'Healthy' patients at high risk of cardiac death identified
2011-02-16
The way the heart responds to an early beat is predictive of cardiac death, especially for people with no conventional markers of cardiovascular disease, according to new research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
The conventional risk factors, such as high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes and high blood pressure, account for many but not all deaths from cardiovascular causes. As a result, doctors are always searching for better ways to identify patients at risk of cardiac death.
The new research indicates that an abnormal response to an early ...
UF leads world in reconfigurable supercomputing
2011-02-16
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — University of Florida researchers say their supercomputer, named Novo-G, is the world's fastest reconfigurable supercomputer and is able to perform some important science applications faster than the Chinese supercomputer touted as the world's most powerful.
In November, the TOP500 list of the world's most powerful supercomputers, for the first time ever, named the Chinese Tianhe-1A system at the National Computer Center in Tainjin, China as No. 1.
In his state of the union speech, President Barack Obama noted, "Just recently, China became home ...
EARTH: Oil and water help US win World War II
2011-02-16
Alexandria, VA – The U.S. had two key strategic advantages over the Axis in World War II: oil and water. Although other factors played major roles in the U.S. and its allies winning the war, these two natural resources played a much larger role than recognized.
World War II was the first highly mechanized war. In the March feature "How Oil and Water Helped the U.S. Win World War II," EARTH magazine explores how the abundance of domestic US oil and water in the South and Pacific Northwest drove not only tanks and planes, but also industrial production and technological ...
Study compares balanced propofol sedation with conventional sedation for therapeutic GI endoscopic procedures
2011-02-16
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Feb. 15, 2011 – Researchers from Korea report that, compared with conventional sedation, balanced propofol sedation (BPS) using propofol in combination with midazolam and meperidine, provided higher health care provider satisfaction, better patient cooperation, and similar adverse event profiles in patients undergoing therapeutic endoscopic procedures. This is the first prospective study of BPS in direct comparison with conventional sedation. The researchers note that this study provides further evidence to support the adoption of endoscopist-directed ...
FASEB praises President Obama for increasing funding for research in his FY 2012 budget
2011-02-16
Bethesda, MD - William T. Talman, MD, President of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB), praised President Barack Obama for his continuing support for science and engineering. "The President recognizes that our future depends on research," Talman stated. In a letter to President Obama, Talman noted that his "support for this critical investment—even during a time of unprecedented budgetary constraints—will help to improve the lives of millions of people."
In his FY 2012 Budget, President Obama proposed a $745 million increase over the ...
A device enables the remote explosion of improvised land-mines
2011-02-16
Composed of diverse elements, mostly of plastic, with little metal used, improvised explosive devices are very difficult to detect. In cooperation with two colombian universities, scientists at EPFL's Electromagnetic Compatibility Laboratory have found a solution. They have developed a device enabling the remote explosion of these mines, by using the energy from their electromagnetic impulses.
This type of mine is often used by guerillas or terrorist groups in conflict zones, and is present in many regions of the world, such as Colombia, Iraq and Afghanistan. They kill ...
University of Miami scientists find new way to estimate global rainfall and track ocean pollution
2011-02-16
MIAMI – Feb 15, 2011 – A study by scientists at the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine & Atmospheric Science suggests a new way to estimate how much of the ocean's pollution is falling from the sky. The new findings can help improve scientific understanding of how toxic airborne chemicals, from the burning of fossil fuels and industrial power plants emissions, are impacting the oceans globally.
By measuring Beryllium-7 (7Be) isotope concentrations in the ocean, which is found naturally throughout Earth's atmosphere, Rosenstiel School scientists David ...
Government mashups -- better contact with public authorities
2011-02-16
Potholes in the road or a park bench in need of repair – we all come across these or similar problems every now and then. If only there were a simple way of reporting them to the right department of the public administration! The latest mashup technology and mobile applications make it possible to come up with solutions.
Inspired by the UK website www.fixmystreet.com, the Fraunhofer Institute for Open Communication Systems FOKUS in Berlin is taking this approach further. Damage reports can be assigned GPS coordinates by cell phone and entered. The system then provides ...
Got a goal?: A helpful partner isn't always helpful
2011-02-16
You might think that a loving partner helps keep you on track—say, when you want to stick to your jogging or concentrate on your studies. But a new study in Psychological Science, a publication of the Association of Psychological Science, reports the opposite: Thinking about the support a significant other offers in pursuing goals can undermine the motivation to work toward those goals—and can increase procrastination before getting down to work.
The study's authors, psychological scientists Gráinne M. Fitzsimons of Duke University and Eli J. Finkel of Northwestern University, ...
Getting cars onto the road faster
2011-02-16
The auto industry faces major challenges. New models are entering the market at ever shorter intervals, products are becoming more complex, and the trend towards electric cars requires modified vehicle structures. European production sites are coming under increasing cost pressure from low-wage countries. Cost reductions, shorter production times, new materials and innovative assembly techniques are needed if companies are to remain competitive. To achieve these goals, 23 business and research organizations are participating in the EU's Pegasus project (www.pegasus-eu.net). ...
2 new plants discovered in Spain
2011-02-16
Just when everyone thought that almost every plant species on the Iberian Peninsula had been discovered, Spanish researchers have discovered Taraxacum decastroi and Taraxacum lacianense, two dandelions from the Pyrenees and the Cordillera Cantábrica mountain range, respectively. This finding confirms Spain's privileged position as a hotbed of biodiversity.
"It's hard to find new species now in Spain. It depends on the complexity of the group of plants you study", Antonio Galán de Mera, lead author of the study and a researcher in the Department of Biology (Botany) at ...
Science alone does not establish source of anthrax used in 2001 mailings
2011-02-16
WASHINGTON – A National Research Council committee asked to examine the scientific approaches used and conclusions reached by the Federal Bureau of Investigation during its investigation of the 2001 Bacillus anthracis mailings has determined that it is not possible to reach a definitive conclusion about the origins of the anthrax in letters mailed to New York City and Washington, D.C., based solely on the available scientific evidence.
Findings of the committee's study include:
The FBI correctly identified the dominant organism found in the letters as the Ames strain ...
Sentries in the garden shed
2011-02-16
Someday, that potted palm in your living room might go from green to white, alerting you to a variety of nasty contaminants in the air, perhaps even explosives.
The stuff of science fiction you say? Not so, says a Colorado State University biologist whose research is funded in part by Homeland Security's Science and Technology Directorate (DHS S&T), as well as by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), the Office of Naval Research (ONR), and others.
Dr. June Medford and her team in the Department of Biology at Colorado State have shown that plants ...
The lock shapes the key
2011-02-16
Interactions between proteins are of fundamental importance for a number of processes in virtually every living cell. However, in order for the proteins to carry out any biological function, they must first assume their specific three-dimensional shape. A number of reactions have been described in recent years, where one of the interaction partners does not assume its active structure until the actual binding process commences. It was still a great mystery, though, how the binding partners could actually recognize such unstructured proteins.
Scientists led by Professor ...
Obesity and knee osteoarthritis shorten healthy years of life
2011-02-16
Boston, MA – An estimated 10 million Americans suffer from knee osteoarthritis (OA), making it one of the most common causes of disability in the US. Due to obesity and symptomatic knee OA, Americans over the age of 50 will together lose the equivalent of 86 million healthy years of life, concluded researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH), who investigated the potential gains in quality and quantity of life that could be achieved averting losses due to obesity and knee OA. These findings are published in the February 15 issue of Annals of Internal Medicine.
"Reducing ...
If greenhouse gas emissions stopped now, Earth still would likely get warmer
2011-02-16
While governments debate about potential policies that might curb the emission of greenhouse gases, new University of Washington research shows that the world is already committed to a warmer climate because of emissions that have occurred up to now.
There would continue to be warming even if the most stringent policy proposals were adopted, because there still would be some emission of heat-trapping greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane. But the new research shows that even if all emissions were stopped now, temperatures would remain higher than pre-Industrial ...
Peer support offers promise for reducing depression symptoms
2011-02-16
Peer support offers promise as an effective, low-cost tool for fighting depression, a new study by the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System and University of Michigan Health System finds.
Programs in which patients and volunteers share information were found to reduce symptoms of depression better than traditional care alone and were about as effective as cognitive behavioral therapy, researchers found after analyzing 10 randomized trials of peer support interventions for depression dating from 1987 to 2009.
The analysis was the first of its kind to look at peer support specifically ...
4.7 million Californians to gain coverage under health reform, new study estimates
2011-02-16
Up to two-thirds of California's 7 million uninsured residents will become eligible for health insurance coverage when health care reform is implemented in 2014, according to a new policy brief from the UCLA Center for Health Policy Research.
The study draws on the latest data from the California Health Interview Survey (CHIS), which will be released shortly.
The policy brief, "Two-thirds of California's 7 Million Uninsured May Obtain Coverage Under Health Care Reform," finds that 4.7 million Californians, including both adults and children, will likely be eligible ...
Payoffs of long-term investment in education research
2011-02-16
WASHINGTON, D.C.—Leading scholars and private foundation presidents shared the Capitol Hill stage to highlight the payoffs of long-term investment in education research at a Capitol Hill briefing on Monday, February 14, 2011. Speakers emphasized that education research based on long-term funding has led to important payoffs for education policy and practice in such areas as resource allocation, school and classroom organization, and the education and evaluation of teachers.
The Education Deans Alliance, American Educational Research Association, and the National Academy ...
NIH-funded study finds new possible risk factor of heart disease
2011-02-16
Abnormal heart rate turbulence is associated with an increased risk of heart disease death in otherwise low-risk older individuals, according to a study funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), part of the National Institutes of Health.
This study appears in the Feb. 15 edition of the Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology.
Among the nearly 1,300 study participants, heart rate turbulence, which reflects how well the heart reacts to occasional premature contractions, was an even stronger heart disease risk factor than elevated levels of C-reactive ...
Designing new molecular tools to study the life and death of a cancer cell
2011-02-16
Basic and translational research on cancer, and development of new cancer therapeutics, has focused on different aspects of cancer cellular function. One area of focus is the life and death of a cancer cell. Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is a fundamental process of cells including cancer cells. The signal transduction pathways of apoptosis involve many different proteins and their interactions with each other. Protein-protein interactions involved in these apoptotic signals, like those in many other biological processes, are often determined or influenced ...
Astronomers identify thick disc of older stars in nearby Andromeda galaxy
2011-02-16
An international team of astronomers has identified for the first time a thick stellar disc in the Andromeda galaxy, the nearest large spiral galaxy to our own Milky Way.
The discovery of the thick disc, a major result from a five-year investigation, will help astronomers better understand the processes involved in the formation and evolution of large spiral galaxies like ours, according to the team, which includes UCLA research astronomer Michael Rich and colleagues from Europe and Australia.
Using the Keck Telescope in Hawaii, the astronomers analyzed the velocities ...
Overabundance of protein expands breast cancer stem cells
2011-02-16
HOUSTON - An essential protein for normal stem cell renewal also promotes the growth of breast cancer stem cells when it's overproduced in those cells, researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center report in the February edition of Cancer Cell.
In mouse and lab experiments, the team also discovered that two drugs block the cascade of molecular events that they describe in the paper, thwarting formation of breast tumor-initiating cells.
"Overexpression of the EZH2 protein has been linked to breast cancer progression, but the molecular details of that ...
New material provides 25 percent greater thermoelectric conversion efficiency
2011-02-16
AMES, Iowa – Automobiles, military vehicles, even large-scale power generating facilities may someday operate far more efficiently thanks to a new alloy developed at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory. A team of researchers at the Lab that is jointly funded by the DOE Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, achieved a 25 percent improvement in the ability of a key material to convert heat into electrical energy.
"What happened here has not happened anywhere else," ...
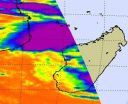
NASA Satellite sees most of Cyclone Bingiza's rainfall over Mozambique Channel
2011-02-16
Infrared data from NASA's AIRS instrument revealed that the low level center of Cyclone Bingiza was still over land in western Madagascar this morning, but the bulk of its rainfall was over the Mozambique Channel.
When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Madagascar this morning, Feb. 15 at 11:11 UTC (6:11 a.m. EST), the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument read the temperatures of the cold thunderstorm cloud tops in Cyclone Bingiza. Most of the strongest thunderstorms were north and west of the center of circulation already over the Mozambique Channel, while Bingiza's ...
[1] ... [7884]
[7885]
[7886]
[7887]
[7888]
[7889]
[7890]
[7891]
7892
[7893]
[7894]
[7895]
[7896]
[7897]
[7898]
[7899]
[7900]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.