Treatments to reduce anesthesia-induced injury in children show promise in animal studies
2012-03-29
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – March 28, 2012 – Recent clinical studies have shown that general anesthesia can be harmful to infants, presenting a dilemma for both doctors and parents. But new research at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center may point the way to treatment options that protect very young children against the adverse effects of anesthesia.
As detailed in a study published in the March 23 online edition of the journal Neuroscience, Wake Forest Baptist scientists explored a number of strategies designed to prevent anesthesia-induced damage to the brain in infants.
Using ...
NJIT mathematician publishes 2012 Major League Baseball projections
2012-03-29
The Philadelphia Phillies, St. Louis Cardinals and Arizona Diamondbacks should win their divisions, while the Atlanta Braves and the Cincinnati Reds will make it to Major League Baseball's post-season as wild card teams in the National League (NL) in 2012, according to NJIT's baseball guru Bruce Bukiet. The San Francisco Giants, Milwaukee Brewers and Florida Marlins could be close on the heels of the Reds and Braves but should miss out on the post-season by 3 or 4 wins. For more than a decade, Bukiet, an associate professor and associate dean, has applied mathematical ...
Give Earth A Break!
2012-03-29
Environmental issues like global warming, climate changes and climate-linked disasters are threats to human beings. They affect access to food, water and housing and they also affect our health and well-being.
The occurrence and severity of extreme weather such as heavy rainfall, floods, storms and hurricanes have risen in recent years. They affect millions of people around the globe and cause damages amounting to billions of dollars.
Immediate action is needed to deal with climate-linked and natural disasters. To bring about changes require coordination and cooperation ...
Researchers: Myeloid malignancies underreported in US
2012-03-29
TAMPA, Fla. (March 28, 2012) – Researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla., and colleagues from the UF Shands Cancer Center in Gainesville, Fla., have found that cases of myeloid malignancies are being underreported since a change in registry protocols and laboratory practices starting in 2001.
Their study is published in a recent issue of Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers and Prevention, a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"Since the 1970s, cancer registries have monitored myeloid leukemia incidence in the United States," said study ...
With you in the room, bacteria counts spike
2012-03-29
New Haven, Conn. — A person's mere presence in a room can add 37 million bacteria to the air every hour — material largely left behind by previous occupants and stirred up from the floor — according to new research by Yale University engineers.
"We live in this microbial soup, and a big ingredient is our own microorganisms," said Jordan Peccia, associate professor of environmental engineering at Yale and the principal investigator of a study recently published online in the journal Indoor Air. "Mostly people are re-suspending what's been deposited before. The floor dust ...
Study unravels health impact, interplay of diet soft drinks and overall diet
2012-03-29
Are diet sodas good or bad for you? The jury is still out, but a new study sheds light on the impact that zero-calorie beverages may have on health, especially in the context of a person's overall dietary habits.
For the average person, the scientific evidence can seem confusing. A number of studies have implicated diet beverage consumption as a cause of cardiovascular disease. However, others have suggested such drinks may be a viable tactic for people who are trying to lose or control their weight.
Either way, most previous research has tended to focus either on ...
Gladstone Scientists identify key mechanism involved in Type 2 diabetes
2012-03-29
Scientists at the Gladstone Institutes have discovered a key protein that regulates insulin resistance—the diminished ability of cells to respond to the action of insulin and which sets the stage for the development of the most common form of diabetes. This breakthrough points to a new way to potentially treat or forestall type 2 diabetes, a rapidly growing global health problem.
In a paper being published online this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers in the laboratory of Gladstone Investigator Katerina Akassoglou, PhD, describe ...
Study: Conservatives' trust in science has fallen dramatically since mid-1970s
2012-03-29
WASHINGTON, DC, March 26, 2012 — While trust in science remained stable among people who self-identified as moderates and liberals in the United States between 1974 and 2010, trust in science fell among self-identified conservatives by more than 25 percent during the same period, according to new research from Gordon Gauchat, a postdoctoral fellow at the University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill's Cecil G. Sheps Center for Health Services Research.
"You can see this distrust in science among conservatives reflected in the current Republican primary campaign," said Gauchat, ...
Emergency dispatchers suffer from symptoms of PTSD, study reveals
2012-03-29
Dispatchers who answer 911 and 999 emergency calls suffer emotional distress which can lead to symptoms of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), a new study reports. The research, published in the Journal of Traumatic Stress, reveals that direct exposure to traumatic events is not necessary to lead to post-trauma disorders.
The research was conducted by Dr Michelle Lilly from Northern Illinois University and researcher Heather Pierce, a former 911 dispatcher.
"Post-Traumatic psychological disorders are usually associated with front line emergency workers, such as police ...
Scientists clone 'survivor' elm trees
2012-03-29
Scientists at the University of Guelph have found a way to successfully clone American elm trees that have survived repeated epidemics of their biggest killer — Dutch elm disease.
The breakthrough, published today in the Canadian Journal of Forest Research, is the first known use of in vitro culture technology to clone buds of mature American elm trees.
"This research has the potential to bring back the beloved American elm population to North America," said Prof. Praveen Saxena, a plant scientist who worked on the project with Professor Alan Sullivan. Both are from ...
Genetic regulators hijacked by avian and swine flu viruses identified: UBC study
2012-03-29
Researchers at the University of British Columbia have identified a number of tiny but powerful "genetic regulators" that are hijacked by avian and swine flu viruses during human infection.
The discovery, published this week in the Journal of Virology, could reveal new targets for broad-spectrum antivirals to combat current – and perhaps future – strains of influenza A viruses.
The study is the first to compare the role played by human microRNAs – small molecules that control the expression of multiple genes – in the life cycle of two viruses of continued concern to ...
Ernst & Partners Offer Free Case Review for Individuals Injured in Atlanta Area Pedestrian Accidents
2012-03-29
The Atlanta accident attorneys at Ernst and Partners are pleased to announce a no cost legal case review service to victims or families of victims injured or killed in pedestrian accidents throughout the Atlanta, GA metro area.
"Pedestrian accidents have become a real concern in the Atlanta metro area. When a pedestrian is struck by an automobile, the outcome is often catastrophic. Most pedestrian accidents result in serious injury or death. Although Georgia has strict pedestrian laws, accidents continue to happen daily, often due to the negligence of distracted ...
Win a GBP1,500 Room Restyle With Next's Room Style Update Competition
2012-03-29
British lifestyle brand Next have launched a Room Style Update competition on Facebook, where one lucky winner can win a GBP1,500 room restyle and design consultation. Next promise to help you style the room of your dreams with items from their huge range of beautifully designed homeware from next.co.uk, up to the value of GBP1,500. From stunning bedroom furniture to stylish sofas, simply visit facebook.com/nextonline and submit up to five URL links of lounge, bedroom furniture and corresponding home accessories you would love to win and why.
Does your bedroom or living ...
E Cigarettes National Announces Their Best Sale Yet
2012-03-29
E Cigarettes National is one of the top e cigarette retailers in the United States and March 28th through March 30th, as advertised on their blog, they're offering 2 Firelight e cigarette starter kits for $65. At a normal price of $49.95 per kit, this is an astounding price break for anyone who's looking to make the switch from smoking regular cigarettes over to their "e" counterpart.
The kit comes with 2 batteries, 2 atomizers, 10 refill cartridges, usb cord, a home charger, and car charger. Most other, more expensive kits only come with one of these charging ...
Study by NOAA and partners shows some Gulf dolphins severely ill
2012-03-27
Bottlenose dolphins in Barataria Bay, Louisiana, are showing signs of severe ill health, according to NOAA marine mammal biologists and their local, state, federal and other research partners.
Barataria Bay, located in the northern Gulf of Mexico, received heavy and prolonged exposure to oil during the Deepwater Horizon oil spill.
Based on comprehensive physicals of 32 live dolphins from Barataria Bay in the summer of 2011, preliminary results show that many of the dolphins in the study are underweight, anemic, have low blood sugar and/or some symptoms of liver and ...
Slime mold mimics Canadian highway network
2012-03-27
Queen's University professor Selim Akl has provided additional proof to the theory that nature computes.
Dr. Akl (School of Computing) placed rolled oats on a map of Canada, covering the major urban areas. One urban area held the slime mold. The slime mold reached out for the food, creating thin tubes that eventually formed a network mirroring the Canadian highway system.
"By showing species as low as slime mold can compute a network as complex as the Canadian highway system, we were able to provide some evidence that nature computes," says Dr. Akl.
Moving forward, Dr. ...
Stem cell study aids quest for motor neurone disease therapies
2012-03-27
A breakthrough using cutting-edge stem cell research could speed up the discovery of new treatments for motor neurone disease (MND).
The international research team has created motor neurones using skin cells from a patient with an inherited form of MND.
The study discovered that abnormalities of a protein called TDP-43, implicated in more than 90 per cent of cases of MND, resulted in the death of motor neurone cells.
This is the first time that scientists have been able to see the direct effect of abnormal TDP-43 on human motor neurons.
The study, led by the ...
US economic woes ripple all the way to Latin America, U-M study shows
2012-03-27
The national recession didn't just hit people living in the U.S. – it's made it more difficult for people to pay for medical bills in poor countries like Honduras, according to a new University of Michigan study.
As employment opportunities have dried up for Latino immigrants in the U.S., so has their ability to send financial assistance to chronically ill family members in their home countries, according to a U-M study published online this week ahead of print in the International Journal of Health Services.
"Remittance payments from relatives living in the United ...
New analysis of premature infants' heartbeats, breathing could be cues for leaving NICU
2012-03-27
Bethesda, Md. -- Late gestation is a busy time for babies getting ready for life outside the womb, particularly for functions critical to life such as breathing and maintaining an adequate heartbeat. These two functions are connected in mature infants and healthy people throughout life, so measuring their level of connectedness can give doctors a cue about whether an infant is ready to head home or needs to remain in the care of the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). Current methods to analyze this connection are not yet fully developed, leaving doctors and nurses without ...
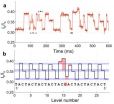
Tiny reader makes fast, cheap DNA sequencing feasible
2012-03-27
Researchers have devised a nanoscale sensor to electronically read the sequence of a single DNA molecule, a technique that is fast and inexpensive and could make DNA sequencing widely available.
The technique could lead to affordable personalized medicine, potentially revealing predispositions for afflictions such as cancer, diabetes or addiction.
"There is a clear path to a workable, easily produced sequencing platform," said Jens Gundlach, a University of Washington physics professor who leads the research team. "We augmented a protein nanopore we developed for ...
Wind energy enhancement: UC research establishes real-world wind turbine performance metrics
2012-03-27
VIDEO:
This shows a simulation of wind turbine performance.
Click here for more information.
The production of wind-derived renewable energy is growing, and so, it's important to help wind farm owners operate at higher efficiencies with lower costs.
In fact, figures from the World Wind Energy Association report that installed global capacity for wind-energy production was approximately 240,000 megawatts of power in 2011, up nearly ten fold since 2001.
That growth, which ...
Geologists correct a rift in Africa
2012-03-27
EAST LANSING, Mich. — The huge changes in the Earth's crust that influenced human evolution are being redefined, according to research published today in Nature Geoscience.
The Great Rift Valley of East Africa – the birthplace of the human species – may have taken much longer to develop than previously believed.
""We now believe that the western portion of the rift formed about 25 million years ago, and is approximately as old as the eastern part, instead of much younger as other studies have maintained," said Michael Gottfried, Michigan State University associate professor ...
A 24-karat gold key to unlock the immune system
2012-03-27
Developing a drug or vaccine requires a delicate balancing act with the immune system. On one hand, medications need to escape detection by the immune system in order to perform their function. But vaccinations — de-activated versions of a disease or virus — need to do the reverse. They prompt the immune system to create protective antibodies. But scientists are still stumped by how the immune system recognizes different particles, and how it chooses whether or not to react against them.
Using nanoparticles made of pure gold, Dr. Dan Peer, head of Tel Aviv University's ...
Progress toward new chemotherapy agents
2012-03-27
Advances in chemotherapy have dramatically improved the outlook for many cancer patients, but the side effects of this treatment are daunting. A new generation of chemotherapy drugs with fewer side effects is the goal of Edward J. Merino, assistant professor of chemistry at the University of Cincinnati.
Merino will discuss his efforts toward designing these new anticancer agents Tuesday, March 27, at The Chemistry of Life: Spring National Meeting and Exposition of the American Chemical Society in San Diego.
At that meeting, Merino will show a new anticancer agent ...
Mommy Esquire, Committee of the OC Bar Association, Supporting Working Parent Lawyers
2012-03-27
Newport Beach estate planning attorney and mom, Darlynn Morgan, along with her colleagues and the OCBA President, has recently spearheaded the formation of Mommy Esquire, a committee of the Orange County Bar Association. Women lawyers nationwide seek to achieve that ever-elusive balance of legal work and family life. Hence, in January 2012, Mommy Esquire was formed—the first OCBA committee that focuses specifically on practicing lawyers with school-age children. Estate planning lawyer, Darlynn Morgan, of Morgan Law Group, will serve as Chair of the newly formed committee.
"Mommy ...
[1] ... [6637]
[6638]
[6639]
[6640]
[6641]
[6642]
[6643]
[6644]
6645
[6646]
[6647]
[6648]
[6649]
[6650]
[6651]
[6652]
[6653]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.