(Press-News.org) Boston, MA – A new study led by researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) and Rush University Medical Center, reveals how early changes in brain DNA methylation are involved in Alzheimer's disease. DNA methylation is a biochemical alteration of the building blocks of DNA and is one of the markers that indicate whether the DNA is open and biologically active in a given region of the human genome.
The study is published online August 17, 2014 in Nature Neuroscience.
According to the researchers, this is the first large-scale study employing epigenome-wide association (EWAS) studies—which look at chromosomal make-up and changes—in relation to the brain and Alzheimer's disease.
"Our study approach may help us to better understand the biological impact of environmental risk factors and life experiences on Alzheimer's disease," said Philip L. De Jager, MD, PhD, Program in Translational Neuropsychiatric Genomics, BWH Departments of Neurology and Psychiatry, lead study author. "There are certain advantages to studying the epigenome, or the chemical changes that occur in DNA. The epigenome is malleable and may harbor traces of life events that influence disease susceptibility, such as smoking, depression and menopause, which may influence susceptibility to Alzheimer's and other diseases."
The researchers analyzed samples from 708 donated brains from subjects in the Religious Orders Study and Rush Memory and Aging Project, conducted by study co-author, David A. Bennett, MD, Rush Alzheimer's Disease Center in Chicago. They found that methylation levels correlated with Alzheimer's disease in 71 of 415,848 CpG markers analyzed (these are a pair of DNA building blocks consisting of a cytosine and a guanine nucleotide that are located next to each other). These 71 markers were found in the ANK1 and RHBDF2 genes, as well as ABCA7 and BIN1 which harbor known Alzheimer's disease susceptibility variants.
Further, investigation of these CpG associations revealed nearby genes whose RNA expression was altered in brain samples with Alzheimer's disease: ANK1, CDH23, DIP2A, RHBDF2, RPL13, RNF34, SERPINF1 and SERPINF2. This suggests that the CpG associations identify genes whose function is altered in Alzheimer's disease.
Further, "because these findings are also found in the subset of subjects that are not cognitively impaired at the time of death, it appears that these DNA methylation changes may play a role in the onset of Alzheimer's disease," said De Jager. "Moreover, our work has helped identify regions of the human genome that are altered over the life-course in a way that is associated with Alzheimer's disease. This may provide clues to treating the disease by using drugs that influence epigenomic function."
INFORMATION:
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01AG036042, R01AG036836, R01 AG17917, R01AG15819, R01 AG032990, R01AG18023, RC2 AG036547, P30 AG10161, P50 AG016574, U01 ES017155, KL2RR024151, K25 AG041906-01, AG036039), Siragusa Foundation, Robert and Clarice Smith and Abigail Van Buren Alzheimer's Disease Research Program, and Alzheimer's Research UK.
Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) is a 793-bed nonprofit teaching affiliate of Harvard Medical School and a founding member of Partners HealthCare. BWH has more than 3.5 million annual patient visits, is the largest birthing center in Massachusetts and employs nearly 15,000 people. The Brigham's medical preeminence dates back to 1832, and today that rich history in clinical care is coupled with its national leadership in patient care, quality improvement and patient safety initiatives, and its dedication to research, innovation, community engagement and educating and training the next generation of health care professionals. Through investigation and discovery conducted at its Brigham Research Institute (BRI), BWH is an international leader in basic, clinical and translational research on human diseases, more than 1,000 physician-investigators and renowned biomedical scientists and faculty supported by nearly $650 million in funding. For the last 25 years, BWH ranked second in research funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) among independent hospitals. BWH continually pushes the boundaries of medicine, including building on its legacy in transplantation by performing a partial face transplant in 2009 and the nation's first full face transplant in 2011. BWH is also home to major landmark epidemiologic population studies, including the Nurses' and Physicians' Health Studies and the Women's Health Initiative. For more information, resources and to follow us on social media, please visit BWH's online newsroom.
DNA methylation involved in Alzheimer's disease
First large-scale study using EWAS to look at brain's chromosomal make-up in relation to Alzheimer's disease
2014-08-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gorges are eradicated by downstream sweep erosion
2014-08-17
Local surface uplift can block rivers, particularly in mountainous regions. The impounded water, however, always finds its way downstream, often cutting a narrow gorge into the rocks. Subsequent erosion of the rocks can lead to a complete eradication of this initial incision, until not a trace is left of the original breakthrough. In extreme cases the whole gorge disappears, leaving behind a broad valley with a flat floodplain. Previously, the assumption was that this transition from a narrow gorge to a wide valley was driven by gorge widening and the erosion of the walls ...
Epigenetic breakthrough bolsters understanding of Alzheimer's disease
2014-08-17
A team led by researchers at the University of Exeter Medical School and King's College London has uncovered some of the strongest evidence yet that epigenetic changes in the brain play a role in Alzheimer's disease.
Epigenetic changes affect the expression or activity of genes without changing the underlying DNA sequence and are believed to be one mechanism by which the environment can interact with the genome. Importantly, epigenetic changes are potentially reversible and may therefore provide targets for the development of new therapies.
Globally, more than 26 million ...
8,000-year-old mutation key to human life at high altitudes
2014-08-17
(SALT LAKE CITY) – In an environment where others struggle to survive, Tibetans thrive in the thin air on the Tibetan Plateau, with an average elevation of 14,800 feet. A study led by University of Utah scientists is the first to find a genetic cause for the adaptation – a single DNA base pair change that dates back 8,000 years – and demonstrate how it contributes to the Tibetans' ability to live in low oxygen conditions. The study appears online in the journal Nature Genetics on Aug. 17, 2014.
"These findings help us understand the unique aspects of Tibetan adaptation ...
Microchip reveals how tumor cells transition to invasion
2014-08-17
VIDEO:
Cancer cells advance across a microchip designed to be an obstacle course for cells. The device sheds new light on how cancer cells invade and could be used to test...
Click here for more information.
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Using a microengineered device that acts as an obstacle course for cells, researchers have shed new light on a cellular metamorphosis thought to play a role in tumor cell invasion throughout the body.
The epithelial-mesenchymal transition ...
'Cavity protection effect' helps to conserve quantum information
2014-08-17
The electronics we use for our computers only knows two different states: zero or one. Quantum systems on the other hand can be in different states at once, they can store a superposition of "zero" and "one". This phenomenon could be used to build ultrafast quantum computers, but there are several technological obstacles that have to be overcome first. The biggest problem is that quantum states are quickly destroyed due to interactions with the environment. At TU Wien (Vienna), scientists have now succeeded in using a protection effect to enhance the stability of a particularly ...
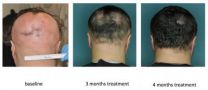
FDA-approved drug restores hair in patients with Alopecia Areata
2014-08-17
NEW YORK, NY (August 17, 2014) —Researchers at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) have identified the immune cells responsible for destroying hair follicles in people with alopecia areata, a common autoimmune disease that causes hair loss, and have tested an FDA-approved drug that eliminated these immune cells and restored hair growth in a small number of patients.
The results appear in today's online issue of Nature Medicine.
In the paper, the researchers report initial results from an ongoing clinical trial of the drug, which has produced complete hair regrowth ...
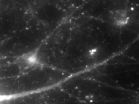
Fascinating rhythm: Light pulses illuminate a rare black hole
2014-08-17
The universe has so many black holes that it's impossible to count them all. There may be 100 million of these intriguing astral objects in our galaxy alone. Nearly all black holes fall into one of two classes: big, and colossal. Astronomers know that black holes ranging from about 10 times to 100 times the mass of our sun are the remnants of dying stars, and that supermassive black holes, more than a million times the mass of the sun, inhabit the centers of most galaxies.
But scattered across the universe like oases in a desert are a few apparent black holes of a more ...
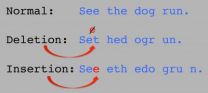
A shift in the code: New method reveals hidden genetic landscape
2014-08-17
Cold Spring Harbor, NY – With three billion letters in the human genome, it seems hard to believe that adding a DNA base here or removing a DNA base there could have much of an effect on our health. In fact, such insertions and deletions can dramatically alter biological function, leading to diseases from autism to cancer. Still, it is has been difficult to detect these mutations. Now, a team of scientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) has devised a new way to analyze genome sequences that pinpoints so-called insertion and deletion mutations (known as "indels") ...
New home for an 'evolutionary misfit'
2014-08-17
One of the most bizarre-looking fossils ever found - a worm-like creature with legs, spikes and a head difficult to distinguish from its tail – has found its place in the evolutionary Tree of Life, definitively linking it with a group of modern animals for the first time.
The animal, known as Hallucigenia due to its otherworldly appearance, had been considered an 'evolutionary misfit' as it was not clear how it related to modern animal groups. Researchers from the University of Cambridge have discovered an important link with modern velvet worms, also known as onychophorans, ...
Stem cells reveal how illness-linked genetic variation affects neurons
2014-08-17
VIDEO:
Human neurons firing
Click here for more information.
A genetic variation linked to schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and severe depression wreaks havoc on connections among neurons in the developing brain, a team of researchers reports. The study, led by Guo-li Ming, M.D., Ph.D., and Hongjun Song, Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and described online Aug. 17 in the journal Nature, used stem cells generated from people with and without mental illness ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] DNA methylation involved in Alzheimer's diseaseFirst large-scale study using EWAS to look at brain's chromosomal make-up in relation to Alzheimer's disease