Apple Orthodontix Orthodontist Kimberly J. McNeal, MS,DMD Wins Ormco Preferred Provider Award
2014-03-01
Kimberly J. McNeal, MS, DMD, who practices in the Rockwall, TX office of Apple Orthodontix, was recently honored by Ormco Corp., distributor and fabricator of the Insignia bracket system. 27 doctors and practices worldwide that treated more than 100 Insignia cases during 2013 were presented with Preferred Provider Awards earlier this year. Apple Orthodontix is one of the top five Insignia providers in the country.
"Insignia is world-class orthodontics at its best," says McNeal. "In my opinion, this bracket system reduces treatment time and addresses patient ...
Robin Ganzert Reflects on Dogs' Ability to Connect with Human Emotions
2014-03-01
There is a unique bond that exists between humans and animals and this is something that the American Humane Association (AHA), led by President and CEO Robin Ganzert, has sought to better understand. Just as animals need humans, humans need animals as well. Both play an integral role in the other's life and provide numerous benefits, both recognized and yet unknown.
As many dog owners will attest, it often seems as though their dog knows what they are thinking or feeling. They know just when they are needed and how to respond. While this is generally supported by anecdotal ...
Robin Ganzert Stands Behind Research Regarding Benefits of Animal-Assisted Therapy for Pediatric Cancer Patients
2014-03-01
In an effort to better understand the effects of animal-assisted therapy on pediatric cancer patients, the American Humane Association, led by Robin Ganzert, and Zoetis Inc. have teamed up to launch a first-of-its-kind clinical trial. The Canines and Childhood Cancer (CCC) Study will explore not only the impact that this type of therapy has on patients, but also on their families and the therapy dogs as well.
"Animal-assisted therapy is used throughout many different settings with great success," says Dr. Robin Ganzert. "Now we are seeking to learn more ...
Statement from Shri Smanto R Roy, Executive Director, Sahara India Pariwar at a Press Conference on 28th February
2014-03-01
Good Morning Everybody
On behalf of the Sahara India Pariwar, We welcome you all.
We are meeting at a time when our organization has been very wrongly interpreted and presented in public against the backdrop of the ongoing Sahara - Sebi case.
As the matter is Sub-judice, we cannot bring forward many things pertaining to the case but being an organization like Sahara India Pariwar with a base of more than crores and crores of investors and having kartvyayogis in tune of 12 lakh, we feel it is our moral right and duty to come forward and dispel some misconceptions ...
Cameron General Dentistry Office Bridges The Gap With Dental Bridges
2014-03-01
A gap in your teeth can feel like a canyon-huge and noticeable. Tooth loss usually occurs unexpectedly, especially if it's due to dental trauma. Unless root canal therapy can save the tooth, a tooth infection is also a reason a patient may need to get a tooth extracted.
"When it comes to tooth loss, no one feels like a winner. To boost a patient's confidence and oral health, dentists are able to replace a tooth with a prosthetic dental piece. Some popular restorative treatments include dentures and dental bridges," explains Dr. Wyckoff.
With one dental ...
Baltimore Dentist Gracefully Passes The Dental Gavel To Fellow Dentist
2014-03-01
What does it mean to be a member of the Baltimore City Dental Society? It's an indication that members are working together to create a better understanding of the new techniques and technology emerging in dentistry. In December 2013, Dr. Michael Murphy handed his presidential gavel to a fellow dentist and member of the Baltimore City Dental Society, Dr. Jerry Kilan.
"I am confident Dr. Jerry Kilan is a perfect fit as the President of the Baltimore City Dental Society. My time in this leadership role was a learning experience in many ways. As of now, I am continuing ...
Henderson, NV Dentist's Years Of Experience Makes It Easy To Place Dental Implants
2014-03-01
For tooth loss, you need a tooth replacement. This is an important step to prevent future dental problems, but it's a hard step to take if you don't know which restorative procedure is right, for you. This isn't a journey you will go on alone-your dentist will be there to help you find the way to a healthier, happier smile. In Henderson, dental implants are available at Moore Family Dentistry. What sets Dr. Moore apart from the rest? One word-experience.
"A dental implant procedure is a groundbreaking restorative treatment, and it's making big strides in the dental ...
Regina Foot Doctor Pairs Foot Treatments For Heel Pain
2014-03-01
Do you have heel pain? Is it weighing heavy on your normal routine? If not treated, foot issues can kick your butt (not literally). However, leaving it untreated can cause further damage or pain. At Regina Podiatry and Orthotic Clinic, Dr. R. Bagha utilizes two different modes of treatment to help patients kick heel pain to the curb. These two treatments are deep tissue laser therapy and orthotic insoles.
"Deep tissue laser therapy and orthotic insoles have proven to be most effective when paired together. Once heel pain is treated, we stress the importance of ...
West Covina Dentist Eases Patients Nerves With Nitrous Oxide
2014-03-01
Have you ever witnessed a parent playing tug-of-war with his/her child before going into a doctor's office? Could you relate to that anxiety? A little anxiety is normal, but you don't want it to deter you from going to the dentist office for annual checkups or treatment, especially when your oral health is at stake.
To help ensure a patient is relaxed, Gregory Robins Family Dentistry office in West Covina offers nitrous oxide for patients needing a little extra help relaxing in the dental chair.
"Many patients are nervous about going to the dentist, and the ...
Denver Tummy Tuck Specialist Launches New Website
2014-03-01
Known for his focus on body and breast cosmetic surgery procedures, Denver plastic surgeon Dr. Frank Campanile recently launched a new website devoted exclusively to tummy tuck surgery (http://www.denvertummy.com). The website provides procedure information, actual patient before and after photos, and stories from just a few of Dr. Campanile's many happy patients who had tummy tuck surgery.
"I have tailored my practice to focus only on procedures that enhance the appearance of the body and breasts," says Dr. Frank Campanile, who is board certified by the American ...
Improved screening means new targets for pediatric neuroblastoma therapies
2014-03-01
SAN ANTONIO – Neuroblastoma is one of the most common and lethal types of childhood cancers. In a paper published online today in OncoTarget, a researcher at the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio unveils the important role of microRNAs in regulating neuroblastoma development, pointing to new therapeutic possibilities.
Neuroblastomas, which account for 15 percent of childhood cancer deaths, happen when some cells do not differentiate and grow as they should. A promising type of therapy called differentiation therapy targets these malignant cells ...
It slices, it dices, and it protects the body from harm (Science)
2014-02-28
An essential weapon in the body's fight against infection has come into sharper view. Researchers at Princeton University have discovered the 3D structure of an enzyme that cuts to ribbons the genetic material of viruses and helps defend against bacteria.
The discovery of the structure of this enzyme, a first-responder in the body's "innate immune system," could enable new strategies for fighting infectious agents and possibly prostate cancer and obesity. The work was published Feb. 27 in the journal Science.
Until now, the research community has lacked a structural ...
Frequent childhood nightmares may indicate an increased risk of psychotic traits
2014-02-28
Children who suffer from frequent nightmares or bouts of night terrors may be at an increased risk of psychotic experiences in adolescence, according to new research from the University of Warwick.
The study, published today in the journal SLEEP, shows that children reporting frequent nightmares before the age of 12 were three and a half times more likely to suffer from psychotic experiences in early adolescence. Similarly, experiencing night terrors doubled the risk of such problems, including hallucinations, interrupted thoughts or delusions. Younger children, between ...
Study links poor sleep quality to reduced brain gray matter in Gulf War vets
2014-02-28
DARIEN, IL – A new study of Gulf War veterans found an association between poor sleep quality and reduced gray matter volume in the brain's frontal lobe, which helps control important processes such as working memory and executive function.
"Previous imaging studies have suggested that sleep disturbances may be associated with structural brain changes in certain regions of the frontal lobe," said lead author Linda Chao, associate adjunct professor in the Departments of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging and Psychiatry at the University of California, San Francisco. "The ...
Researchers identify brain differences linked to insomnia
2014-02-28
Johns Hopkins researchers report that people with chronic insomnia show more plasticity and activity than good sleepers in the part of the brain that controls movement.
"Insomnia is not a nighttime disorder," says study leader Rachel E. Salas, M.D., an assistant professor of neurology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. "It's a 24-hour brain condition, like a light switch that is always on. Our research adds information about differences in the brain associated with it."
Salas and her team, reporting in the March issue of the journal Sleep, found that ...
UCLA study finds robotic-assisted prostate surgery offers better cancer control
2014-02-28
An observational study from UCLA's Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center has found that prostate cancer patients who undergo robotic-assisted prostate surgery have fewer instances of cancer cells at the edge of their surgical specimen and less need for additional cancer treatments like hormone or radiation therapy than patients who have traditional "open" surgery.
The study, published online Feb. 19 in the journal European Urology, was led by Dr. Jim Hu, UCLA's Henry E. Singleton Professor of Urology and director of robotic and minimally invasive surgery in the urology ...
Let there be tissue-penetrating light: Scientists develop new nanoscale method to fight cancer
2014-02-28
Researchers from UCLA's Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center have developed an innovative cancer-fighting technique in which custom-designed nanoparticles carry chemotherapy drugs directly to tumor cells and release their cargo when triggered by a two-photon laser in the infrared red wavelength.
The research findings by UCLA's Jeffrey Zink, a professor of chemistry and biochemistry, and Fuyu Tamanoi, a professor of microbiology, immunology and molecular genetics, and their colleagues were published online Feb. 20 in the journal Small and will appear in a later print ...
Robert Avery, D.O., M.S.C.E., studies innovations to improve vision in children with tumors
2014-02-28
Robert Avery, DO, MSCE, of Children's National Health System and colleagues are establishing innovative approaches with technology and medication to improve the vision of young children who have visual pathway glioma, a type of brain tumor.
Most optic pathway gliomas cause vision loss in children between one and eight years of age. As many as 20 percent of children with neurofibromatosis type 1 -- a genetic disorder that occurs in 1 in every 4,000 births – may develop these tumors. It is estimated that nearly half of those children may experience vision problems from ...
Tackling tumors with space station research
2014-02-28
In space, things don't always behave the way we expect them to. In the case of cancer, researchers have found that this is a good thing: some tumors seem to be much less aggressive in the microgravity environment of space compared to their behavior on Earth. This observation, reported in research published in February by the FASEB Journal, could help scientists understand the mechanism involved and develop drugs targeting tumors that don't respond to current treatments. This work is the latest in a large body of evidence on how space exploration benefits those of us on ...
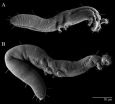
Worm-like mite species discovered on Ohio State's campus
2014-02-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – It looks like a worm and moves like a worm – sort of. But it is a previously unidentified microscopic species of mite that was discovered by a graduate student on The Ohio State University campus.
Affectionately dubbed the "Buckeye Dragon Mite" by Ohio State's Acarology Laboratory, the mite is officially named Osperalycus tenerphagus, Latin for "mouth purse" and "tender feeding," in a nod to its complex and highly unusual oral structure.
This mite doesn't resemble a mythological winged dragon, but the snake-like Chinese dancing dragons that appear in ...
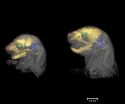
3-D imaging sheds light on Apert syndrome development
2014-02-28
Three dimensional imaging of two different mouse models of Apert Syndrome shows that cranial deformation begins before birth and continues, worsening with time, according to a team of researchers who studied mice to better understand and treat the disorder in humans.
Apert Syndrome is caused by mutations in FGFR2 -- fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 -- a gene, which usually produces a protein that functions in cell division, regulation of cell growth and maturation, formation of blood vessels, wound healing, and embryonic development. With certain mutations, this gene ...
GOES-West satellite eyes soggy storm approaching California
2014-02-28
A swirling Eastern Pacific Ocean storm system headed for California was spotted by NOAA's GOES-West satellite on February 28. According to the National Weather Service, this storm system has the potential to bring heavy rainfall to the drought-stricken state.
The storm was captured using visible data from NOAA's GOES-West or GOES-15 satellite on Feb. 28 at 1430 UTC/6:30 a.m. PST was made into an image by NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. The storm's center appeared as a tight swirl, with bands of clouds and showers already ...
NASA satellite sees great freeze over Great Lakes
2014-02-28
At night, as cold settles in, lake ice creaks and groans. It's been excessively cold, and I camped exposed on the snow-swept surface. Other than the lack of vegetation and the sounds at night, you'd never know you were on a lake. It feels like an empty plain. In some places, you see pressure ridges where ice has pushed into itself, sticking up like clear blue stegosaurus plates. -- Craig Childs
Author Craig Childs is not describing an Arctic lake. He's describing the bitterly cold and frozen scene on Lake Superior, during his February 2014 trek on the ice near the coast ...
Ultra-fast laser spectroscopy lights way to understanding new materials
2014-02-28
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory are revealing the mysteries of new materials using ultra-fast laser spectroscopy, similar to high-speed photography where many quick images reveal subtle movements and changes inside the materials. Seeing these dynamics is one emerging strategy to better understanding how new materials work, so that we can use them to enable new energy technologies.
Physicist Jigang Wang and his colleagues recently used ultra-fast laser spectroscopy to examine and explain the mysterious electronic properties of iron-based superconductors. ...
Detection of water vapor in the atmosphere of a hot jupiter
2014-02-28
Although liquid water covers a majority of Earth's surface, scientists are still searching for planets outside of our solar system that contain water. Researchers at Caltech and several other institutions have used a new technique to analyze the gaseous atmospheres of such extrasolar planets and have made the first detection of water in the atmosphere of the Jupiter-mass planet orbiting the nearby star tau Boötis. With further development and more sensitive instruments, this technique could help researchers learn about how many planets with water—like Earth—exist within ...
[1] ... [3922]
[3923]
[3924]
[3925]
[3926]
[3927]
[3928]
[3929]
3930
[3931]
[3932]
[3933]
[3934]
[3935]
[3936]
[3937]
[3938]
... [8812]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.