Quantum computing has applications in magnetic imaging, say Pitt researchers
2011-12-19
Quantum computing -- considered the powerhouse of computational tasks -- may have applications in areas outside of pure electronics, according to a University of Pittsburgh researcher and his collaborators.
Working at the interface of quantum measurement and nanotechnology, Gurudev Dutt, assistant professor in Pitt's Department of Physics and Astronomy in the Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences, and his colleagues report their findings in a paper published online Dec. 18 in Nature Nanotechnology. The paper documents important progress towards realizing a ...
Corporate Investigations Needed as Employee Theft Increases
2011-12-19
Employee theft has unfortunately reached an all-time high with over $40 billion lost per year, and Phenix Investigations, a leader in corporate investigative services, has seen a sharp increase in cases involving scrap metal and raw material theft.
To combat employee theft and decrease losses in the retail sector, which average around 1.6% of yearly sales, Phenix Investigations has formed a specialized team of professional investigators with the experience and resources to identify employee theft, organized retail crime and vendor fraud. Additionally, the team has expertise ...
Consumers Support Wind and Solar Power 'Overwhelmingly', says Solar Panel Company Solar Panels Direct
2011-12-19
The poll by YouGov on behalf of the Sunday Times found that far from not featuring high on consumers' list of priority, climate change and environmental issues are still very much supported by the majority of the public.
Of 1696 people who responded to the poll, 56% wanted to see more wind energy capacity in the UK while 74% wanted to see solar energy capacity increased. Only 19% of survey respondents wanted to see less emphasis on wind power, which dropped to 12% for solar panels.
The encouraging news comes in the wake of high profile stories in the media criticizing ...
The Standard Chartered Marathon Comes to Dubai
2011-12-19
The 12th annual Standard Chartered Dubai Marathon is slated to commence on Friday, January 27, 2012. The event will include the main marathon, scheduled to begin at 7:00 am, the 10K road race at 7:15 am and the 3K Fun Run at 10:30 am. All three races will start at the same location in downtown Dubai. The start gantry will be just outside the Pavilion at the Burj Khalifa. The races will finish at the finish gantry located on the opposite side of the street.
The 2012 Standard Chartered Dubai Marathon marks the first marathon in the Middle East to be awarded Gold Label ...
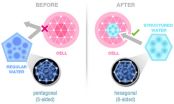
Researchers Find 4 of Every 5 Glasses of Regular Water You Drink Go Down the Toilet
2011-12-19
On top of the Himalayan Mountains, Hunza people enjoys the best glacier water that nature offers. Captain Water researchers discovered that this glacier water is formed of perfectly structured water molecules. This means it can actually be fully absorbed to support the body instead of just going through the system and mainly being flushed out.
"Most people are not aware that up to 80% of tap water and bottled water that they consume actually may not get absorbed, because it isn't structured at the molecular level properly. Our water ionizer technology directly ...
Hedge fund share restrictions favor managers over investors
2011-12-19
Chestnut Hill, MA – Armed with insider knowledge, managers of share-restricted hedge funds sell off their own holdings ahead of their investors in order to avoid low returns produced by an outflow of shareholder dollars, according to a new study by researchers from Boston College and EDHEC Business School in France.
The practice, known as front running, pits the interests of managers against those of investors in hedge funds where shareholder actions are limited by contract and there is scant disclosure of fund details. Managers act in advance on the information they ...
Designer Fitness Hosts New Studio Open House on January 6, 2012
2011-12-19
Designer Fitness is hosting an Open House on January 6, 2012, to celebrate the opening of its new studio. Started by Darla O'Brien in 1989, Designer Fitness moved to 32 S. Osprey Avenue, Suite 204, from its former location on Palm Avenue.
The Open House, scheduled from 5:30 to 8 pm, has a 50th Anniversary of "Breakfast at Tiffany's" theme, complete with an Audrey Hepburn look-alike contest.
Designer Fitness has a unique approach to fitness training called Motion Empowered, or the ME System . Created by O'Brien and drawing from her more than 25 years of ...
Babies remember even as they seem to forget
2011-12-19
Fifteen years ago, textbooks on human development stated that babies 6 months of age or younger had no sense of "object permanence" – the psychological term that describes an infant's belief that an object still exists even when it is out of sight. That meant that if mom or dad wasn't in the same room with junior, junior didn't have the sense that his parents were still in the world.
These days, psychologists know that isn't true: for young babies, out of sight doesn't automatically mean out of mind. But how much do babies remember about the world around them, and what ...
Report identifies health, environmental issues and best practices
2011-12-19
WASHINGTON — A number of health and environmental issues and related risks need to be addressed when considering whether to lift the almost 30-year moratorium on uranium mining in Virginia, says a new report from the National Research Council, the operating arm of the National Academy of Sciences and National Academy of Engineering.
"Internationally accepted best practices, which include timely and meaningful public participation, are available to mitigate some of the risks involved," said Paul Locke, chair of the committee that wrote the report and associate professor, ...
Facts of "Hot Coffee" Case Show True Role of Personal Injury Litigation
2011-12-19
Facts of "Hot Coffee" Case Show True Role of Personal Injury Litigation
Urban myths often do not correspond to the truth. In fact, they can be downright false -- perpetuating half-truths and outright lies. Such is the case with the infamous McDonald's "hot coffee" case, involving a woman who sought compensation for injuries caused by excessively hot coffee served in a flimsy cup at McDonald's.
After the woman obtained substantial compensation in her personal injury case, critics of America's legal system tried to portray it as an example of an ...
Location, location, location: Economists document key role of spatial component in economic growth
2011-12-19
(Chicago, IL) - Location and other geographical factors play an important role in supporting economic growth and development in emerging markets, a new study from the Consortium on Financial Systems and Poverty has found.
The study, which examines growth in the Thai economy between 1986 and 1996, shows that a high concentration of enterprise in an area predicts high subsequent growth in and around that area. Entrepreneurial activity decreases virtually by the mile the further away one gets from centers of economic concentration.
In addition, other geographic conditions, ...
NIH scientists find a potential new avenue for cancer therapies
2011-12-19
Recent findings in mice suggest that blocking the production of small molecules produced in the body, known as epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), may represent a novel strategy for treating cancer by eliminating the blood vessels that feed cancer tumors. This research is the first to show that EETs work in concert with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a protein known to induce blood vessel growth. Together, EETs and VEGF promote metastasis, or the spread of cancer, by encouraging the growth of blood vessels that supply nutrients to cancer cells.
The research ...
Aggressively Pursuing the Compensation Brooklyn Scaffolding Accident Victims Deserve
2011-12-19
Brooklyn has seen more than its fair share of construction projects in recent years. While the scope of these developments varies in size from small restoration and maintenance projects costing only thousands of dollars to the multibillion-dollar Atlantic Yards project in Prospect Heights, they all involve the potential for scaffolding accidents or ladder falls that may cause serious injury to those working on site.
At Simon Eisenberg & Baum, our Brooklyn construction accident lawyers help injured construction workers and families obtain compensation for damages ...
Acupuncture reduces protein linked to stress in first of its kind animal study
2011-12-19
Washington, DC — Acupuncture significantly reduces levels of a protein in rats linked to chronic stress, researchers at Georgetown University Medical Center (GUMC) have found. They say their animal study may help explain the sense of well-being that many people receive from this ancient Chinese therapy.
Published online in December in Experimental Biology and Medicine, the researchers say that if their findings are replicated in human studies, acupuncture would offer a proven therapy for stress, which is often difficult to treat.
"It has long been thought that acupuncture ...
San Diego Zoo researchers contribute to project using mummy DNA to differentiate croc species
2011-12-19
The Nile crocodile is a species that was identified by ancient Egyptians. Genetic analysis done by a group of geneticists using samples taken from species throughout the animal's range and including DNA from mummified crocodile remains indicates that more than one species is known by this name.
"This paper provides a remarkable surprise: the Nile crocodile is not a single species, as previously thought, but instead demonstrates two species - living side-by side - constitute what has been called the Nile croc." Said Marlys Houck, geneticist with San Diego Zoo Global's ...
Elves Pull Off Daring Rescue Of Santa Claus And Reindeer
2011-12-19
It started out like any other Christmas Eve, but before the night was over, things would never be the same for Santa Claus and the reindeer. For the first time, the story of the Elves daring rescue of Santa Claus is revealed on a new free website, The Santa Claus Sleigh.
For years the number of good little girls and boys had been growing and growing, so the number of toys to deliver was through the roof. But Santa Claus was still using the same little red sleigh to deliver the toys. So every year, it took more and more trips back to the North Pole to reload the sleigh. ...
A major step forward towards drought tolerance in crops
2011-12-19
RIVERSIDE, Calif. – When a plant encounters drought, it does its best to cope with this stress by activating a set of protein molecules called receptors. These receptors, once activated, turn on processes that help the plant survive the stress.
A team of plant cell biologists has discovered how to rewire this cellular machinery to heighten the plants' stress response – a finding that can be used to engineer crops to give them a better shot at surviving and displaying increased yield under drought conditions.
The discovery, made in the laboratory of Sean Cutler, an ...
Study: African-American men don't reap same career benefits from mentoring as Caucasians
2011-12-19
Athens, Ga. – Networking within an organization and having a mentor are widely thought to promote career success, but a new University of Georgia study finds that African-American men don't receive the same measurable benefits from these professional connections that Caucasians do.
Study co-author Lillian Eby, a professor in the Industrial-Organizational Psychology Program in the UGA Franklin College of Arts and Sciences, said the finding shouldn't discourage African Americans from seeking mentoring and networking opportunities. Rather, it emphasizes the need for women ...
Grafting of human spinal stem cells into ALS rats best with immunosuppressant combination
2011-12-19
Tampa, Fla. (Dec, 19 2011) – A team of researchers grafting human spinal stem cells into rats modeled with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as "Lou Gehrig's Disease," a degenerative, lethal, neuromuscular disease, have tested four different immunosuppressive protocols aimed at determining which regimen improved long-term therapeutic effects. Their study demonstrated that a combined, systematically delivered immunosuppression regimen of two drugs significantly improved the survival of the human spinal stem cells. Their results are published in the current ...
UCF nanotechnology may speed up drug testing
2011-12-19
Testing the effectiveness of new pharmaceuticals may get faster thanks to a new technique incorporating quantum dots developed at the University of Central Florida.
Some drug testing can take a decade or more, but UCF associate professor Swadeshmukul Santra and his team have created an electronic quantum dots (Qdots) probe that "lights up" when a drug it is delivering attaches to cancer cells. The research appears online in this month's Biomaterials. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142961211012841#FCANote
A researcher can use a microscope to see ...
Bone marrow-derived cells differentiate in the brain through mechanisms of plasticity
2011-12-19
Tampa, Fla. (Dec, 19 2011) – Bone marrow-derived stem cells (BMDCs) have been recognized as a source for transplantation because they can contribute to different cell populations in a variety of organs under both normal and pathological conditions. Many BMDC studies have been aimed at repairing damaged brain tissue or helping to restore lost neural function, with much research focused on BMDC transplants to the cerebellum at the back of the brain. In a recent study, a research team from Spain has found that BMDCs, can contribute to a variety of neural cell types in other ...
Fletcher Jones Motorcars Appeals Arbitration Loss To Orange County Lemon Law Attorney
2011-12-19
On December 13, 2011, Michael R. Vachon, Esq., a California lemon law attorney practicing in Orange County, California filed the Respondent's Brief in the Orange County Court of Appeals case Lewis v. Fletcher Jones Motorcars, Inc., et al. (Appellate Case No. Case No. G045603). At issue in the appeal is whether Orange County Superior Court Judge Thierry P. Colaw was correct in denying Fletcher Jones Motorcars's July 22, 2011 motion to compel arbitration. Arbitration is a form of private litigation, in which the parties agree to have their dispute settled by an "arbitrator" ...
Research could improve laser-manufacturing technique
2011-12-19
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. ╨ Engineers have discovered details about the behavior of ultrafast laser pulses that may lead to new applications in manufacturing, diagnostics and other research.
Ultrafast laser pulses are used to create features and surface textures in metals, ceramics and other materials for applications including the manufacture of solar cells and biosensors. The lasers pulse at durations of 100 femtoseconds, or quadrillionths of a second, and cause electrons to reach temperatures greater than 60,000 degrees Celsius during the pulse duration. The ...
All American Trivia Games Releases First iPhone App
2011-12-19
All American Trivia Games, LLC and the Computer Science Department at High Point University, High Point, North Carolina, are pleased to announce that the presidential trivia game HAIL TO THE CHIEF is now available for download from the iTunes Store. Playable on the iPhone, iPad, and iPod, there are two apps to choose from. One download is a FREE version which includes twenty questions while the other app is the complete game including all 232 questions for a fee of $1.99. The $1.99 app was designed so that up to four people can challenge one another on the same device. ...
All I Want For Christmas is Help From Blue Tax in Releasing My IRS Liens!
2011-12-19
No time is a good one for IRS liens or wage garnishments, but the holidays are the worst time of all for such things. Jermal and Karen (Atlanta, GA) came to Blue Tax with a $28,000 debt for 2006, 2008, 2009 and 2010. They did have an IRS installment agreement in place but had defaulted on those payments and so a wage garnishment was placed at Jermal's employer. The challenge for Blue Tax was going to be getting the garnishment removed and determining whether or not Jermal and Karen would qualify for a hardship program or a payment plan.
The experts at Blue Tax got right ...
[1] ... [6856]
[6857]
[6858]
[6859]
[6860]
[6861]
[6862]
[6863]
6864
[6865]
[6866]
[6867]
[6868]
[6869]
[6870]
[6871]
[6872]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.