Breakthrough in Niemann-Pick Type C research reported by Notre Dame and Cornell scientists
2011-03-22
A paper announcing a breakthrough discovery in the fight against Niemann-Pick Type C, coauthored by Olaf Wiest and Paul Helquist of the University of Notre Dame's Department Chemistry & Biochemistry and Frederick Maxfield, Chair of Biochemistry at Cornell University Weill College of Medicine, appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences this week. The paper shows how use of a histone deacetylase inhibitor correct the damage done by the genetic disorder and allowed once-diseased cells to function normally.
Niemann-PickType C (NPC) involves a genetic flaw ...
Study shows polypill to be safe and accepted by physicians and patients in developing countries
2011-03-22
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Monday, March 21, 2011 – For a patient at high risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), keeping up with what pills to take at different times of the day can be tedious. Window sills lined with prescription bottles – a pill for cholesterol, another for blood pressure, and an aspirin to keep blood thin and flowing – the list can get quite long and, as a result, many people, especially the elderly, often forget doses or take the wrong pill at the wrong time.
But what if there was a single pill that had all the benefits of multiple medications in one dose? ...
Trauma patients protected from worse outcomes associated with so-called 'weekend effect'
2011-03-22
PHILADELPHIA -- Patients who've been hurt in car or bike crashes, been shot or stabbed, or suffered other injuries are more likely to live if they arrive at the hospital on the weekend than during the week, according to new University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine research published in the March 21 issue of Archives of Surgery. The findings, which also showed that trauma patients who present to the hospital on weeknights are no more likely to die than those who presented during the day, contrast with previous studies showing a so-called "weekend effect" in which patients ...
Webb sunshield like an umbrella on the shores of the universe
2011-03-22
The James Webb Space Telescope has a unique shield to protect its sensitive instruments from the heat and light of the sun. The sunshield is like an umbrella popping open on the shores of the cosmos that allows the instruments beneath it to see far into the universe.
Like a beach umbrella protects people from the sun's heat and ultraviolet radiation, the sunshield protects the telescope and the sensitive infrared instruments that fly beneath the Webb telescope's sunshield from our sun's heat and light. "Each of the five layers of the shield is less than half the thickness ...
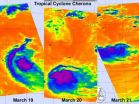
NASA infrared satellite imagery shows Cyclone Cherono dwindling
2011-03-22
Three days of NASA infrared satellite imagery provides a clear picture to forecasters of the effect wind shear has had on former Cyclone Cherono. Wind shear increased near Cyclone Cherono this weekend and weakened it down to a remnant low pressure area in the Southern Indian Ocean. Today, March 21, Cherono's remnants are moving away from Mauritius and still causing ocean swells.
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over former Tropical Cyclone Cherono each day over the last three days and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured the effects of the increased ...
Study finds reports of domestic violence rise 10 percent after NFL upsets
2011-03-22
Calls to the police reporting men's assaults on their wives or intimate partners rose 10 percent in areas where the local National Football League team lost a game they were favored to win, according to an analysis of 900 regular-season NFL games reports researchers in a paper in the Quarterly Journal of Economics.
Football games are emotionally laden events of widespread interest, typically garnering 25 percent or more of a local television viewing audience. The disappointment of an unexpected loss, the researchers concluded, raises the risk that football fans may react ...
The BCG World Atlas: a world first in the fight against tuberculosis
2011-03-22
Tuberculosis (TB) continues to pose a major global health threat. Someone in the world is newly infected with TB bacteria every second. Every year, more than 9 million people develop active TB and it claims about 2 million lives. In Canada, the overall incidence of TB has declined, but rates remain high among immigrants from endemic countries and among Aboriginal populations. Currently, Nunavut is facing the largest TB outbreak in the territory's 10- year history.
In the days leading up to World TB Day 2011 on March 24, a team of researchers from McGill University and ...
Scott Parkinson of All America Transportation Designated Certified Transportation Broker By The TIA
2011-03-22
All America Transportation Inc. is proud to announce company Vice President Scott Parkinson has been designated "Certified Transportation Broker" by the Transportation Intermediaries Association (TIA). The CTB is awarded in recognition of Scott' s successful completion of a rigorous course of study and passing a thorough and comprehensive examination. This is the highest certification for participants in the 3PL industry.
This program was created in 1986 to significantly increase the professionalism and integrity of property brokers. The CTB program tests the knowledge ...
Advertising Women of New York to Honor 16 Industry Revolutionaries at "Changing the Game", April 14
2011-03-22
On April 14, Advertising Women of New York (www.awny.org) will present a day-long tribute to 16 executive women from across the United States who have taken risks and made a difference at its fifth annual "Changing the Game" celebration at the New York Hilton.
Diane Brady, Senior Editor, Bloomberg Businessweek, will moderate a morning discussion on business and industry trends with panelist/honorees Dana Anderson, SVP-Marketing Strategy & Communication, Kraft, Wendy Clark, SVP-Integrated Marketing, Communications & Capabilities, Coca-Cola, Fiona Morrison, Director-Brand ...
Skylight Launches New Features Including Basecamp Import, Media Files and Timezone Support for a Growing Number of Small Business to Increase Collaboration and Productivity at Skylightit.com
2011-03-22
Skylight's collection of project management and collaboration features has consistently grown since the company's recent launch of the software-as-a-service toolset for small business users. Today, Skylight is pleased to announce compatibility with 37signals' Basecamp platform, and the ability to import Basecamp data directly into Skylight.
"We're committed to consistently delivering value to our users by adding functionality, and providing a comprehensive and affordable platform for managing the entire business," said Taimur Khan, Director of Skylight Interactive. "Our ...
EFMD Excellence in Practice Awards 2011 - Submit Cases Now
2011-03-22
EFMD is a leading international network of business schools, companies and consultancies at the forefront or raising the standards of management education and development globally. The Annual Excellence in Practice Awards recognise outstanding partnerships in Learning and Development.
Winning case-studies must demonstrate Operational Excellence (e.g. sustainable partnership & effective learning environment etc.); Excellent Programme Management (e.g. design, delivery, evaluation, selection methodology of participants etc.); and above all Strong Business Impact (e.g. ...
Plackers Offers Tax Season Relief with Grind-No-More Giveaway
2011-03-22
Tax season is stressful for many Americans, and even the IRS's extension of this year's filing deadline to April 18 may not provide much relief. To help prevent tooth damage caused by night time teeth grinding and clenching associated with tax season stress, Plackers, a leading brand of consumer oral care products, is providing complimentary Grind-No-More dental night protector samples including free shipping and handling to the first 10,000 people who sign-up on its website at www.plackers.com.
Bruxism, the medical term for teeth grinding or clenching, is a common sleep ...
Newport Jazz Festival Celebrates 2011 Schedule and New Sponsor Alex and Ani
2011-03-22
Newport Festivals Foundation, Inc. today announced the support of a new sponsor, Alex and Ani, and the schedule of the 2011 Newport Jazz Festival, which is set for August 5 - 7. Tickets go on sale worldwide March 25, at 10:00 am through TicketMaster and www.newportjazzfest.net.
Rhode Island jewelry designer and manufacturer Alex and Ani join the ranks of dedicated corporate sponsors to help continue the legacy of the Newport Jazz Festival. Headquartered in Cranston, RI, with its flagship store at Newport's Bowen's Wharf, the company will sponsor the Harbor Stage at ...
Lloyds TSB Acts on Call for First Time Buyer Innovation
2011-03-22
Lloyds TSB today introduces Local Lend a Hand - a new concept designed to help first time buyers purchase a home with a deposit of just 5%.
Raising a deposit is a crucial challenge for many first time buyers looking to take their first steps onto the property ladder, and is highlighted by many as the key hurdle to buying their first home.
Responding to calls for further innovation in the first time buyer mortgage market, Lloyds TSB has worked with Sector Treasury Services, part of the Capita Group, to develop its unique Lend a Hand product to address this problem. ...
2010 Break-Through Author Caleb Bell Publishes "Decoding Modern Love | A Powerful Journey of Understanding, Intimacy and Insight" in Print and eBook
2011-03-21
2010 Break-through Author Caleb Bell publishes "Decoding Modern Love | A Powerful Journey of Understanding, Intimacy and Insight" in Print and eBook through Amazon.com and Kindle eBook. Caleb Bell's writing follows closely in the footsteps of Randy Pausch, author of the book "The Last Lecture: Really Achieving Your Childhood Dreams" and Dr. Gary Chapman's acclaimed "The Five Love Languages." Caleb Bell is best known for innovative short stories and articles on relationships, love and intimacy.
Amazon.com is the direct publisher for Caleb Bell's book "Decoding Modern ...
El Toronto Web Design Launches Affordable Website Design Packages for Toronto Businesses
2011-03-21
El Toronto Web Design is pleased to announce the launch of their new small business web package product for the Toronto, ON market and surrounding areas. With years of experience in the Toronto web design industry, El Toronto Web Design is extending affordable one-time-cost web design packages to Toronto startups and small Toronto businesses with an easy to manage platform.
As an introductory promotion blitz, El Toronto Web Design is offering their Toronto Website Design Package for $459.95 instead of $599.95. The Toronto Website Design Package includes domain registration ...
Announcing the Launch of Your Document Professionals
2011-03-21
This week, Your Document Professionals announces the launch of their business-to-business service model. The company offers top notch, professional documents to small and mid-sized business that cannot typically budget for a communications department or even an individual to professionally handle their communications needs.
"The type of work that we offer has always been available via freelance work," Jennifer Walker, President of YDP, said, "but what is really exciting is the format in which we now offer it. We want to build relationships with our clients so we can ...
Property Appraisals Significantly Affect Short Sales And Foreclosures
2011-03-21
Property values have changed dramatically and the premiere Los Angeles Appraisers, Appraisal Evaluations, Inc., have recently begun to focus on assisting their clients with Short Sale transactions in Southern California, with accurate appraisals based on over 100 years of combined experience.
The number of short sales and foreclosures taking place has occurred in numbers that are only eclipsed by the Great Depression. Individuals and companies are turning in greater numbers to the services of Appraisal Evaluations, Inc. in Los Angeles, Ca. The firm provides property ...
Rosendin Electric Rallies to Help Rebuild Haitian Sacred Heart Hospital
2011-03-21
Rosendin Electric, Inc., the nation's largest private electrical contractor and a 100% employee-owned company, has been working behind the scenes with their own Haitian Earthquake Relief program. When the Bay Area office was approached by Mazzetti Nash Lipsey Burch (M+NLB) to help find materials needed to rewire Hopital Sacre Coeur in the north Haitian town of Milot, the Rosendin Electric procurement team was able provide electrical supplies, tools, and equipment within two weeks to meet a tight shipping deadline.
As one of the few hospitals still operating after the ...
Best Selling Author John Eldredge Talks Shop in Audio Interview with Vaughn Street
2011-03-21
The terms Wild at Heart, Love and War, and Sacred Romance have become everyday language for followers of best-selling author and speaker John Eldredge. His and his wife Stasi's books have resonated with millions of men and women who are described as "allies" for their devotion to the message. Eldredge's books and other resources have sold approximately ten million copies globally and coveted access to Ransomed Heart Ministries' (of which Eldredge is President) successful "Bootcamps" is by lottery.
Eldredge sat down for a rare and in-depth audio interview with Sr. Producer ...
South Bay California Writing School Classes in San Pedro, Torrance, Los Angeles
2011-03-21
Published writer and former magazine editor, Lara Sterling, announces the launch of Your Plot Thickens, a new writing school for the South Bay of Los Angeles and on-line. Workshops currently offered at Your Plot Thickens include "Story Structure 101" and a seminar "How to Self-Publish Your Novel". Your Plot Thickens will also begin offering "Beginning Screenwriting", "How to Write for Magazines" as well as classes that inform about how to write specific genres (e.g., the Romantic Comedy or the Thriller). Workshops and seminars at Your Plot Thickens are suitable for both ...
NBSA Invites Basketball Shooters To Compete for the title of the World's Best Senior Free Throw Shooter
2011-03-21
The Huntsman World Senior Games and the National Basketball Shooters Association have partnered to hold the first annual Huntsman/NBSA World Senior Free Throw Championship on October 10th, 2011 in St. George, Utah.
The Huntsman World Senior Games is the largest annual olympic style games of its kind. More than 10,000 senior athletes from all over the US and from around the world participated in the 2010 Games. The 2011 Games marks its 25th anniversary of the running of the St. George, UT games and it is expected to be the largest field of participation ever.
In just ...
A singles solution.... eLove enters Philadelphia market, opens matchmaking office in King of Prussia.
2011-03-21
eLove is the first company within the dating industry offering both online dating and matchmaking services. They recently opened a new matchmaking office at 630 Freedom Business Center, Third Floor, in King of Prussia.
"Let's face it. If you live in the northeast, you are already challenged because the winters can make it difficult to get out there and meet somebody," said Paul A. Falzone, CEO of eLove, one of the largest online dating and matchmaking services in the world. "But, Spring is practically here and there's not a better time for Philadelphia area singles to ...
Poggi Bonsi now offers Quick Pop Maker and Accessories in it's Seattle-area retail stores as well as online and PoggiBonsiGifts.com
2011-03-21
The unique Quick Pop Maker unit freezes ice pops in as little as seven minutes right on your countertop without electricity. Quickly make striped pops, yogurt pops or (for the first time ever at home) flavored core pops. To enjoy Quick Pops at a moment's notice, simply store the compact base in your freezer. The kit includes six durable, reusable plastic pop sticks that have unique ridged designs that allow pops to adhere securely, with special drip guards for tidy eating. A specially designed Super Tool helps to quickly release the frozen treats from their molds. The unit ...
Susan Murphy Milano Instructing at National Conference
2011-03-21
March 24-27, CUE Center for Missing Persons holds its 7th annual National Conference in Wilmington, NC, titled, "Hope Lights the Way." Eachyear the Board of Directors, and Founder of CUE Center, Monica Caison, welcome speakers, presenters, and instructors which lend their expertise to educating the attendees, mostly family members of missing persons, but including all who work in the arena from advocating, volunteerism, investigation, search and rescue and identification process of those who are lost. This event is open to all who support the mission of finding a resolution ...
[1] ... [7683]
[7684]
[7685]
[7686]
[7687]
[7688]
[7689]
[7690]
7691
[7692]
[7693]
[7694]
[7695]
[7696]
[7697]
[7698]
[7699]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.