(Press-News.org) Children of college-educated parents eat more vegetables and drink less sugar, according to a new study from the University of British Columbia. But it's still not enough, the study goes on to say, as all kids are falling short when it comes to eating healthier at school
The research suggests a parent's educational attainment, an indicator of socioeconomic status, may inform a child's diet.
The study found Vancouver school children whose parents completed some post-secondary education were 85 per cent more likely to eat vegetables during the school week than those with parents who completed high school or less. Children whose parents graduated from college or university were 67 per cent less likely to consume sugary drinks, like soda pop.
"We can only speculate on the reasons for the disparities," says co-author Jennifer Black, a food, nutrition and health professor in the Faculty of Land and Food Systems. "Higher priced products, like vegetables, may not be the food that gets packed first for vulnerable families that need to make tough choices about school lunches."
The study revealed, however, that the majority of children, regardless of socioeconomic status, do not consume enough low-fat milk or whole grains on school days, opting instead for packaged snack foods like potato chips or fast-food style items, like French fries, high in sodium and saturated fat.
"While there are still barriers that exist for low-income children, families from across the socioeconomic spectrum are struggling to get their kids to eat healthy food at school," says Black. "Our findings challenge this common notion that only low-income families feed their kids junk food because it appears wealthy families are not always making healthier choices either."
Background
The study surveyed nearly 1,000 students in Grades 5 to 8, asking them to report their daily food consumption at school, or while travelling to and from school. Less than half of the kids reported consuming fruit, vegetables, whole grains or low-fat milk. Seventeen per cent reported eating fast food, 20 per cent reported eating packaged snack foods and 31 per cent reported drinking sugary drinks daily. Fifteen per cent of the students reported going hungry.
"Our study provides new insight on what kids are eating, or not eating, in Vancouver public schools," says co-author Naseam Ahmadi, a M.Sc. graduate in human nutrition. "Overall, things aren't looking so good. More work is needed to address the dietary needs of children when they go off to school."
INFORMATION:
The study, Associations between socio-economic status and school-day dietary intake in a sample of grade 5-8 students in Vancouver, Canada, took place at 26 public schools in 2012. To read the full study, published in Public Health Nutrition, click here: http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=9315744&fileId=S1368980014001499
The study is part of a larger UBC project, Think & Eat Green @ School, which researches and develops policies and programs to help build healthier and sustainable food systems in schools.
Kids eat better if their parents went to college
2014-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dogs can be pessimists too
2014-09-18
Dogs generally seem to be cheerful, happy-go-lucky characters, so you might expect that most would have an optimistic outlook on life.
In fact some dogs are distinctly more pessimistic than others, research from the University of Sydney shows.
"This research is exciting because it measures positive and negative emotional states in dogs objectively and non-invasively. It offers researchers and dog owners an insight into the outlook of dogs and how that changes," said Dr Melissa Starling, from the Faculty of Veterinary Science. Her PhD research findings are published ...
The viability of premature babies is minimal at 22 weeks' gestation
2014-09-18
A new study analyses the survival rates in Spain of newborns with a gestational age under 26 weeks. The results show that survival under 23 weeks is 'exceptional', although other factors such as birth weight and sex also have an influence.
Experts from the Spanish Society of Neonatology have studied the survival rates in Spain of newborns with a gestational age under 26 weeks, taking into account that a newborn carried to term is between 37 and 42 weeks.
The data have been drawn from the national database that gathers information on all babies born weighing less than ...
A second look at glaucoma surgery
2014-09-18
New research led by Queen's University professor Robert Campbell (Ophthalmology) has revealed using anti-inflammatory medications after glaucoma laser surgery is not helpful or necessary.
Glaucoma is the most common cause of irreversible blindness in the world and about 400,000 Canadians are afflicted with the disease, which is mainly caused by pressure within the eye being high enough to damage the optic nerve. The optic nerve is responsible for sending messages from the eye to the brain and is a vital part of vision.
"The use of strong anti-inflammatory therapies after ...
Tropical fish a threat to Mediterranean Sea ecosystems
2014-09-18
The tropical rabbitfish which have devastated algal forests in the eastern Mediterranean Sea pose a major threat to the entire Mediterranean basin if their distribution continues to expand as the climate warms, a new study warns.
The study, by an international team of researchers led by Dr Adriana Vergés of UNSW Australia and Dr Fiona Tomas of the Mediterranean Institute for Advanced Studies in Spain, is published in the Journal of Ecology.
Members of the team surveyed more than 1000 kilometres of coastline in Turkey and Greece, where two species of rabbitfish have become ...
University of Kentucky research explores STXBP5 gene and its role in blood clotting
2014-09-18
LEXINGTON, Ky (Sept. 17, 2014) -- Two independent groups of researchers led by Sidney (Wally) Whiteheart, PhD, of the University of Kentucky, and Charles Lowenstein, MD, of the University of Rochester, have published important studies exploring the role that a gene called STXBP5 plays in the development of cardiovascular disease.
According to Whiteheart, previous genome-wide association studies (GWAS) identified a gene called STXBP5 as a factor that regulates a protein called Von Willebrand factor (VWF).
VWF is an important contributor to normal blood clotting. When ...
UT Dallas study uncovers factors in students' reporting of weapons at school
2014-09-18
As a result of outbreaks of violence in the nation's schools, concerns have grown about school safety and the overall well-being of students.
In a new study, UT Dallas criminology researchers have found that certain factors affect students' willingness to report weapons at school.
"A big part of adolescent development is figuring out your identity, and that does not always mean talking to grown-ups about what is going on," said Dr. Nadine Connell, assistant professor of criminology in the School of Economic, Political and Policy Sciences. "We can't stop students from ...
Improving medicines for children in Canada
2014-09-18
Ottawa (September 18, 2014) – A new expert panel report, Improving Medicines for Children in Canada, released today by the Council of Canadian Academies, addresses the importance of developing safe and effective medicines for children. Each year about half of Canada's seven million children use at least one prescription drug. Much of this prescribing is done off-label (i.e. the prescription differs from the authorized use), creating potential health risks.
Children have historically been excluded in drug research and development, including clinical trials. As a result, ...
Rosuvastatin treatments particularly effective among prediabetic patients
2014-09-18
Los Angeles, CA (September 18, 2014) Cardiovascular disease is the leading causes of death worldwide and high cholesterol plays a major role in accelerating its progression. Medical practitioners have turned to statins as a treatment to decrease cholesterol-carrying lipoproteins such as small dense lipoproteins (sdLDL), considered to be especially harmful. A new study, out today in the Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics finds that rosuvastatin may be more effective among prediabetic patients than patients with normal glucose levels.
Study author ...
Middle school dilemma: Girls' body image affected by older peers
2014-09-18
Los Angeles, CA (September 18, 2014) The media is highly criticized for contributing to body image issues in adolescents. However, a study out today in Psychology of Women Quarterly finds a different source for body dissatisfaction among young girls: older girls at school.
A research team led by Jaine Strauss, Professor of Psychology at Macalester College, surveyed 1,536 5th through 8th-grade female students attending schools with different grade groupings. Some 5th and 6th graders attended school with older students (i.e. in districts that follow the "middle school" ...
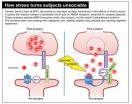
How stress tears us apart
2014-09-18
Why is it that when people are too stressed they are often grouchy, grumpy, nasty, distracted or forgetful? Researchers from the Brain Mind Institute (BMI) at EPFL have just highlighted a fundamental synaptic mechanism that explains the relationship between chronic stress and the loss of social skills and cognitive impairment. When triggered by stress, an enzyme attacks a synaptic regulatory molecule in the brain. This was revealed by a work published in Nature Communications.
Carmen Sandi's team went to look for answers in a region of the hippocampus known for its involvement ...