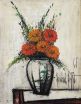Atlanta Bankruptcy Experts, Clark & Washington, Note Business Mogul William Fox's Financial Strife
2013-05-22
William Fox was a pioneer in the American film industry. Turning a once-bankrupt theater in Brooklyn into a successful venture, he later went into movie distribution and finally opened his own company (Fox Film Corporation) to make his own movies. One of the most powerful and influential men in the movie industry during his time, he was poised to take over Loews and the MGM studios when he lost his fortune in the stock market crash of 1929. He never recovered from this setback.
It can sometimes be difficult to imagine how someone who has enjoyed incredible success can ...
Accounting Firm's Clients Love New Cloud-Reporting Tool From Qvinci Software
2013-05-22
An accounting and bookkeeping firm has found an innovative way to leverage Qvinci Software's free version of Qvinci, called Solo, to streamline its operations and deliver value to clients.
The firm has become the channel through which clients receive current financial data quickly, easily, and on demand - and in a format they actually use to run their businesses better.
It's a double win, because Qvinci Solo has also enabled the firm to "recoup" a significant amount of monthly staff time by eliminating a cumbersome reporting process that the firm's owner ...
miEdge Appoints Darin S. Vick as Chief Sales Officer
2013-05-22
miEdge, business intelligence system for Insurance Professionals, today announced a key addition to its leadership team with the hiring of Darin S. Vick as Chief Sales Officer. With over 25 years of experience in the insurance industry, Mr. Vick will focus on continued growth of the miEdge system.
Mark J. Smith - ACIC, CIC, Founder and CEO of miEdge said, "Darin is a well-respected leader in the Insurance Technology space and brings a wealth of talent to miEdge. Darin will lead the miEdge sales team across the country and help miEdge maintain and grow its industry ...
Signalman Publishing Announces Release of "The Miracle Landing", True Story of the Minneapolis Lakers Crash Landing in Iowa
2013-05-22
Signalman Publishing is pleased to announce the release in paperback and as an ebook for the Amazon Kindle, the Barnes & Noble nook, and the Apple iBookstore of The Miracle Landing: The true story of how the NBA's Minneapolis Lakers almost perished in an Iowa cornfield during a January blizzard by Harold Gifford of Woodbury, Minnesota.
The Miracle Landing is about an incident that happened over fifty years ago - an incident that could have changed U.S. sports history. On the evening of January 17, 1960 after a game in St. Louis, the Minneapolis Lakers boarded their ...
Fresh to Market Rare and Important Art, French Objects and Furniture, Russian Silver, and Asian Items Featured at Clarke Auction on June 3rd at 5 P.M.
2013-05-22
On Monday, June 3rd at 5 pm, Clarke Auction will present what might be one of its best auctions to date. Gernerally, a press release highlights one or two rare and important items. Clarke's June 3rd auction offers rare and wonderful pieces in each and every category.
Leading off the art section is a freshly discovered large and important oil on canvas by German surrealist artist, Richard Oelze (est. $60,000 - 80,000). This magnificent painting is well supported by works from other artists including an oil still life by Bernard Buffet (pictured, est. $35,000 - $45,000), ...
MacARTHUR vs. University of Maryland
2013-05-22
The University of Maryland has been chasing the Sikorsky Prize for the last five years. The prize will be presented to the first team to build a human powered helicopter that can climb 10 feet and stay airborne for 60 seconds. The University of Maryland team, also known as Team Gamera, has come within a whisper on several recent attempts.
George MacARTHUR has launched a campaign to challenge the University of Maryland.
http://www.indiegogo.com/projects/godzilla-vs-gamera
www.godzillahovers.com
Contact: George MacARTHUR 705-878-9878 ...
Singapore Private Home Sales Drop Due to Cooling Measures in 1st Quarter 2013
2013-05-22
Amidst of all the decrease in revenue the construction industry is still optimistic and are continuously developing projects that will suits everyone. They are making sure that the development in their field will go pass the current hardships that the industry is experiencing.
Jones Lang La Salle was quoted for the drastic drop of the revenue in the classified home sales that is for the first quarter of 2013. The revenue plunge was forecasted already that once the cooling measure takes place the drop in returns will happen. This is due to the surplus from the previous ...
3D Model Marketplace CGTrader Looks For The Next 3D Printable Innovation
2013-05-22
"The next industrial revolution already has a name - 3D printing. 3D printing is affecting how products are created and consumed. In order to work, this technology needs professional-level 3D models, but there is a surprising gap between 3D printing industry and professional 3D designers. CGTrader aims to bridge this gap and help the 3D designer community take a plunge and start modeling for the exciting 3D printing technology. Professional 3D designers have the skills and creativity needed to bring the next big thing in 3D printing, and we aim to encourage them to ...
Vancouver, B.C. Pigeons Are Winning the War!
2013-05-22
Despite having installed more than 250,000 feet of bird spikes and a million feet of netting to keep pigeons off residential and commercial buildings in and around Vancouver, pigeon patrol expert Andrew MacBain from www.pigeonpatrol.ca says the pesky birds are winning the war.
"It's worse than ever," says the Surrey-based entrepreneur who has installed bird spikes and netting at BC Place, the BC Ferries terminals, BC Transit and other buildings throughout the Lower Mainland. "The pigeon population doubles every year."
The mushrooming pigeon population ...
UCSB study shows where scene context happens in our brain
2013-05-21
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– In a remote fishing community in Venezuela, a lone fisherman sits on a cliff overlooking the southern Caribbean Sea. This man –– the lookout –– is responsible for directing his comrades on the water, who are too close to their target to detect their next catch. Using abilities honed by years of scanning the water's surface, he can tell by shadows, ripples, and even the behavior of seabirds, where the fish are schooling, and what kind of fish they might be, without actually seeing the fish. This, in turn, changes where the boats go, and how the ...
WCS informs discussion of responses to a changing Arctic
2013-05-21
New York (May 20, 2013) – In two critical reports released at the Arctic Council Ministerial Meeting in Kiruna, Sweden on May 15th, the scientific expertise of the Wildlife Conservation Society helped inform an international body of senior government officials about changing conditions in the Arctic, and potential responses to those changes.
The scientific reports reviewed by the ministers are products of contributions from various experts, representing a range of knowledge and traditions—including indigenous perspectives.
The first report, entitled "Arctic Biodiversity ...
Abundance and distribution of Hawaiian coral species predicted by model
2013-05-21
Researchers from the University of Hawaii – Manoa (UHM) School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST) developed species distribution models of the six dominant Hawaiian coral species around the main Hawaiian Islands including two species currently under consideration as threatened or endangered. They found the order of coral abundance (from highest to lowest) around the main Hawaiian Islands to be Porites lobata, Montipora patula, Pocillopora meandrina, Montipora capitata, Porites compressa, and Montipora flabellata.
Environmental factors (wave energy, shape ...
Soft matter offers new ways to study how ordered materials arrange themselves
2013-05-21
A fried breakfast food popular in Spain provided the inspiration for the development of doughnut-shaped droplets that may provide scientists with a new approach for studying fundamental issues in physics, mathematics and materials.
The doughnut-shaped droplets, a shape known as toroidal, are formed from two dissimilar liquids using a simple rotating stage and an injection needle. About a millimeter in overall size, the droplets are produced individually, their shapes maintained by a surrounding springy material made of polymers. Droplets in this toroidal shape made of ...
Racial disparities in the surgical management of non-small cell lung cancer
2013-05-21
ATS 2013, PHILADELPHIA – The surgical management of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in U.S. hospitals varies widely depending on the race of the patient, according to a new study.
"In most patients, the initial treatment for Stage I and Stage II NSCLC is surgery," said researcher Jayanth Adusumalli, MBBS, of the Creighton University Medical Center in Omaha, Nebraska. "In our study of more than 1,200,000 patients diagnosed with NSCLC in US hospitals between the years 2000 and 2010, we found statistically significant racial disparities in the surgical management of these ...
Delayed transfer to the ICU increases risk of death in hospital patients
2013-05-21
ATS 2013, PHILADELPHIA ─ Delayed transfer to the intensive care unit (ICU) in hospitalized patients significantly increases the risk of dying in the hospital, according to a new study from researchers in Chicago.
"Early intervention improves outcomes for many of the conditions that are indications for inpatient transfer to the ICU. This suggests that delaying ICU transfer may increase the risk of death in these patients," said lead author Matthew Churpek, MD, MPH, of the University of Chicago Medical Center. "Using a vital sign-based early warning score, the Cardiac ...
Antibiotic therapy appears beneficial for patients with COPD
2013-05-21
ATS 2013, PHILADELPHIA ─ Extended use of a common antibiotic may prolong the time between hospitalizations for patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), according to a post-hoc analysis of a multicenter study which compared the hospitalization rates of patients treated with a 12-month course of azithromycin to the rates of those treated with placebo.
The results of the current analysis will be presented at the ATS 2013 International Conference.
"Preventing respiratory-related re-hospitalizations is a key component of COPD therapy, ...
Asthma symptoms impair sleep quality and school performance in children
2013-05-21
ATS 2013, PHILADELPHIA ─ The negative effects of poorly controlled asthma symptoms on sleep quality and academic performance in urban schoolchildren has been confirmed in a new study.
"While it has been recognized that missed sleep and school absences are important indicators of asthma morbidity in children, our study is the first to explore the associations between asthma, sleep quality, and academic performance in real time, prospectively, using both objective and subjective measures," said principal investigator Daphne Koinis-Mitchell, PhD, Associate Professor ...
Challenges encountered in surgical management of spine trauma in morbidly obese patients
2013-05-21
Charlottesville, VA (May 21, 2013). Physicians at Monash University and The Alfred Hospital in Melbourne, Australia describe the logistic, medical, and societal challenges faced in treating spine trauma in morbidly obese patients. Based on a case series of six patients injured in high-speed motor vehicle accidents, the authors categorize difficulties faced in the care of morbidly obese patients from on-scene immobilization and medical transport through spinal imaging, surgery, and postoperative care. Details of the six cases and a thorough discussion of challenges posed ...
Study shows COPD is associated with significant and persistent pain
2013-05-21
ATS 2013, PHILADELPHIA – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is primarily associated with the respiratory symptoms that are its hallmark, but in fact, patients who struggle with the disease also experience significant amounts of chronic pain. A new study conducted by researchers in Pennsylvania and New Mexico estimates the degree of pain suffered by these patients to be close to that experienced by patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
The research results will be presented at the ATS 2013 International Conference.
"Several studies have found ...
Inflammation is associated with depression in COPD patients
2013-05-21
ATS 2013, PHILADELPHIA ─ Depression is common in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and has been linked with disease severity and impaired quality of life. Now, for the first time, researchers at the University of Pittsburgh have linked the systemic inflammation associated with COPD with depression in these patients.
"Systemic inflammation is thought to be an important mediator of comorbidities in COPD, but the relationship between inflammation and depression has not been explored," said researcher Hilary Strollo, M.S., a graduate of the ...
Sexual function in older adults with thoracolumbar–pelvic instrumentation
2013-05-21
Charlottesville, VA (May 21, 2013). Surgeons investigated sexual function in 62 patients, 50 years and older, who had received extensive spinal–pelvic instrumentation for spinal deformity at the University of Virginia Health Center. Based on their results, the surgeons found that it is very possible for older people to achieve satisfactory sexual function despite having extensive spinal–pelvic instrumentation. Details of this study are disclosed in "Sexual function in older adults following thoracolumbar to pelvic instrumentation for spinal deformity. Clinical article," ...
Exercise levels may predict hospitalizations in COPD population
2013-05-21
ATS 2013, PHILADELPHIA ─ Clinical measurement of physical activity appears to be an independent predictor of whether or not patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) will end up being hospitalized, according to a new study conducted by researchers in Connecticut. The study also corroborates an earlier investigation that linked higher levels of inactivity with an increased incidence of hospitalizations among patients with COPD.
The results of the study will be presented at the ATS 2013 International Conference.
"Physical inactivity is common in ...
Monoclonal antibody appears effective and safe in asthma Phase IIa trial
2013-05-21
ATS 2013, PHILADELPHIA ─ A novel approach to obstructing the runaway inflammatory response implicated in some types of asthma has shown promise in a Phase IIa clinical trial, according to U. S. researchers.
Their research will be presented at the American Thoracic Society 2013 International Conference and published simultaneously online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial tested the efficacy and safety of the monoclonal antibody, dupilumab, in patients with "persistent, moderate-to-severe asthma" and elevated ...
Teens exposed to schoolmate's death by suicide much more likely to consider or attempt suicide
2013-05-21
Youth who had a schoolmate die by suicide are significantly more likely to consider or attempt suicide, according to a study in published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal). This effect can last 2 years or more, which has implications for strategies following schoolmate suicides.
"We found that exposure to suicide predicts suicidality," writes senior author Dr. Ian Colman, Canada Research Chair in Mental Health Epidemiology and Assistant Professor, University of Ottawa, with lead author Sonja Swanson, from Harvard School of Public Health, Boston. "This was ...
Treatment with A1-PI slows the progression of emphysema in Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
2013-05-21
ATS 2013, PHILADELPHIA─Treatment with an Alpha-1 proteinase inhibitor (A1-PI), a naturally occurring protein that protects lung tissue from breakdown and protects the lung's elasticity, is effective in slowing the progression of emphysema in patients with Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), a life-threatening genetic disorder, according to a new study presented at the 2013 American Thoracic Society International Conference.
The study showed the efficacy of A1-PIin preventing the loss of lung tissue as measured by computed tomography (CT) scan lung density at ...
[1] ... [4685]
[4686]
[4687]
[4688]
[4689]
[4690]
[4691]
[4692]
4693
[4694]
[4695]
[4696]
[4697]
[4698]
[4699]
[4700]
[4701]
... [8827]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.