U-M researchers find protein that fuels repair of treatment-resistant cancer cells
2014-07-31
ANN ARBOR—Imagine you're fighting for your life but no matter how hard you hit, your opponent won't go down.
The same can be said of highly treatment-resistant cancers, such as head and neck cancer, where during radiation and chemotherapy some cancer cells repair themselves, survive and thrive. Head and neck cancer is the sixth most common cancer in the world, but the late detection and treatment resistance result in a high mortality rate.
Now, University of Michigan researchers have found that a particular protein—TRIP13—encourages those cancer cells to repair themselves. ...
Boat noise impacts development and survival of sea hares
2014-07-31
While previous studies have shown that marine noise can affect animal movement and communication, with unknown ecological consequences, scientists from the Universities of Bristol and Exeter and the École Pratique des Hautes Études (EPHE) CRIOBE in France have demonstrated that boat noise stops embryonic development and increases larval mortality in sea hares.
Sea hares, (specifically the sea slug Stylocheilus striatus used in this study) usually hatch from their eggs to swim away and later feed on toxic alga but this study, conducted in a coral reef lagoon in French ...
New international tree nut council study looks at nuts, diabetes and metabolic syndrome
2014-07-31
Two new meta-analyses involving tree nuts (almonds, Brazil nuts, cashews, hazelnuts, macadamias, pecans, pine nuts, pistachios and walnuts) were recently published in the online publications, British Medical Journal Open (BMJ Open) (i) and PLOS ONE (ii). The BMJ Open article looked at the effects of tree nuts on metabolic syndrome (MetS) criteria and showed that tree nut consumption resulted in a significant decrease in triglycerides and fasting blood glucose. The PLOS ONE article focused on the effect of tree nuts on glycemic control in diabetes and showed significant ...
Vets' alcohol problems linked to stress on the home front
2014-07-31
VIDEO:
Research findings show the important role civilian life and the accompanying stress plays in cases of alcohol use disorder among returning National Guardsmen.
Click here for more information.
Regardless of traumatic events experienced during deployment, returning National Guard soldiers were more likely to develop a drinking problem if faced with civilian life setbacks, including job loss, legal problems, divorce, and serious financial and legal problems—all commonplace ...
Veterans' alcohol problems linked to stress on the home front
2014-07-31
Ann Arbor, MI, July 31, 2014 — Regardless of traumatic events experienced during deployment, returning National Guard soldiers were more likely to develop a drinking problem if faced with civilian life setbacks, including job loss, legal problems, divorce, and serious financial and legal problems — all commonplace in military families. Results of the study by researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health are published online in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Alcohol abuse is a major concern for reservists returning home. Nearly 7% ...
Research proves there is power in numbers to reduce electricity bills
2014-07-31
Consumers can save money on their electricity bills and negotiate better deals by joining forces with similar groups of customers to switch energy suppliers according to new research.
Collective switching or group buying schemes, where thousands of consumers join forces to negotiate cheaper electricity tariffs, are becoming more popular in the UK as bills continue to rise putting increasing pressure on household budgets. Initiatives like Which?'s Big Switch, People Power or the Big Deal have helped thousands of consumers to save, on average, up to a third of their yearly ...
Engineering a protein to prevent brain damage from toxic agents
2014-07-31
Research at New York University is paving the way for a breakthrough that may prevent brain damage in civilians and military troops exposed to poisonous chemicals—particularly those in pesticides and chemical weapons.
An article in the current issue of the journal ChemBioChem outlines the advancement in detoxifying organophosphates, which are compounds commonly used in pesticides and warfare agents. The patent-pending process was developed by NYU School of Engineering Associate Professor of Chemical and Biological Engineering Jin Kim Montclare, along with Richard Bonneau, ...
Transplantation shown to be highly effective in treating immune deficiency in children
2014-07-31
Babies who are born with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) can be successfully treated with a transplant of blood-forming stem cells, according to experts led by Memorial Sloan Kettering's Richard J. O'Reilly, MD, a world-renowned pioneer in the development of transplant protocols. Their review will be published in the July 30 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine.
SCID is a group of inherited disorders that cause the immune system to severely malfunction. When this breakdown occurs, babies no longer have the ability to fight off routine infections because ...
Journal supplement details progress in African medical education
2014-07-31
Medical education in sub-Saharan Africa is being revitalized and expanded through a U.S.-funded effort that is dramatically increasing enrollment, broadening curricula, upgrading Internet access and providing cutting-edge skills labs and other technologies.
In the first substantial publication by participants of the $130 million Medical Education Partnership Initiative (MEPI), more than 225 authors detailed progress being made at the African institutions. Their reports are in a supplement being published today by the journal Academic Medicine. Begun in 2010, MEPI is ...
Resistance to key malaria drug spreading at alarming rate in Southeast Asia
2014-07-31
WHAT:
Resistance to artemisinin, the main drug to treat malaria, is now widespread throughout Southeast Asia, among the Plasmodium falciparum (P. falciparum) parasites that cause the disease and is likely caused by a genetic mutation in the parasites. However, a six-day course of artemisinin-based combination therapy—as opposed to a standard three-day course—has proved highly effective in treating drug-resistant malaria cases, according to findings published today in the New England Journal of Medicine. The research was conducted by an international team of scientists ...
Biologists describe mechanism promoting multiple DNA mutations
2014-07-30
DNA mutations—long known to fuel cancer as well as evolutionary changes in a living organism—had been thought to be rare events that occur randomly throughout the genome.
However, recent studies have shown that cancer development frequently involves the formation of multiple mutations that arise simultaneously and in close proximity to each other. These groups of clustered mutations are frequently found in regions where chromosomal rearrangements take place.
The discovery, published in the journal Cell Reports, may one day lead to new cancer therapies, according to ...
Classic Lewis Carroll character inspires new ecological model
2014-07-30
Inspired by the Red Queen in Lewis Carroll's Through the Looking Glass, collaborators from the University of Illinois and National University of Singapore improved a 35-year-old ecology model to better understand how species evolve over decades to millions of years.
The new model, called a mean field model for competition, incorporates the "Red Queen Effect," an evolutionary hypothesis introduced by Lee Van Valen in the 1970s, which suggests that organisms must constantly increase their fitness (or ability to survive and reproduce) in order to compete with other ever-evolving ...
Diverticulitis patients reveal psychological, physical symptoms long after acute attacks
2014-07-30
UCLA researchers interviewed people with diverticulitis and confirmed that many suffer psychological and physical symptoms long after their acute illness has passed.
For the study, published this week in the peer-reviewed journal Quality of Life Research, a UCLA team led by Dr. Brennan Spiegel interviewed patients in great detail about the symptoms they experience weeks, months or even years after an acute diverticulitis attack. Their striking findings add to growing evidence that, for some patients, diverticulitis goes beyond isolated attacks and can lead to a chronic ...
Finding quantum lines of desire
2014-07-30
Groundskeepers and landscapers hate them, but there is no fighting them. Called desire paths, social trails or goat tracks, they are the unofficial shortcuts people create between two locations when the purpose-built path doesn't take them where they want to go.
There's a similar concept in classical physics called the "path of least action." If you throw a softball to a friend, the ball traces a parabola through space. It doesn't follow a serpentine path or loop the loop because those paths have higher "actions" than the true path.
But what paths do quantum particles, ...
Tidal forces gave moon its shape, according to new analysis
2014-07-30
The shape of the moon deviates from a simple sphere in ways that scientists have struggled to explain. A new study by researchers at UC Santa Cruz shows that most of the moon's overall shape can be explained by taking into account tidal effects acting early in the moon's history.
The results, published July 30 in Nature, provide insights into the moon's early history, its orbital evolution, and its current orientation in the sky, according to lead author Ian Garrick-Bethell, assistant professor of Earth and planetary sciences at UC Santa Cruz.
As the moon cooled and ...
Target growth-driving cells within tumors, not fastest-proliferating cells
2014-07-30
BOSTON –– Of the many sub-groups of cells jockeying for supremacy within a cancerous tumor, the most dangerous may not be those that can proliferate the fastest, researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute report in a paper appearing in an advance online publication of the journal Nature. The findings have important implications for the treatment of cancer with precision medicines, the study authors explained: Doctors need to ascertain which cell subgroups are truly driving the tumor's growth and metastasis and select drugs that target the critical genes within those cells. ...
ALMA finds double star with weird and wild planet-forming discs
2014-07-30
BOWLING GREEN, O.—From movies to television, obesity is still considered "fair game" for jokes and ridicule. A new study from researchers at Bowling Green State University took a closer look at weight-related humor to see if anti-fat attitudes played into a person's appreciation or distaste for fat humor in the media.
"Weight-Related Humor in the Media: Appreciation, Distaste and Anti-Fat Attitudes," by psychology Ph.D. candidate Jacob Burmeister and Dr. Robert Carels, professor of psychology, is featured in the June issue of Psychology of Popular Media Culture.
Carels ...
Innovative scientists update old-school pipetting with new-age technology
2014-07-30
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (July 30, 2014) A team of Whitehead Institute researchers is bringing new levels of efficiency and accuracy to one of the most essential albeit tedious tasks of bench science: pipetting. And, in an effort to aid the scientific community at large, the group has established an open source system that enables anyone to benefit from this development free of charge.
Dubbed "iPipet," the system converts an iPad or any tablet computer into a "smart bench" that guides the execution of complex pipetting protocols. iPipet users can also share their pipetting designs ...
Mapping the optimal route between 2 quantum states
2014-07-30
As a quantum state collapses from a quantum superposition to a classical state or a different superposition, it will follow a path known as a quantum trajectory. For each start and end state there is an optimal or "most likely" path, but it is not as easy to predict the path or track it experimentally as a straight-line between two points would be in our everyday, classical world.
In a new paper featured this week on the cover of Nature, scientists from the University of Rochester, University of California at Berkeley and Washington University in St. Louis have shown ...
Young binary star system may form planets with weird and wild orbits
2014-07-30
Unlike our solitary Sun, most stars form in binary pairs -- two stars that orbit a common center of mass. Though remarkably plentiful, binaries pose a number of questions, including how and where planets form in such complex environments.
While surveying a series of binary stars with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), astronomers uncovered a striking pair of wildly misaligned planet-forming disks in the young binary star system HK Tau. These results provide the clearest picture ever of protoplanetary disks around a double star and could reveal important ...
Scientists reproduce evolutionary changes by manipulating embryonic development of mice
2014-07-30
A group of researchers from the University of Helsinki and the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona have been able experimentally to reproduce in mice morphological changes which have taken millions of years to occur. Through small and gradual modifications in the embryonic development of mice teeth, induced in the laboratory, scientists have obtained teeth which morphologically are very similar to those observed in the fossil registry of rodent species which separated from mice millions of years ago.
To modify the development of their teeth, the team from the Institute ...
Conservation scientists asking wrong questions on climate change impacts on wildlife
2014-07-30
Scientists studying the potential effects of climate change on the world's animal and plant species are focusing on the wrong factors, according to a new paper by a research team from the Wildlife Conservation Society, University of Queensland, and other organizations. The authors claim that most of the conservation science is missing the point when it comes to climate change.
While the majority of climate change scientists focus on the "direct" threats of changing temperatures and precipitation after 2031, far fewer researchers are studying how short-term human adaptation ...
Antarctic ice sheet is result of CO2 decrease, not continental breakup
2014-07-30
DURHAM, N.H. – Climate modelers from the University of New Hampshire have shown that the most likely explanation for the initiation of Antarctic glaciation during a major climate shift 34 million years ago was decreased carbon dioxide (CO2) levels. The finding counters a 40-year-old theory suggesting massive rearrangements of Earth's continents caused global cooling and the abrupt formation of the Antarctic ice sheet. It will provide scientists insight into the climate change implications of current rising global CO2 levels.
In a paper published today in Nature, Matthew ...
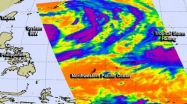
NASA catches two tropical troublemakers in Northwestern Pacific: Halong and 96W
2014-07-30
There are two tropical low pressure areas in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean today and they're close enough to each other to be captured in one image generated from data gathered by NASA's Aqua satellite.
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over both Tropical Storm Halong and developing System 96W early on July 30 and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured infrared data on them in one image. Both systems show powerful thunderstorms stretching high into the troposphere with cloud top temperatures as cold as -63F/-52C. Those thunderstorms have the potential for ...
Watching Schrödinger's cat die (or come to life)
2014-07-30
One of the famous examples of the weirdness of quantum mechanics is the paradox of Schrödinger's cat.
If you put a cat inside an opaque box and make his life dependent on a random event, when does the cat die? When the random event occurs, or when you open the box?
Though common sense suggests the former, quantum mechanics – or at least the most common "Copenhagen" interpretation enunciated by Danish physicist Neils Bohr in the 1920s – says it's the latter. Someone has to observe the result before it becomes final. Until then, paradoxically, the cat is both dead and ...
[1] ... [3406]
[3407]
[3408]
[3409]
[3410]
[3411]
[3412]
[3413]
3414
[3415]
[3416]
[3417]
[3418]
[3419]
[3420]
[3421]
[3422]
... [8788]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.