NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Atsani bow out
2015-08-25
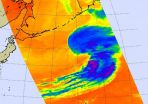
(Press-News.org) Tropical Cyclone Atsani appeared to look more like a frontal system in infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite.Early on August 26, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center issued their final bulletin on the system as it was transitioning into an extra-tropical cyclone,
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument that also flies aboard Aqua captured infrared data on the storm on August 25 at 14:47 UTC (10:47 a.m. EDT). Cloud top temperatures in thunderstorms northeast of the center were colder than -63F/-52C, indicating high, strong thunderstorms with the potential for heavy rainfall. Areas around the rest of the system appeared almost cloud-free.
At 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EDT) on April 6, 2015, Tropical Cyclone Atsani's maximum sustained winds were near 60 knots (69 mph/111 kph). It was located 1,065 nautical miles (1,226 miles/1,972 km) south of Petropavlovsk, Russia, near 35.2 north latitude and 155.8 east longitude. Astani was moving to the east-northeast at 28 knots (32.2 mph/51.8 kph).
In the final bulletin on Atsani Joint Typhoon Warning Center, Atsani was transitioning into an extra-tropical low and is expected to make landfall south of eastern Russia on August 26.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-25
Bats are natural reservoirs of several important emerging viruses, and because cross-species transmission appears to be quite common among bats, it's important to study bats in a community context rather than concentrating on individual species.
Researchers have now used such an approach to identify characteristics of cross-species virus transmission in bats and rodents, another important viral host. The investigators uncovered evidence to suggest that viruses pass more easily between bat species than between rodent species, and they found that characteristics unique ...
2015-08-25
In a new review of all relevant medical research on breastfeeding practices, infants 0 to 5 months of age who were predominantly, partially, or not breastfed had 1.5-, 4.8-, and 14.4-times higher risks of dying, respectively, compared with exclusively breastfed infants. Also, children aged 6 to 23 months who were not breastfed had about a 2-times higher risk of dying than children who were continued on breastfeeding.
"The findings underscore the importance of optimal breastfeeding practices during infancy and early childhood," said Dr. M. Jeeva Sankar, lead author of ...
2015-08-25
(Boston)--Twenty-five percent of men currently taking Finasteride or Dutasteride, popularly known as Proscar and Avodart, for the treatment of benign prostate enlargement (BPH), appear not to benefit from taking these medications. Those prescribed Propecia or Avodart for male pattern hair loss (known as alopecia) are also at risk for adverse events elicited by these drugs.
These findings are part of an international, collaborative review currently online in the journal Endocrine Reviews and Metabolic Disorders. Led by Abdulmaged Traish, PhD, professor of biochemistry ...
2015-08-25
In early August, biologist Peter Ward returned from the South Pacific with news that he encountered an old friend, one he hadn't seen in over three decades. The University of Washington professor had seen what he considers one of the world's rarest animals, a remote encounter that may become even more infrequent if illegal fishing practices continue.
The creature in question is Allonautilus scrobiculatus, a species of nautilus that Ward and a colleague had previously discovered off of Ndrova Island in Papua New Guinea. Nautiluses are small, distant cousins of squid and ...
2015-08-25
RIVERSIDE, Calif. - Barley, a widely grown cereal grain commonly used to make beer and other alcoholic beverages, possesses a large and highly repetitive genome that is difficult to fully sequence. Now a team led by scientists at the University of California, Riverside has reached a new milestone in its work, begun in 2000, on sequencing the barley genome. The researchers have sequenced large portions of the genome that together contain nearly two-thirds of all barley genes.
The new information, published in The Plant Journal, will not only expand geneticists' knowledge ...
2015-08-25
A recent randomized trial conducted by researchers at Abbott Northwestern Hospital, part of Allina Health, found that inpatient palliative care (PC) visits were associated with improved quality of life and symptom burden for patients with heart failure (HF).
Because of these results, Abbott Northwestern conducted a new study, "A Description of Inpatient Palliative Care Actions for Patients with Acute Heart Failure," published June 30 by the American Journal of Hospice and Palliative Medicine. The study aimed to identify and describe what actions PC providers took to ...
2015-08-25
BOSTON - A new study led by researchers at Boston Medical Center (BMC) indicates that variations in opioid receptor genes are associated with more severe neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) in newborn babies. The findings, published online in Drug & Alcohol Dependence, could help lead to the development of individualized treatment plans tailored to each infants' risk of requiring medication to curb their NAS symptoms, which could help improve these patients' outcomes and reduce how long some stay in the hospital.
NAS is present in newborn babies who have been exposed ...
2015-08-25
Jaclyn Tabor and Jessica Calarco tap a novel data source to track changing attitudes toward parenting during the 20th and early 21st centuries: cartoons in the New Yorker magazine.
"We find that portrayals of children and child-rearing are both more varied and more fluctuating than existing research would suggest," said Tabor, an Indiana University Bloomington doctoral student in sociology. "Contemporary cartoons celebrate children but also recognize the significant challenges children create for parents. Cartoons from the 1920s and 1930s -- when rates of childlessness ...
2015-08-25
Less than a month before Congress votes on whether to reauthorize a controversial program mandating healthier school lunches, a new study confirms the suspicions of school officials - many students are putting the fruits and vegetables they're now required to take straight into the trash, consuming fewer than they did before the law took effect.
The new study, published online in Public Health Reports on Aug. 25, is the first to use digital imaging to capture students' lunch trays before and after they exited the lunch line.
It is also one of the first to compare fruit ...
2015-08-25
People of all ages recently lined up to do some fishing at the Museum of Science in Boston. And oddly, the fish they hoped to hook were not good ones.
Museum goers were invited to play "Fish Police!!" is a video game that challenged players to rid a river of its bad fish, while sparing its good ones. The catch? All the fish looked exactly alike, and could be told apart only by the way a fish puffed in size: a bad fish puffed just a little faster. After all, it was nervous that it would be caught.
The game's premise may sound a little fishy, but it has helped a team ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Atsani bow out