happens in the moments just before death is widely believed to be a slowdown of the body's systems as the heart stops beating and blood flow ends.
But a new laboratory study by the University of Michigan Medical School reveals a storm of brain activity that erupts as the heart deteriorates and plays a surprising destabilizing role in heart function.
This near-death brain signaling may be targeted to help cardiac arrest patients survive. Most of the more than 400,000 Americans who experience cardiac arrest at home, at work or in public die without ...
Study reveals Internet-style 'local area networks' in cerebral cortex of rats
2015-04-06
Researchers sketching out a wiring diagram for rat brains -- a field known as "connectomics" -- have discovered that its structure is organized like the Internet.
For years, scientists looking for clues to brain function through its structure focused on what could be seen -- the brain's lobes, grooves and folds. Now, with a more comprehensive picture of how neurons connect to one another, they've discovered local networks of neurons nested into one another like shells.
"The cerebral cortex is like a mini-Internet," said Larry Swanson, professor at the USC Dornsife College ...
NIH-funded scientists identify receptor for asthma-associated virus
2015-04-06
Scientists funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, have identified a cellular receptor for rhinovirus C, a cold-causing virus that is strongly associated with severe asthma attacks. A variant in the gene for this receptor previously had been linked to asthma in genetic studies, but the potential role of the receptor, called CDHR3, in asthma was unknown. The new findings help clarify the function of CDHR3 and point to a novel target for the development of prevention and treatment strategies against ...
Computers that mimic the function of the brain
2015-04-06
Researchers are always searching for improved technologies, but the most efficient computer possible already exists. It can learn and adapt without needing to be programmed or updated. It has nearly limitless memory, is difficult to crash, and works at extremely fast speeds. It's not a Mac or a PC; it's the human brain. And scientists around the world want to mimic its abilities.
Both academic and industrial laboratories are working to develop computers that operate more like the human brain. Instead of operating like a conventional, digital system, these new devices ...
Breastfeeding women and sex: Higher sex drive or relationship management?
2015-04-06
New mothers in the Philippines spend more time in the bedroom with their partner in the first few weeks after giving birth than they did before they became pregnant. This might be a type of survival strategy to keep the relationships with the fathers of their new babies alive and well, to ensure continued support for their offspring. So says Michelle Escasa-Dorne of the University of Colorado in the US, after studying how women from a society with a low divorce rate such as the Philippines adapt to being both mothers and lovers. The study appears in Springer's journal Human ...
Common antidepressant increased coronary atherosclerosis in animal model
2015-04-06
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - April 6, 2015 - A commonly prescribed antidepressant caused up to a six-fold increase in atherosclerosis plaque in the coronary arteries of non-human primates, according to a study by researchers at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center. Coronary artery atherosclerosis is the primary cause of heart attacks.
The study is published in the current online issue of the journal Psychosomatic Medicine.
"The medical community has known for years that depression is closely associated with heart disease, but we didn't know if treating it would reduce the heart ...
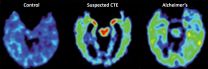
Characteristic pattern of protein deposits in brains of retired NFL players who suffered concussions
2015-04-06
A new UCLA study takes another step toward the early understanding of a degenerative brain condition called chronic traumatic encephalopathy, or CTE, which affects athletes in contact sports who are exposed to repetitive brain injuries. Using a new imaging tool, researchers found a strikingly similar pattern of abnormal protein deposits in the brains of retired NFL players who suffered from concussions.
The innovative imaging technique uses a chemical marker combined with positron emission tomography, or PET scan, and was initially tested in five retired NFL players ...
New research complicates seismic hazard for British Columbia, Alaska region
2015-04-06
SAN FRANCISCO--The Pacific and North America plate boundary off the coast of British Columbia and southeastern Alaska is a complex system of faults capable of producing very large earthquakes. The recent 2012 Mw 7.8 Haida Gwaii and 2013 Mw 7.5 Craig earthquakes released strain built up over years, but did not release strain along the Queen Charlotte Fault, which remains the likely source of a future large earthquake, according to reports published in a special issue of the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America (BSSA).
"The study of these two quakes revealed ...
Study identifies protein that triggers lupus-associated immune system activation
2015-04-06
Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators have identified an inflammatory molecule that appears to play an essential role in the autoimmune disorder systemic lupus erythematosus, commonly known as lupus. In their report being published online in Nature Immunology, the researchers describe finding that a protein that regulates certain cells in the innate immune system - the body's first line of defense against infection - activates a molecular pathway known to be associated with lupus and that the protein's activity is required for the development of lupus symptoms ...
Better sensors for medical imaging, contraband detection
2015-04-06
MIT researchers have developed a new, ultrasensitive magnetic-field detector that is 1,000 times more energy-efficient than its predecessors. It could lead to miniaturized, battery-powered devices for medical and materials imaging, contraband detection, and even geological exploration.
Magnetic-field detectors, or magnetometers, are already used for all those applications. But existing technologies have drawbacks: Some rely on gas-filled chambers; others work only in narrow frequency bands, limiting their utility.
Synthetic diamonds with nitrogen vacancies (NVs) -- ...
Researchers track protein 'hitchhiker' in fluorescent worms
2015-04-06
Dividing cells--whether they're in an embryo or an adult--rely on the right processes happening at the right time to turn out healthy.
Now, researchers at the University of Iowa have identified a mechanism that dividing cells in worms use to ensure their proper development, and they believe the same process could be going on in humans. The mechanism, unknown until now, describes one part of the cell, called the centrosome, as an "internal timekeeper"--like a train conductor. A crucial protein in charge of gene expression, beta-catenin, is described as a "hitchhiker"--it ...
Working up a sweat -- it could save your life
2015-04-06
Physical activity that makes you puff and sweat is key to avoiding an early death, a large Australian study of middle-aged and older adults has found.
The researchers followed 204,542 people for more than six years, and compared those who engaged in only moderate activity (such as gentle swimming, social tennis, or household chores) with those who included at least some vigorous activity (such as jogging, aerobics or competitive tennis).
They found that the risk of mortality for those who included some vigorous activity was 9 to 13 per cent lower, compared with those ...
We can fix the Great Barrier Reef
2015-04-06
Leading coral reef scientists say Australia could restore the Great Barrier Reef to its former glory through better policies that focus on science, protection and conservation.
In a paper published in the journal Nature Climate Change, the authors argue that all the stressors on the Reef need to be reduced for it to recover.
An Australian Government report into the state of the Great Barrier Reef found that its condition in 2014 was "poor and expected to further deteriorate in the future". In the past 40 years, the Reef has lost more than half of its coral cover and ...
Many nursing home residents die, don't walk after lower extremity revascularization
2015-04-06
Many nursing home residents who underwent lower extremity revascularization died, did not walk or had functional decline following the procedure, which is commonly used to treat leg pain caused by peripheral arterial disease, wounds that will not heal or worsening gangrene, according to an article published online by JAMA Internal Medicine.
Lower extremity revascularization is often performed so patients with peripheral arterial disease can maintain the ability to walk, which is a key component of functional independence. But outcomes among patients with high levels of ...
Neurologic function, temperature management in patients after cardiac arrest
2015-04-06
Quality of life was good and cognitive function was similar in patients with cardiac arrest who received targeted body-temperature management as a neuroprotective measure in intensive care units in Europe and Australia, according to an article published online by JAMA Neurology.
Brain injury is the primary cause of death for patients treated in intensive care units after suffering cardiac arrest (CA) outside of a hospital. Targeted temperature management (TTM) has been implemented as a neuroprotective treatment for comatose CA survivors because of reports of improved ...
Using pediatric cholesterol guidelines for teens, young adults would increase statin use
2015-04-06
Application of pediatric guidelines for lipid levels for persons 17 to 21 years of age who have elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels would result in statin treatment for more than 400,000 additional young people than the adult guidelines, according to an article published online by JAMA Pediatrics.
Adolescence is a common time for the emergence of risk factors for cardiovascular disease, including abnormal cholesterol levels. The 2011 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction in ...
Lower extremity revascularization not effective in majority of nursing home residents
2015-04-06
Only a few U.S. nursing home residents who undergo lower extremity revascularization procedures are alive and ambulatory a year after surgery, according to UCSF researchers, and most patients still alive gained little, if any, function.
The study appears in the April 6 issue of JAMA Internal Medicine.
"Our findings can inform conversations among physicians, patients and families about the risks and expected outcomes of surgery and whether the surgery is likely to allow patients to achieve their treatment goals," said senior author Emily Finlayson, MD, MS, associate ...
Western Canada to lose 70 percent of glaciers by 2100
2015-04-06
Seventy per cent of glacier ice in British Columbia and Alberta could disappear by the end of the 21st century, creating major problems for local ecosystems, power supplies, and water quality, according to a new study by University of British Columbia researchers.
The study found that while warming temperatures are threatening glaciers in Western Canada, not all glaciers are retreating at the same rate. The Rocky Mountains, in the drier interior, could lose up to 90 per cent of its glaciers. The wetter coastal mountains in northwestern B.C. are only expected to lose about ...
[1] ... [3059]
[3060]
[3061]
[3062]
[3063]
[3064]
[3065]
[3066]
3067
[3068]
[3069]
[3070]
[3071]
[3072]
[3073]
[3074]
[3075]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.