Medical societies unite on patient-centered measures for nonsurgical stroke interventions
2013-01-29
FAIRFAX, Va.—The first outcome-based guidelines for interventional treatment of acute ischemic stroke—providing recommendations for rapid treatment—will benefit individuals suffering from brain attacks, often caused by artery-blocking blood clots. Representatives from the Society of Interventional Radiology and seven other medical societies created a multispecialty and international consensus on the metrics and benchmarks for processes of care and technical and clinical outcomes for stroke patients.
In February, the guidelines will be published first in SIR's Journal ...
New options for transparent contact electrodes
2013-01-29
This press release is available in German.
Found in flat screens, solar modules, or in new organic light-emitting diode (LED) displays, transparent electrodes have become ubiquitous. Typically, they consist of metal oxides like In2O3, SnO2, ZnO and TiO2.
But since raw materials like indium are becoming more and more costly, researchers have begun to look elsewhere for alternatives. A new review article by HZB scientist Dr. Klaus Ellmer, published in the renowned scientific journal Nature Photonics, is hoping to shed light on the different advantages and disadvantages ...
Epigenetic control of cardiogenesis
2013-01-29
This press release is available in German.
Many different tissues and organs form from pluripotent stem cells during embryonic development. To date it had been known that these processes are controlled by transcription factors for specific tissues. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics in Berlin, in collaboration with colleagues at MIT and the Broad Institute in Boston, have now been able to demonstrate that RNA molecules, which do not act as templates for protein synthesis, participate in these processes as well. The scientists knocked down ...
New insights into conquering influenza
2013-01-29
As influenza spreads through the northern hemisphere winter, Dr Linda Wakim and her colleagues in the Laboratory of Professor Jose Villadangos from the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, and the Department of Microbiology and Immunology, believe they have a new clue to why some people fight infections better than others.
The lab has been investigating the 'defensive devices' contained within the T- cells that are located on exposed body surfaces such as skin and mucosal surfaces to ward off infection. T-cells detect cells infected with viruses and kill ...
Survival of the prettiest: Sexual selection can be inferred from the fossil record
2013-01-29
Detecting sexual selection in the fossil record is not impossible, according to scientists writing in Trends in Ecology and Evolution this month, co-authored by Dr Darren Naish of the University of Southampton.
The term "sexual selection" refers to the evolutionary pressures that relate to a species' ability to repel rivals, meet mates and pass on genes. We can observe these processes happening in living animals but how do palaeontologists know that sexual selection operated in fossil ones?
Historically, palaeontologists have thought it challenging, even impossible, ...
New insights into managing our water resources
2013-01-29
Dr Tim Peterson, from the School of Engineering at the University of Melbourne has offered new theories that will lead to a deeper knowledge of how water catchments behave during wet and dry years. His research was published recently in the leading international hydrology journal "Water Resources Research" and was selected by the American Geophysical Union as a highlight of the society's 13 international journals.
Dr Peterson's work shows that some catchments have a finite resilience to wet and dry years because they have two steady states. The traditionally held view ...
Study reveals 2-fold higher incidence of non-melanoma skin cancers for HIV patients
2013-01-29
OAKLAND, Calif., January 29 — HIV-positive patients have a higher incidence of non-melanoma skin cancers, according to a Kaiser Permanente study that appears in the current online issue of the Journal of the National Cancer Institute. Specifically, basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas occur more than twice as often among HIV-positive individuals compared to those who are HIV-negative.
The study cohort of 6,560 HIV-positive and almost 37,000 HIV-negative subjects was drawn from members of Kaiser Permanente Northern California from 1996 to 2008.
Overall, HIV-positive ...
Indoor air puts Chinese women nonsmokers at risk
2013-01-29
BUFFALO, N.Y. – The hazards of breathing outdoor air in some Chinese cities have been well-documented. Now a University at Buffalo study confirms that breathing indoor air also carries significant cancer risks, especially for Chinese women.
The UB study, published online this month, in the journal Cancer Causes & Control, found that indoor air pollution that generates fine particulate matter is a key contributor to the high rates of lung cancer among Chinese women, despite the fact that few of them smoke.
The research found indoor particulate matter levels that are ...
Researchers generate a mutant mouse model useful in the treatment of neuromuscular diseases
2013-01-29
In three to six months of life, this genetic alteration in mice –similar to that occurred in human– causes a rapid degeneration in the lower limbs to death for cardiac arrest.
For the first time in the world, researchers at the Center for Biomedical Research of the University of Granada have created mice with a genetic mutation inducing a deficiency in the coenzyme Q10, a rare mitochondrial disease prevailingly affecting children. These mutant mice –which lack the Coq9 gene– will be "a valuable tool for the study and treatment of metabolic encephalopathies and neuromuscular ...
Center-based child care: Long hours do not cause aggression and disobedience
2013-01-29
Spending many hours in centre-based child care does not lead to more aggression and disobedience in children, according to a new study using data from the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study (MoBa).
Data from 72,000 mothers and their children, including siblings, were obtained from MoBa. Using questionnaires, mothers were asked about aggression and obedience at both 18 and 36 months and the amount of time their children spent in child care. In addition to comparing children from different families, the researchers compared siblings who had different amounts of child ...
Satellite visualization tool for high-res observation accessible from anywhere with internet access
2013-01-29
Amsterdam, January 29, 2013 – A paper published in the February issue of Computers & Geosciences, describes a case study in which an earth-observing satellite tool, the Tool for High-Resolution Observation Review (THOR), using minimal coding effort, is converted into a practical web-based application, THOR-Online. In addition, a 3D visualization technique is also described in this paper.
Initially only operable from a desktop computer, with the approach outlined in the study, THOR is now accessible online from NASA's Precipitation Processing System website. This allows ...
Simulations' Achille's heel
2013-01-29
In an article about to be published in EPJ Plus, Daan Frenkel from the University of Cambridge, UK, outlines the many pitfalls associated with simulation methods such as Monte Carlo algorithms or other commonly used molecular dynamics approaches.
The context of this paper is the exponential development of computing power in the past 60 years, estimated to have increased by a factor of 1015, in line with Moore's law. Today, short simulations can reproduce a system the size of a bacterium.
The author outlines diverse examples of issues arising when seemingly simple simulation ...
Scientists create 1-step gene test for mitochondrial diseases
2013-01-29
More powerful gene-sequencing tools have increasingly been uncovering disease secrets in DNA within the cell nucleus. Now a research team is expanding those rapid next-generation sequencing tests to analyze a separate source of DNA—within the genes inside mitochondria, cellular power plants that, when abnormal, contribute to complex, multisystem diseases.
The study team, headed by a specialist in mitochondrial medicine at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP), adapted next-generation sequencing to simultaneously analyze the whole exome (all the protein-coding ...
Dendritic cell vaccine for relapsed neuroblastoma patient induces complete remission
2013-01-29
One year after his last treatment, a six-year-old boy with recurrent neuroblastoma is in complete remission for his high-risk metastatic cancer. Doctors reported this case study in the January 2013 issue of Pediatrics, the journal of the American Academy of Pediatrics, which was funded in part by a joint grant from the Andrew McDonough B+ Foundation, Pierce Phillips Charity and Solving Kids' Cancer.
Current treatments for high-risk neuroblastoma patients include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, stem cell transplant, and immunotherapy. Less than half of the children ...
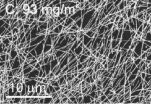
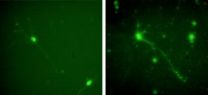
Researchers find a better way to culture central nervous cells
2013-01-29
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A protein associated with neuron damage in people with Alzheimer's disease is surprisingly useful in promoting neuron growth in the lab, according to a new study by engineering researchers at Brown University. The findings, in press at the journal Biomaterials, suggest a better method of growing neurons outside the body that might then be implanted to treat people with neurodegenerative diseases.
The research compared the effects of two proteins that can be used as an artificial scaffold for growing neurons (nerve cells) from the ...
BUSM study highlights attitudes toward HPV vaccination for boys
2013-01-29
(Boston)- A new Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) study has found that low-income and minority parents/guardians were receptive toward vaccinating boys against Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). However, racial/ethnic differences emerged in attitudes regarding school-entry mandates. The findings appear online in the journal Clinical Pediatrics.
Although low-income and minority men have higher rates of oral HPV infection and are more likely to suffer from HPV-related diseases including penile, anal and oral cancers, few studies have examined parental attitudes after ...
Ants' behavior leads to research method for optimizing product development time, costs
2013-01-29
DETROIT – Trying to find just the right balance of time spent in meetings and time performing tasks is a tough problem for managers, but a Wayne State University researcher believes the behavior of ants may provide a useful lesson on how to do it.
Using computer simulations derived from the characteristics of ants seeking food, Kai Yang, Ph.D., professor of industrial and systems engineering in the College of Engineering, has developed a mathematical model-based methodology to estimate the optimal amount of time spent to develop a product, as well as the cost, in overlapped ...
Holocaust Edition: 'The Sources Speak'
2013-01-29
This press release is available in German.
A collection of historical documents from a major project funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) will be made publicly available over the next several months and years. On 25 January 2013, German radio broadcaster Bayerischer Rundfunk will launch a 'documentary audio edition' entitled Die Quellen sprechen ('The Sources Speak'). The series of 16 episodes, to be broadcast on radio and made available online, will present hundreds of letters, diary entries, decrees, orders, newspaper reports ...
Personalized plans to address barriers to HIV drug adherence boost chances of successful therapy
2013-01-29
PHILADELPHIA – HIV patients who participated in an intervention that helped them identify barriers to taking their drugs properly and develop customized coping strategies took a significantly greater amount of their prescribed doses than those receiving standard care, according to a new study from researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The results, published this week in JAMA Internal Medicine, may point to a new strategy to improve adherence to medications for many other conditions.
"Nonadherence to medical therapy is a silent ...
Cultural evolution changes bird song
2013-01-29
Thanks to cultural evolution, male Savannah sparrows are changing their tune, partly to attract "the ladies."
According to a study of more than 30 years of Savannah sparrows recordings, the birds are singing distinctly different songs today than their ancestors did 30 years ago – changes passed along generation to generation, according to a new study by University of Guelph researchers.
Integrative biology professors Ryan Norris and Amy Newman, in collaboration with researchers at Bowdoin College and Williams College in the U.S., analyzed the songs of male Savannah ...
'Moral realism' may lead to better moral behavior
2013-01-29
CHESTNUT HILL, Mass. — Getting people to think about morality as a matter of objective facts rather than subjective preferences may lead to improved moral behavior, Boston College researchers report in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology.
In two experiments, one conducted in-person and the other online, participants were primed to consider a belief in either moral realism (the notion that morals are like facts) or moral antirealism (the belief that morals reflect people's preferences) during a solicitation for a charitable donation. In both experiments, those ...
New American Chemical Society podcast: Boosting the sensitivity of airport security screening
2013-01-29
The latest episode in the American Chemical Society's (ACS') award-winning Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions podcast series reports a simple way to improve the sensitivity of the test often used to detect traces of explosives on the hands, carry-ons and other possessions of passengers at airport security screening stations.
Based on a report by Yehuda Zeiri, Ph.D., and colleagues in ACS' The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, the new podcast is available without charge at iTunes and from www.acs.org/globalchallenges.
In the new episode, Zeiri explains that most ...
NSF-funded team samples Antarctic lake beneath the ice sheet
2013-01-29
In a first-of-its-kind feat of science and engineering, a National Science Foundation (NSF)-funded research team has successfully drilled through 800 meters (2,600 feet) of Antarctic ice to reach a subglacial lake and retrieve water and sediment samples that have been isolated from direct contact with the atmosphere for many thousands of years.
Scientists and drillers with the interdisciplinary Whillans Ice Stream Subglacial Access Research Drilling project (WISSARD) announced Jan. 28 local time (U.S. stations in Antarctica keep New Zealand time) that they had used a ...
Fossilized conduits suggest water flowed beneath Martian Surface
2013-01-29
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Networks of narrow ridges found in impact craters on Mars appear to be the fossilized remnants of underground cracks through which water once flowed, according to a new analysis by researchers from Brown University.
The study, in press in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, bolsters the idea that the subsurface environment on Mars once had an active hydrology and could be a good place to search for evidence of past life. The research was conducted by Lee Saper, a recent Brown graduate, with Jack Mustard, professor of geological ...
Researchers find gene that turns up effect of chemotherapy
2013-01-29
Chemotherapy is one of the most common treatments for cancer patients. However, many patients suffer from serious side-effects and a large proportion does not respond to the treatment. Researchers from the Biotech Research and Innovation Centre (BRIC) and Center for Healthy Aging, University of Copenhagen, now show that the gene FBH1 helps turn up the effect of chemotherapy.
"Our results show that the gene FBH1 is crucial in order for some chemotherapeutics to become active in the body and kill the cancer cells. If we can find a feasible method to increase the activity ...
[1] ... [5297]
[5298]
[5299]
[5300]
[5301]
[5302]
[5303]
[5304]
5305
[5306]
[5307]
[5308]
[5309]
[5310]
[5311]
[5312]
[5313]
... [8826]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.