Scientists engineer mosquito immune system to fight Malaria
2011-12-23
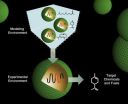
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Malaria Research Institute have demonstrated that the Anopheles mosquito's innate immune system could be genetically engineered to block the transmission of malaria-causing parasites to humans. In addition, they showed that the genetic modification had limited impact on the mosquito's fitness under laboratory conditions. The researchers' findings are published December 22nd in the Open Access journal PLoS Pathogens.
In this study, Dimopoulos and his team genetically engineered Anopheles mosquitoes to produce higher than normal levels ...
Double trouble: Concomitant immune challenges result in CNS disease
2011-12-23
A research team led by Glenn Rall at the Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia, PA developed a novel mouse model to show that a fatal central nervous system (CNS) disease can be caused by a pathogen that does not replicate in the CNS. The results of this new study are published December 22nd in the Open Access journal PLoS Pathogens.
The authors found that the immune response induced in response to a peripheral viral infection can be "mis-recruited" to the brain, where these activated immune cells can then lead to inflammation-induced neuropathology and disease. While ...
CAD for RNA
2011-12-23
The computer assisted design (CAD) tools that made it possible to fabricate integrated circuits with millions of transistors may soon be coming to the biological sciences. Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI) have developed CAD-type models and simulations for RNA molecules that make it possible to engineer biological components or "RNA devices" for controlling genetic expression in microbes. This holds enormous potential for microbial-based sustainable production of advanced biofuels, biodegradable plastics, therapeutic ...
For every road there is a tire
2011-12-23
KANSAS CITY, MO -- Life is complicated enough, so you can forgive the pioneers of DNA biology for glossing over transcriptional elongation control by RNA polymerase II, the quick and seemingly bulletproof penultimate step in the process that copies the information encoded in our DNA into protein-making instructions carried by messenger RNA.
In a new report appearing in the Dec. 23, 2011, issue of Molecular Cell, researchers at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research add not just a new layer, but a whole new dimension to transcriptional elongation control with evidence ...
Facebook Marketing Strategist Shows Chiropractors How to Get Endless New Patient Referrals from Social Media
2011-12-23
Chiropractic Internet marketing strategist and social media expert, Dr. Matthew Loop, has announced he'll continue to show DCs how to create an overwhelming presence on Facebook, which can easily net doctors an extra 20-30 new patients per month just from the social network. Dr. Loop's been helping fellow chiropractors master social media marketing since 2005-2006, which gives him an experience-based edge over other industry consultants.
He's garnered a well deserved reputation as the "go-to" guy for chiropractors that want to dramatically improve their new ...
Gene fusion in lung cancer afflicting never-smokers may be target for therapy
2011-12-23
December 22, 2011 – Smoking is a well-known risk factor for lung cancer, but nearly 25% of all lung cancer patients have never smoked. In a study published online today in Genome Research (www.genome.org), researchers have identified a previously unknown gene fusion event that could explain a significant proportion of lung cancer cases in never-smokers, and might serve as a target for new therapies.
Recent strides have been made to identify gene mutation events driving cases of lung adenocarcinoma in never-smokers, but the underlying genetic events leading to these lung ...
DNA mismatch repair happens only during a brief window of opportunity
2011-12-23
In eukaryotes – the group of organisms that include humans – a key to survival is the ability of certain proteins to quickly and accurately repair genetic errors that occur when DNA is replicated to make new cells.
In a paper published in the December 23, 2011 issue of the journal Science, researchers at the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research and the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have solved part of the mystery of how these proteins do their job, a process called DNA mismatch repair (MMR).
"One of the major questions in MMR is how MMR proteins ...
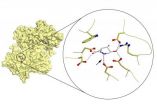
Biochemists develop promising new treatment direction for rare metabolic diseases
2011-12-23
AMHERST, Mass. – A research team led by biochemist Scott Garman at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has discovered a key interaction at the heart of a promising new treatment for a rare childhood metabolic disorder known as Fabry disease. The discovery will help understanding of other protein-folding disorders such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Huntington's diseases, as well. Findings are featured as the cover story in the current issue of Chemistry & Biology.
People born with Fabry disease have a faulty copy of a single gene that codes for the alpha-galactosidase ...
UT-ORNL research reveals aquatic bacteria more recent move to land
2011-12-23
Research by University of Tennessee, Knoxville, faculty has discovered that bacteria's move from sea to land may have occurred much later than thought. It also has revealed that the bacteria may be especially useful in bioenergy research.
Igor Jouline, UT-Oak Ridge National Laboratory joint faculty professor of microbiology and researcher at ORNL's Joint Institute for Computational Sciences, performed a genome sequence analysis of the soil bacteria Azospirillum, a species' whose forbearers made the sea-to-land move. The analysis indicates the shift may have occurred ...
Long intervening non-coding RNAs play pivotal roles in brain development
2011-12-23
FINDINGS: Whitehead Institute scientists have identified conserved, long intervening non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) that play key roles during brain development in zebrafish, and went on to show that the human versions of these RNAs can substitute for the zebrafish lincRNAs.
RELEVANCE: Despite their prevalence in the cell, lincRNAs have been referred to as the "dark matter" of all the transcribed RNAs because little is known of their functions or mechanisms. Until now, lincRNAs have been studied primarily in cell lines rather than at the organismal level, which has precluded ...
Unnatural disasters
2011-12-23
Global wildlife is facing an unprecedented threat from natural disasters exacerbated by climate change, warn scientists in a paper published in Trends in Ecology and Evolution.
Hurricanes, droughts, flooding and wildfires are predicted to increase in frequency and severity – but despite being able to spot human populations at risk, there is currently no mechanism for identifying vulnerable animal populations.
Now scientists from the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) have come up with a method to identify populations likely to experience drastic changes in their population ...
NIH researchers uncover clues related to metal-on-metal hip implants
2011-12-23
A new study, bringing together an interdisciplinary team of physicians and engineers from the United States and Germany, made a surprising finding about implants used in hip replacement surgery: Graphite carbon is a key element in the lubricating layer that forms on metal-on-metal hip implants. The lubricant has more in common with the lubrication of a combustion engine than that of a natural joint. The study was funded by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS), part of the National Institutes of Health.
Made possible by an ...
Carlsbad Mayor, CDOD: Positive News About WIPP 2012 Budget
2011-12-23
Members of New Mexico's congressional delegation have shown their strong support of the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant's safety record and operational success by fighting to keep the Department of Energy facility sufficiently funded.
The Waste Isolation Pilot Plant, or WIPP, is the Department of Energy's underground repository for defense-generated, transuranic (TRU) waste. Since WIPP opened in 1999, more than 10,000 shipments of TRU waste have been permanently disposed of in salt beds 2,150 feet below the surface. WIPP is located about 26 miles outside of Carlsbad, New ...
'Nanoantennas' show promise in optical innovations
2011-12-23
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Researchers have shown how arrays of tiny "plasmonic nanoantennas" are able to precisely manipulate light in new ways that could make possible a range of optical innovations such as more powerful microscopes, telecommunications and computers.
The researchers at Purdue University used the nanoantennas to abruptly change a property of light called its phase. Light is transmitted as waves analogous to waves of water, which have high and low points. The phase defines these high and low points of light.
"By abruptly changing the phase we ...
New Dabota Chairs and Skidmore Chairs From Rattanland
2011-12-23
RattanLand, a Company specializing in the import and export of home furniture, has new products to offer to its customers worldwide - Dabota Chairs and Skidmore Chairs.
New Skidmore and Dabota Chairs
The Company is proud to announce two new products that have been added to its already impressive product range - Skid and Dabota chairs.
Skidmore chairs are classic looking chairs that come with a simple design. There are no armrests, and the chairs sit on four legs each. These chairs are ideal for the outdoor garden or porch.
Dabota chairs also come in a simple ...
Blood progenitor cells receive signals from niche cells and the daughter blood cells they create
2011-12-23
Maintaining balance is crucial. In Drosophila, the common fruit fly, the creation and maintenance of the blood supply requires such balance.
UCLA stem cell scientists have now uncovered that two-way signaling from two different sets of cells is necessary for that balance, both to ensure enough blood cells are made to respond to injury and infection and that the blood progenitor cell population remains available for future needs.
The stem cell-like blood progenitor cells – which contribute to the cells of the adult fruit fly's blood supply – receive signals from cells ...
Defending the genome
2011-12-23
WORCESTER, Mass. – Small, mobile sequences of DNA left over from viruses, called transposons or "jumping genes" because of their ability to move around the genome, pose a significant threat to the genetic integrity and stability of an organism. Considered genetic parasites, these transposable elements are believed to comprise as much as 50 percent of the human genome. Because of the damage transposons can do to an organism's DNA, an immune-like response has evolved to turn off, or silence, these mobile genetic elements.
New research published in the journal Cell by the ...
UNC HIV prevention research named scientific breakthrough of the year
2011-12-23
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – The HIV Prevention Trials Network 052 study, led by Myron S. Cohen, MD of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, has been named the 2011 Breakthrough of the Year by the journal Science.
HPTN 052 evaluated whether antiretroviral drugs can prevent sexual transmission of HIV among couples in which one partner has HIV and the other does not. The research found that early treatment with antiretroviral therapy reduced HIV transmission in couples by at least 96 percent.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, ...
Built-in 'self-destruct timer' causes ultimate death of messenger RNA in cells
2011-12-23
December 22, 2011—(BRONX, NY) —Researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University have discovered the first known mechanism by which cells control the survival of messenger RNA (mRNA) —arguably biology's most important molecule. The findings pertain to mRNAs that help regulate cell division and could therefore have implications for reversing cancer's out-of-control cell division. The research is described in today's online edition of the journal Cell.
"The fate of the mRNA molecules we studied resembles a Greek tragedy," said the study's senior ...
Bacteria battle against toxic fluoride
2011-12-23
Regular use of fluoride-containing toothpaste and mouthwash has long been known to strengthen the enamel on teeth. But new research by Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) scientists finds that fluoride also has dramatic effects on bacteria inside the mouth -- including those that form plaque and can cause cavities.
HHMI researcher Ronald Breaker of Yale University has discovered the cellular chain of events that occurs inside a bacterium after it encounters fluoride in its environment. His team's findings reveal that many bacteria try to fend off fluoride – which the ...
Second Annual Holiday Fashion Show Benefit in New York City
2011-12-23
Long Island Exchange columnist Cognac Wellerlane interviews celebrities during a benefit for kidney transplant awareness.
On Tuesday December 6th an organization called the Flood Sisters hosted an annual Holiday Fashion Show Benefit to support their national kidney foundation. The organization, started by three sisters, is designed to support those willing to donate kidneys as well as those awaiting transplants. They believe that no one should have to suffer through painful treatments while waiting for an expendable organ.
The event was held at the Scandinavia House ...
Severe congenital disorder successfully treated in a mouse model for the first time
2011-12-23
Using a mouse model, Heidelberg University Hospital researchers have for the first time successfully treated a severe congenital disorder in which sugar metabolism is disturbed. The team headed by Prof. Christian Körner, group leader at the Center for Child and Adolescent Medicine, demonstrated that if female mice are given mannose with their drinking water prior to mating and during pregnancy, their offspring will develop normally even if they carry the genetic mutation for the congenital disorder. The team's outstanding work will contribute to better understanding of ...
Boxer Puts a Price on TV2
2011-12-23
At Boxer, we have decided to include TV2 in each of our four TV-packages, so our customers can keep viewing the channel. And on top of this, we are also making Danish TV-history by making it possible for our customers to purchase the channel (in Danish the term is Tv kanaler) separately. For the first time ever, our customers can choose to pay for a single channel without purchasing a full TV-package.
Here are the prices for TV2 purchased separately:
-19 kr./monthly subscription
-199 kr./annual card fee (primarily running and maintenance costs). The fee makes ...
When the mountains call . . .
2011-12-23
When the Mountains Call . . .
. . . don't climb too fast! Lack of acclimatization and excessively rapid ascent are the main risk factors for acute mountain sickness, as Kai Schommer and Peter Bärtsch explain in this issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2011; 108 [49]: 839-48).
More and more tourists are climbing up mountains that are 5000 to almost 7000 meters high, such as Kilimanjaro, without any prior experience at high altitudes. The low oxygen content in the air can cause altitude sicknesses of various kinds.
For example, sudden vomiting ...
Umbria Jazz Winter Festival Returns to Orvieto, Italy
2011-12-23
Most of the concerts will be held at the Arena Santa Giuliana on either the main stage or restaurant stage. Other venues include the Teatro Pavone and the Giardini Carducci Conad Stage and restaurant. This year's theme emphasizes the Latin sounds of jazz, delivered by international and Italian jazz and gospel soloists and groups. Among the many featured performers this year are Stan Tracy, Michel Camilo, the Gonzalo Rubalcaba Trio, Chano Dominguez, Fabrizio Bosso, The Harlem Jubilee Singers and la Lydian Sound Orchestra.
Travel to the Umbria Jazz Winter Festival from ...
[1] ... [6845]
[6846]
[6847]
[6848]
[6849]
[6850]
[6851]
[6852]
6853
[6854]
[6855]
[6856]
[6857]
[6858]
[6859]
[6860]
[6861]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.