(Press-News.org) OAK BROOK, Ill. - Degeneration of the white matter of the brain may be an early marker of specific types of Alzheimer's disease (AD), including early-onset AD, according to results of a new study published in the journal Radiology.
"Alzheimer's is a gray matter disease," said Federica Agosta, M.D., Ph.D., co-author of the study conducted at the Neuroimaging Research Unit, San Raffaele Scientific Institute in Milan, Italy. "However, white matter damage has a central role in how the disease strikes and progresses."
AD is an irreversible, progressive brain disease that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills. The disease is characterized by abnormal deposits of proteins that form amyloid plaques and tau tangles throughout the brain and a loss of neurons that causes brain tissue to shrink over time. Where or how the disease begins is not completely understood.
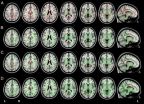
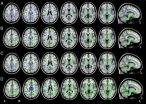
Study leader Massimo Filippi, M.D., and his team of researchers used diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to assess the white matter tracts in 53 patients with three types of AD: early-onset AD and two atypical types of AD called focal syndromes because they affect localized parts of the brain.
Unlike late-onset AD that occurs after age 65 and is characterized primarily by progressive memory loss, patients with early-onset AD have impairment in several regions of the brain, including deficits in executive functioning and visuospatial abilities. Focal AD syndromes may cause visual disturbances or language deficits.
DTI, a specialized magnetic resonance imaging technique that uses the movement of water molecules to characterize the microstructure of biological tissues, is highly sensitive to white matter degeneration.
"Our goal was to use DTI to identify similarities and differences in white tract damage across the AD spectrum and in relation to patterns of cortical atrophy," Dr. Agosta said.
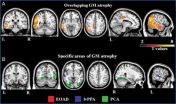
The researchers' analysis of the images revealed that all of the patients had extensive white matter damage, and showed regional gray matter damage.
"The white matter damage in patients with focal AD syndromes was much more severe and widespread than expected and cannot be explained solely by gray matter atrophy which was more localized," Dr. Agosta said.
She said the team's findings support the theory that AD pathology may travel along white matter fibers from one region of the brain to another.
"In early-onset AD and atypical AD forms, white matter degeneration may be an early marker that precedes gray matter atrophy," Dr. Agosta said. "DTI has the potential to assess the extensive disorganization of brain networks in focal AD even before overt cognitive deficits become apparent."
Dr. Agosta said the study's findings also underline the importance of identifying and diagnosing patients with early onset and focal AD syndromes.
"Because there is not much structural damage in the early stages of focal Alzheimer's disease, there is a risk that patients may be misdiagnosed and excluded from clinical trials," she said.
INFORMATION:
"White Matter Degeneration in Atypical Alzheimer Disease." Collaborating with Drs. Filippi and Agosta were Francesca Caso, M.D., Daniele Mattavelli, M.D., Raffaella Migliaccio, M.D., Ph.D., Elisa Canu, Ph.D., Giuseppe Magnani, M.D., Alessandra Marcone, M.D., Massimiliano Copetti, Ph.D., Monica Falautano, M.D., Giancarlo Comi, M.D., Andrea Falini, M.D.
Radiology is edited by Herbert Y. Kressel, M.D., Harvard Medical School, Boston, Mass., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (http://radiology.rsna.org/)
RSNA is an association of more than 54,000 radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Ill. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on MRI of the brain, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
The first practical guide to ensure the safe use of flavourings in e-cigarettes has been published (Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology DOI: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2015.05.018).
E-cigarettes and other vaping products contain a nicotine-based liquid that is vapourised and inhaled. There is no combustion so the user inhales vapour, not smoke. This means that e-cigarettes deliver nicotine without smoke toxicants. However, some in the public health community still have expressed concerns over the potential health impacts of flavourings used in e-cigarettes.
This is why the ...
The spinal tumor grew back. Even though the 16-year old patient endured surgery a year earlier to remove and diagnose the lesion, it was back and its cause unknown. Determined to identify the tumor tissue and set the patient on an appropriate treatment regimen, Albert Telfeian, M.D., a neurosurgeon at Rhode Island Hospital and Hasbro Children's Hospital, performed the first reported case of extracting the tumor endoscopically while the patient was awake and under a local anesthetic. The minimally invasive procedure enabled accurate diagnosis, which evaded multiple physicians ...
New research published today in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes) indicates that consuming greater quantities of dietary fibre reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Over 360 million people worldwide are estimated to be affected by diabetes, and this number is projected to increase to more than 550 million by 2030, with serious consequences for the health and economy of both developed and developing countries. While previous research has found an association between increased dietary fibre intake and a reduced risk ...
Professor Teppo Järvinen and colleagues say drug treatment "can achieve at best a marginal reduction in hip fractures at the cost of unnecessary harms and considerable waste of monetary resources." The article is part of The BMJ's Too Much Medicine campaign -- to highlight the threat to human health and the waste of resources caused by unnecessary care.
Worldwide, about 1.5 million hip fractures occur each year. They impose an enormous burden on healthcare resources and, with a growing elderly population, their incidence is predicted to rise.
Before the late ...
The results show that pills containing one of the newer types of progestogen hormone (drospirenone, desogestrel, gestodene, and cyproterone) are associated with an increased risk of VTE than pills containing older progestogens (levonorgestrel and norethisterone).
The researchers, based at the University of Nottingham, say this is "an important clarifying study" that "has sufficient power to provide reliable comparative findings for different formulations of combined oral contraceptives."
About 9% of women of reproductive age worldwide use oral contraceptives, rising ...
James Rucker, a psychiatrist and honorary lecturer at the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience, King's College London, describes how these drugs "were extensively used and researched in clinical psychiatry" before their prohibition in 1967.
He explains that many trials of psychedelics published before prohibition, in the 1950s and 1960s, suggested "beneficial change in many psychiatric disorders".
However, research ended after 1967. In the UK psychedelic drugs were legally classified as schedule 1 class A drugs - that is, as having "no accepted medical ...
PHILADELPHIA -- HDL is the 'good cholesterol' that helps remove fat from artery walls, reversing the process that leads to heart disease. Yet recent drug trials and genetic studies suggest that simply pushing HDL levels higher doesn't necessarily reduce the risk of heart disease. Now, a team led by scientists from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania has shown in a large, forward-looking epidemiological study that a person's HDL function -- the efficiency of HDL molecules at removing cholesterol -- may be a better measure of coronary heart disease ...
A risk gene for dyslexia is associated with impairments in visual motion detection, according to a study published May 27 in The Journal of Neuroscience. Mutations in the gene DCDC2 have previously been associated with dyslexia, and this study found that dyslexics with an altered copy of the gene are unable to detect certain types of visual motion.
The researchers used a series of visual tests to compare typical readers with two groups of dyslexics -- one with and one without a specific deletion in the DCDC2 gene.
The subjects were presented with images of patterned ...
Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation scientists have pinpointed a cell that begins the process of scarring in fatty tissue. The findings cast new light on a biological process that occurs with obesity and can lead to diabetes.
"Scarring can be an important part of the healing process when a person suffers an injury," said OMRF's Lorin Olson, Ph.D., who led the research. "But excessive scarring, or fibrosis, can contribute to many dangerous health conditions."
The new research appears in the June 1 issue of the journal Genes & Development.
Using experimental models, ...
One of the major challenges of cocaine addiction is the high rate of relapse after periods of withdrawal and abstinence. But new research reveals that changes in our DNA during drug withdrawal may offer promising ways of developing more effective treatments for addiction.
Withdrawal from drug use results in reprogramming of the genes in the brain that lead to addictive personality, say researchers from McGill University and Bar Ilan University in a new study published in the Journal of Neuroscience.
"We inherit our genes from our parents and these genes remain fixed ...