Study identifies 'bonus effect' for certain multiracial daters
2014-08-18
SAN FRANCISCO — While previous research has documented the existence of a racial hierarchy within the dating world with white women and men on top, a new study finds that in certain circumstances multiracial daters are actually seen as more desirable than individuals from all other racial groups, including whites.
"The most interesting and surprising finding from our study is that some white-minority multiracial daters are, in fact, preferred over white and non-white daters," said Celeste Vaughan Curington, a doctoral student in sociology at the University of Massachusetts-Amherst ...
'Super-parent' cultural pressures can spur mental health conditions in new moms and dads
2014-08-18
SAN FRANCISCO — Mental health experts in the past three decades have emphasized the dangers of post-partum depression for mothers, but a University of Kansas researcher says expanding awareness of several other perinatal mental health conditions is important for all new parents, including fathers.
This awareness has become even more critical as "super mom" and "super dad" pressures continue to grow, said Carrie Wendel-Hummell, a KU doctoral candidate in sociology, who will present her study on perinatal mental health disorders at the 109th Annual Meeting of the American ...
Surprising number of older adults weathered the 'Great Recession' without financial strain
2014-08-18
SAN FRANCISCO — The "Great Recession" may have put a dent in many older adults' pocketbooks, but a new study, which will be presented at the 109th Annual Meeting of the American Sociological Association, finds that more than 40 percent reported a decrease in "financial strain" between 2006 and 2010.
Researcher Lindsay R. Wilkinson, an assistant professor of sociology in Baylor University's College of Arts & Sciences, drew on 5,205 respondents from the Health and Retirement Study (HRS) to examine the effect of financial strain on the mental health and use of mood-altering ...
High-intensity exercise found safe and effective in long-term heart transplant recipients
2014-08-18
High-intensity exercise can help stable heart transplant patients reach higher levels of exercise capacity, and gain better control of their blood pressure than moderate intensity exercise, investigators report in a new study published in the American Journal of Transplantation.
Recent research shows that high-intensity interval exercise—training for a few minutes at close to the maximum heart rate—is safe and more efficient than moderate exercise for improving exercise capacity in different groups of patients with heart disease. Researchers led by Christian Dall, PhD ...
DNA methylation involved in Alzheimer's disease
2014-08-17
Boston, MA – A new study led by researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) and Rush University Medical Center, reveals how early changes in brain DNA methylation are involved in Alzheimer's disease. DNA methylation is a biochemical alteration of the building blocks of DNA and is one of the markers that indicate whether the DNA is open and biologically active in a given region of the human genome.
The study is published online August 17, 2014 in Nature Neuroscience.
According to the researchers, this is the first large-scale study employing epigenome-wide association ...
Gorges are eradicated by downstream sweep erosion
2014-08-17
Local surface uplift can block rivers, particularly in mountainous regions. The impounded water, however, always finds its way downstream, often cutting a narrow gorge into the rocks. Subsequent erosion of the rocks can lead to a complete eradication of this initial incision, until not a trace is left of the original breakthrough. In extreme cases the whole gorge disappears, leaving behind a broad valley with a flat floodplain. Previously, the assumption was that this transition from a narrow gorge to a wide valley was driven by gorge widening and the erosion of the walls ...
Epigenetic breakthrough bolsters understanding of Alzheimer's disease
2014-08-17
A team led by researchers at the University of Exeter Medical School and King's College London has uncovered some of the strongest evidence yet that epigenetic changes in the brain play a role in Alzheimer's disease.
Epigenetic changes affect the expression or activity of genes without changing the underlying DNA sequence and are believed to be one mechanism by which the environment can interact with the genome. Importantly, epigenetic changes are potentially reversible and may therefore provide targets for the development of new therapies.
Globally, more than 26 million ...
8,000-year-old mutation key to human life at high altitudes
2014-08-17
(SALT LAKE CITY) – In an environment where others struggle to survive, Tibetans thrive in the thin air on the Tibetan Plateau, with an average elevation of 14,800 feet. A study led by University of Utah scientists is the first to find a genetic cause for the adaptation – a single DNA base pair change that dates back 8,000 years – and demonstrate how it contributes to the Tibetans' ability to live in low oxygen conditions. The study appears online in the journal Nature Genetics on Aug. 17, 2014.
"These findings help us understand the unique aspects of Tibetan adaptation ...
Microchip reveals how tumor cells transition to invasion
2014-08-17
VIDEO:
Cancer cells advance across a microchip designed to be an obstacle course for cells. The device sheds new light on how cancer cells invade and could be used to test...
Click here for more information.
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Using a microengineered device that acts as an obstacle course for cells, researchers have shed new light on a cellular metamorphosis thought to play a role in tumor cell invasion throughout the body.
The epithelial-mesenchymal transition ...
'Cavity protection effect' helps to conserve quantum information
2014-08-17
The electronics we use for our computers only knows two different states: zero or one. Quantum systems on the other hand can be in different states at once, they can store a superposition of "zero" and "one". This phenomenon could be used to build ultrafast quantum computers, but there are several technological obstacles that have to be overcome first. The biggest problem is that quantum states are quickly destroyed due to interactions with the environment. At TU Wien (Vienna), scientists have now succeeded in using a protection effect to enhance the stability of a particularly ...
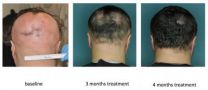
FDA-approved drug restores hair in patients with Alopecia Areata
2014-08-17
NEW YORK, NY (August 17, 2014) —Researchers at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) have identified the immune cells responsible for destroying hair follicles in people with alopecia areata, a common autoimmune disease that causes hair loss, and have tested an FDA-approved drug that eliminated these immune cells and restored hair growth in a small number of patients.
The results appear in today's online issue of Nature Medicine.
In the paper, the researchers report initial results from an ongoing clinical trial of the drug, which has produced complete hair regrowth ...
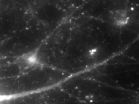
Fascinating rhythm: Light pulses illuminate a rare black hole
2014-08-17
The universe has so many black holes that it's impossible to count them all. There may be 100 million of these intriguing astral objects in our galaxy alone. Nearly all black holes fall into one of two classes: big, and colossal. Astronomers know that black holes ranging from about 10 times to 100 times the mass of our sun are the remnants of dying stars, and that supermassive black holes, more than a million times the mass of the sun, inhabit the centers of most galaxies.
But scattered across the universe like oases in a desert are a few apparent black holes of a more ...
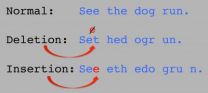
A shift in the code: New method reveals hidden genetic landscape
2014-08-17
Cold Spring Harbor, NY – With three billion letters in the human genome, it seems hard to believe that adding a DNA base here or removing a DNA base there could have much of an effect on our health. In fact, such insertions and deletions can dramatically alter biological function, leading to diseases from autism to cancer. Still, it is has been difficult to detect these mutations. Now, a team of scientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) has devised a new way to analyze genome sequences that pinpoints so-called insertion and deletion mutations (known as "indels") ...
New home for an 'evolutionary misfit'
2014-08-17
One of the most bizarre-looking fossils ever found - a worm-like creature with legs, spikes and a head difficult to distinguish from its tail – has found its place in the evolutionary Tree of Life, definitively linking it with a group of modern animals for the first time.
The animal, known as Hallucigenia due to its otherworldly appearance, had been considered an 'evolutionary misfit' as it was not clear how it related to modern animal groups. Researchers from the University of Cambridge have discovered an important link with modern velvet worms, also known as onychophorans, ...
Stem cells reveal how illness-linked genetic variation affects neurons
2014-08-17
VIDEO:
Human neurons firing
Click here for more information.
A genetic variation linked to schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and severe depression wreaks havoc on connections among neurons in the developing brain, a team of researchers reports. The study, led by Guo-li Ming, M.D., Ph.D., and Hongjun Song, Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and described online Aug. 17 in the journal Nature, used stem cells generated from people with and without mental illness ...
New Stanford research sheds light on how children's brains memorize facts
2014-08-17
As children learn basic arithmetic, they gradually switch from solving problems by counting on their fingers to pulling facts from memory. The shift comes more easily for some kids than for others, but no one knows why.
Now, new brain-imaging research gives the first evidence drawn from a longitudinal study to explain how the brain reorganizes itself as children learn math facts. A precisely orchestrated group of brain changes, many involving the memory center known as the hippocampus, are essential to the transformation, according to a study from the Stanford University ...
Suspect gene corrupts neural connections
2014-08-17
Researchers have long suspected that major mental disorders are genetically-rooted diseases of synapses – the connections between neurons. Now, investigators supported in part by the National Institutes of Health have demonstrated in patients' cells how a rare mutation in a suspect gene disrupts the turning on and off of dozens of other genes underlying these connections.
"Our results illustrate how genetic risk, abnormal brain development and synapse dysfunction can corrupt brain circuitry at the cellular level in complex psychiatric disorders," explained Hongjun Song, ...
Stuck in neutral: Brain defect traps schizophrenics in twilight zone
2014-08-17
People with schizophrenia struggle to turn goals into actions because brain structures governing desire and emotion are less active and fail to pass goal-directed messages to cortical regions affecting human decision-making, new research reveals.
Published in Biological Psychiatry, the finding by a University of Sydney research team is the first to illustrate the inability to initiate goal-directed behaviour common in people with schizophrenia.
The finding may explain why people with schizophrenia have difficulty achieving real-world goals such as making friends, completing ...
Virginity pledges for men can lead to sexual confusion -- even after the wedding day
2014-08-17
Bragging of sexual conquests, suggestive jokes and innuendo, and sexual one-upmanship can all be a part of demonstrating one's manhood, especially for young men eager to exert their masculinity.
But how does masculinity manifest itself among young men who have pledged sexual abstinence before marriage? How do they handle sexual temptation, and what sorts of challenges crop up once they're married?
"Sexual purity and pledging abstinence are most commonly thought of as feminine, something girls and young women promise before marriage," said Sarah Diefendorf, a sociology ...
Study finds range of skills students taught in school linked to race and class size
2014-08-17
SAN FRANCISCO -- Pressure to meet national education standards may be the reason states with significant populations of African-American students and those with larger class sizes often require children to learn fewer skills, finds a University of Kansas researcher.
"The skills students are expected to learn in schools are not necessarily universal," said Argun Saatcioglu, a KU associate professor of education and courtesy professor of sociology.
In effort to increase their test scores and, therefore, avoid the negative consequences of failing to meet the federal standards ...
Study suggests federal law to combat use of 'club drugs' has done more harm than good
2014-08-17
SAN FRANCISCO — A federal law enacted to combat the use of "club drugs" such as Ecstasy — and today's variation known as Molly — has failed to reduce the drugs' popularity and, instead, has further endangered users by hampering the use of measures to protect them.
University of Delaware sociology professor Tammy L. Anderson makes that case in a paper she will present at the 109th Annual Meeting of the American Sociological Association. The paper, which has been accepted for publication this fall in the American Sociological Association journal Contexts, examines the unintended ...
Risky situations increase women's anxiety, hurt their performance compared to men
2014-08-17
SAN FRANCISCO — Risky situations increase anxiety for women but not for men, leading women to perform worse under these circumstances, finds a study to be presented at the 109th Annual Meeting of the American Sociological Association.
"On the surface, risky situations may not appear to be particularly disadvantageous to women, but these findings suggest otherwise," said study author Susan R. Fisk, a doctoral candidate in sociology at Stanford University, who defines a risky situation as any setting with an uncertain outcome in which there can be both positive or negative ...
Most temporary workers from Mexico no better off than undocumented workers
2014-08-17
SAN FRANCISCO -- Many politicians see the temporary worker program in the U.S. as a solution to undocumented immigration from Mexico. But an Indiana University study finds that these legal workers earn no more than undocumented immigrants, who unlike their legal counterparts can improve their situation by changing jobs or negotiating for better pay.
"Just because temporary workers are legally present in the country does not mean that they will have better jobs or wages than undocumented workers," said Lauren Apgar, lead researcher of the study "Temporary Worker Advantages? ...
Bone chemistry reveals royal lifestyle of Richard III
2014-08-17
Oxford, August 17, 2014 - A recent study by the British Geological Survey, in association with researchers at the University of Leicester, has delved into the bone and tooth chemistry of King Richard III and uncovered fascinating new details about the life and diet of Britain's last Plantagenet king. The study, published in Elsevier's Journal of Archaeological Science indicates a change in diet and location in his early childhood, and in later life, a diet filled with expensive, high status food and drink. This forensic study, the most complete to have been conducted on ...
'Getting-by girls' straddle gap between academic winners and losers
2014-08-17
Everyone notices the academic superstars and failures, but what about the tens of millions of American teens straddling these two extremes? A new study from the University of California, Berkeley, has spotlighted a high school subculture that has made an art of slacking – even with ample educational resources – and may be destined to perpetuate the nation's struggling lower-middle class.
UC Berkeley sociologist Michele Rossi studied white teenage girls in their last year of a well-funded high school. What she found was a group she dubbed "getting-by girls," whose coping ...
[1] ... [3409]
[3410]
[3411]
[3412]
[3413]
[3414]
[3415]
[3416]
3417
[3418]
[3419]
[3420]
[3421]
[3422]
[3423]
[3424]
[3425]
... [8829]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.