Fukushima's legacy
2014-08-14
Following the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear power plant meltdown, biological samples were obtained only after extensive delays, limiting the information that could be gained about the impacts of that historic disaster. Determined not to repeat the shortcomings of the Chernobyl studies, scientists began gathering biological information only a few months after the disastrous meltdown of the Fukushima Daiichi power plant in Japan in 2011. Results of these studies are now beginning to reveal serious biological effects of the Fukushima radiation on non-human organisms ranging from ...
Immune cell discovery could help to halt cancer spread
2014-08-14
Melbourne researchers have revealed the critical importance of highly specialised immune cells, called natural killer cells, in killing melanoma cells that have spread to the lungs.
These natural killer cells could be harnessed to hunt down and kill cancers that have spread in the body.
The team, from the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute, also found natural killer cells were critical to the body's rejection of donor bone marrow transplants and in the runaway immune response during toxic shock syndrome.
The discoveries came after the team showed that a protein called ...
Newborns' genetic code sends infection distress signal
2014-08-14
Babies suffering from life-threatening bacterial infections such as sepsis could benefit from improved treatment, thanks to a ground-breaking study.
For the first time, researchers have been able to detect and decode a signal generated from a baby's DNA that can tell doctors whether or not a bacterial infection is present in the bloodstream.
The findings could help develop a test for bacterial infection in newborns, using a single drop of blood.
Immediate detection of such infections, which are a major cause of death among young children, is currently impossible ...
Bypass commands from the brain to legs through a computer
2014-08-14
VIDEO:
The right arm muscles and the locomotion center of the man are artificially connected through a computer. His legs are in a relaxed state. When he moves his right hand,...
Click here for more information.
Gait disturbance in individuals with spinal cord injury is attributed to the interruption of neural pathways from brain to the spinal locomotor center, whereas neural circuits locate below and above the lesion maintain most of their functions. An artificial connection ...
Aspirin may slow recurrence in breast cancer patients
2014-08-14
SAN ANTONIO (August 14, 2014) — New findings published today in the journal Cancer Research reveal that some postmenopausal overweight breast cancer patients who use common anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin or ibuprofen have significantly lower breast cancer recurrence rates.
Researchers from the Cancer Therapy & Research Center at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio and the University of Texas at Austin began by examining blood serum from CTRC breast cancer patients, said CTRC oncologist Andrew Brenner, M.D., Ph.D.
Studying Blood Serum
They ...
Protein found to block benefits of vitamin A cancer therapy
2014-08-14
Retinoic acid is a form of vitamin A that is used to treat and help prevent the recurrence of a variety of cancers, but for some patients the drug is not effective. The reason for this resistance was unclear until this week when researchers from Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU) Massey Cancer Center demonstrated that a protein known as AEG-1 blocks the effects of retinoic acid in leukemia and liver cancer. Because AEG-1 is overexpressed in nearly every cancer, these findings could impact the care of countless cancer patients.
Details of the study were published ...
Lionfish characteristics make them more 'terminator' than predator
2014-08-14
SACRAMENTO, Calif. – New research on the predatory nature of red lionfish, the invasive Pacific Ocean species that is decimating native fish populations in parts of the Caribbean Sea and Atlantic Ocean, seems to indicate that lionfish are not just a predator, but more like the "terminator" of movie fame.
The finding of behavior that was called "alarming" was presented today by Kurt Ingeman, a researcher from Oregon State University, at the annual meeting of the Ecological Society of America.
Most native predatory fish are attracted to prey when their numbers are high, ...
NSAIDs may lower breast cancer recurrence rate in overweight and obese women
2014-08-14
PHILADELPHIA — Recurrence of hormone-related breast cancer was cut by half in overweight and obese women who regularly used aspirin or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), according to data published in Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"Our studies suggest that limiting inflammatory signaling may be an effective, less toxic approach to altering the cancer-promoting effects of obesity and improving patient response to hormone therapy," said Linda A. deGraffenried, PhD, associate professor of nutritional sciences ...
Mayo Clinic challenges some recommendations in updated cholesterol treatment guideline
2014-08-14
A Mayo Clinic task force challenges some recommendations in the updated guideline for cholesterol treatment unveiled by the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and American Heart Association (AHA) in 2013. The task force concludes, based on current evidence, that not all patients encouraged to take cholesterol-lowering medications, such as statins, may benefit from them and that the guideline missed some important conditions that might benefit from medication.
Furthermore, the task force believes an emphasis needs to be placed on an individualized treatment approach ...
NSAIDs benefit overweight breast cancer patients, study finds
2014-08-14
AUSTIN, Texas — Researchers have determined that postmenopausal overweight or obese breast cancer patients receiving hormone therapy as part of their treatment and who use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin or ibuprofen have significantly lower breast cancer recurrence rates and a sizable delay in time to cancer recurrence.
The findings, published in the Aug. 14 edition of Cancer Research, suggest a new possibility for reducing the incidence of breast cancer recurrence among overweight and obese postmenopausal women, who have a comparatively ...
Scientists make major breakthrough in understanding leukemia
2014-08-14
Scientists from Queen Mary University of London (QMUL) have discovered mutations in genes that lead to childhood leukaemia of the acute lymphoblastic type – the most common childhood cancer in the world.
The study was conducted amongst children with Down's syndrome – who are 20-50 times more prone to childhood leukaemias than other children – and involved analysing the DNA sequence of patients at different stages of leukaemia.
The researchers uncovered that two key genes (called RAS and JAK) can mutate to turn normal blood cells into cancer cells. However, these ...
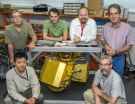
Can our computers continue to get smaller and more powerful?
2014-08-13
From their origins in the 1940s as sequestered, room-sized machines designed for military and scientific use, computers have made a rapid march into the mainstream, radically transforming industry, commerce, entertainment and governance while shrinking to become ubiquitous handheld portals to the world.
This progress has been driven by the industry's ability to continually innovate techniques for packing increasing amounts of computational circuitry into smaller and denser microchips. But with miniature computer processors now containing millions of closely-packed transistor ...
UT Arlington team's work could lead to earlier diagnosis, treatment of mental diseases
2014-08-13
A computer science and engineering associate professor and her doctoral student graduate are using a genetic computer network inference model that eventually could predict whether a person will suffer from bipolar disorder, schizophrenia or another mental illness.
The findings are detailed in the paper "Inference of SNP-Gene Regulatory Networks by Integrating Gene Expressions and Genetic Perturbations," which was published in the June edition of Biomed Research International. The principal investigators were Jean Gao, an associate professor of computer science and engineering, ...
Three radars are better than one: Field campaign demonstrates two new instruments
2014-08-13
Putting three radars on a plane to measure rainfall may seem like overkill. But for the Integrated Precipitation and Hydrology Experiment field campaign in North Carolina recently, more definitely was better.
The three instruments, developed by the High Altitude Radar group at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, flew as part of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission's six-week ground-validation program that took place May 1 through June 15 in the southern Appalachians, specifically to measure rain in difficult-to-forecast mountain regions. ...
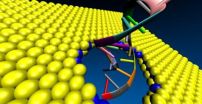
New material could enhance fast and accurate DNA sequencing
2014-08-13
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Gene-based personalized medicine has many possibilities for diagnosis and targeted therapy, but one big bottleneck: the expensive and time-consuming DNA-sequencing process.
Now, researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have found that nanopores in the material molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) could sequence DNA more accurately, quickly and inexpensively than anything yet available.
"One of the big areas in science is to sequence the human genome for under $1,000, the 'genome-at-home,'" said Narayana Aluru, a professor of mechanical ...
Patent examiners more likely to approve marginal inventions when pressed for time
2014-08-13
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Haste makes waste, as the old saying goes. And according to research from a University of Illinois expert in patent law, the same adage could be applied to the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, where high-ranking examiners have a tendency to rubber-stamp patents of questionable merit due to time constraints.
The less time patent examiners are given to review an application, the more likely they are to grant patent protection to inventions "on the margin," says a study co-authored by Melissa Wasserman, the Richard and Anne Stockton Faculty Scholar and ...
Bones from nearly 50 ancient flying reptiles discovered
2014-08-13
Scientists discovered the bones of nearly 50 winged reptiles from a new species, Caiuajara dobruskii, that lived during the Cretaceous in southern Brazil, according to a study published August 13, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Paulo Manzig from Universidade do Contestado, Brazil, and colleagues.
The authors discovered the bones in a pterosaur bone bed in rocks from the Cretaceous period. They belonged to individuals ranging from young to adult, with wing spans ranging from 0.65-2.35m, allowing scientists to analyze how the bones fit into their clade, but ...
Embalming study 'rewrites' chapter in Egyptian history
2014-08-13
The origins of mummification may have started in ancient Egypt 1,500 years earlier than previously thought, according to a study published August 13, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Stephen Buckley from University of York and colleagues from Macquarie University and University of Oxford.
Previous evidence suggests that between ~4500 B.C. and 3100 B.C., Egyptian mummification consisted of bodies desiccating naturally through the action of the hot, dry desert sand. The early use of resins in artificial mummification has, until now, been limited to isolated occurrences ...
Little penguins forage together
2014-08-13
Most little penguins may search for food in groups, and even synchronize their movements during foraging trips, according to a study published August 13, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Maud Berlincourt and John Arnould from Deakin University in Australia.
Little penguins are the smallest penguin species and they live exclusively in southern Australia, New Zealand, and the Chatham Islands, but spend most of their lives at sea in search of food. Not much is known about group foraging behavior in seabirds due to the difficulty in observing their remote feeding ...
Young blue sharks use central North Atlantic nursery
2014-08-13
Blue sharks may use the central North Atlantic as a nursery prior to males and females moving through the ocean basin in distinctly different patterns, according to a study published August 13, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Frederic Vandeperre from University of the Azores, Portugal, and colleagues.
Shark populations typically organize by location and separate by sex and size, but these patterns remain poorly understood, particularly for exploited oceanic species such as the blue shark. The authors of this study employed a long-term electronic tagging experiment ...
Bacterial biosurgery shows promise for reducing the size of inoperable tumors
2014-08-13
Kansas City, MO. — Deep within most tumors lie areas that remain untouched by chemotherapy and radiation. These troublesome spots lack the blood and oxygen needed for traditional therapies to work, but provide the perfect target for a new cancer treatment using bacteria that thrive in oxygen-poor conditions. Now, researchers have shown that injections of a weakened version of one such anaerobic bacteria -- the microbe Clostridium novyi -- can shrink tumors in rats, pet dogs, and a human patient.
The findings from BioMed Valley Discoveries and a nationwide team of collaborators ...
Embalming study 'rewrites' key chapter in Egyptian history
2014-08-13
Researchers from the Universities of York, Macquarie and Oxford have discovered new evidence to suggest that the origins of mummification started in ancient Egypt 1,500 years earlier than previously thought.
The scientific findings of an 11-year study by a researcher in the Department of Archaeology at York, and York's BioArCh facility, and an Egyptologist from the Department of Ancient History at Macquarie University, push back the origins of a central and vital facet of ancient Egyptian culture by over a millennium.
Traditional theories on ancient Egyptian mummification ...
Injected bacteria shrink tumors in rats, dogs and humans
2014-08-13
A modified version of the Clostridium novyi (C. noyvi-NT) bacterium can produce a strong and precisely targeted anti-tumor response in rats, dogs and now humans, according to a new report from Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center researchers.
In its natural form, C. novyi is found in the soil and, in certain cases, can cause tissue-damaging infection in cattle, sheep and humans. The microbe thrives only in oxygen-poor environments, which makes it a targeted means of destroying oxygen-starved cells in tumors that are difficult to treat with chemotherapy and radiation. The ...
Treatment with lymph node cells controls dangerous sepsis in animal models
2014-08-13
An immune-regulating cell present in lymph nodes may be able to halt severe cases of sepsis, an out-of-control inflammatory response that can lead to organ failure and death. In the August 13 issue of Science Translational Medicine, a multi-institutional research team reports that treatment with fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs) significantly improved survival in two mouse models of sepsis, even when delivered after the condition was well established. Even after treatment with antibiotics, sepsis remains a major cause of death.
"Our findings are important because, ...
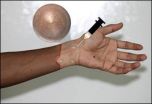
Stimuli-responsive drug delivery system prevents transplant rejection
2014-08-13
Boston, MA – Following a tissue graft transplant—such as that of the face, hand, arm or leg—it is standard for doctors to immediately give transplant recipients immunosuppressant drugs to prevent their body's immune system from rejecting and attacking the new body part. However, there are toxicities associated with delivering these drugs systemically, as well as side effects since suppressing the immune system can make a patient vulnerable to infection.
A global collaboration including researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH); Institute for Stem Cell Biology ...
[1] ... [3415]
[3416]
[3417]
[3418]
[3419]
[3420]
[3421]
[3422]
3423
[3424]
[3425]
[3426]
[3427]
[3428]
[3429]
[3430]
[3431]
... [8829]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.