New survey on Americans' views on papal encyclical on climate change
Catholics mirror non-Catholic Americans in key attitudes about global warming
2015-08-26
(Press-News.org) A new national survey conducted by The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research and researchers at Yale University found that fewer than 1 in 3 Americans, and 40 percent of Catholics, are aware of Pope Francis's efforts to publicize global warming as a priority issue for the Catholic Church. While there is relatively low awareness of the papal encyclical, a majority of Americans say it is appropriate for the pope to take a public position on the issue of global warming. This is true even though very few Americans consider global warming as an issue of religion, social justice, or poverty. The nationwide poll was collected July 17 to 19, 2015, using the AmeriSpeak Omnibus, the probability-based panel of NORC at the University of Chicago. Online and telephone interviews using landlines and cell phones were conducted with 1,030 adults.
"This survey indicates that the Pope's message on global warming has not broken through to a majority of Catholics or Americans," said Trevor Tompson, director of The AP-NORC Center. "The survey found that few people consider the issue a religious or social justice one."
Some of the poll's key findings include:
Few Americans, just 31 percent, have heard about Pope Francis's encyclical on global warming.
Most Americans say they think it's appropriate for the pope to take a public stand on global warming despite few viewing it as a religious issue.
Catholics mirror non-Catholic Americans in their attitudes about whether global warming is happening and their views about the appropriateness of the pope's recent encyclical.
Over three-quarters of Americans say climate change is an environmental and scientific issue. Few consider it to be an issue relating to social justice, poverty, or religion.
"Even though the Pope's Encyclical is a major theological statement, fewer than 2 in 5 churchgoing Catholics heard about it from their priest in the month after it was released," said Anthony Leiserowitz, a faculty member of the Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies. "But this may change when Pope Francis visits the United States in September to bring his message personally."
INFORMATION:
About the Survey
This survey was conducted by The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research with input and funding from Yale University. Data were collected using AmeriSpeak®, which is a probability-based panel designed to be representative of the U.S. household population. Interviews for this survey were conducted July 17 to 19, 2015, with adults age 18 and over from the 50 states and the District of Columbia. Panel members were randomly drawn from AmeriSpeak®, and 1,030 completed the survey--894 via the web and 136 via telephone. The overall margin of sampling error is +/- 4.4 percentage points at the 95 percent confidence level, including the design effect. The margin of sampling error may be higher for subgroups.
About The Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies
Founded in 1900, FES is the oldest institution of higher learning devoted to conservation and natural resource management in the United States. Now in its second century, the school prepares new leadership and creates new knowledge to sustain and restore the long-term health of the biosphere and the well-being of its people. We educate women and men to guide human activity at the local, national, and global levels with a comprehensive understanding of the environmental, economic, and social effects of their choices. We create new knowledge in the science of sustainability and new methods of applying that knowledge to the challenge of environmental management, the restoration of degraded environments, and the pursuit of sustainable development.
http://environment.yale.edu/
About The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research
The AP-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research taps into the power of social science research and the highest-quality journalism to bring key information to people across the nation and throughout the world.
http://www.apnorc.org
The Associated Press is the essential global news network, delivering fast, unbiased news from every corner of the world to all media platforms and formats. Founded in 1846, AP today is the most trusted source of independent news and information. On any given day, more than half the world's population sees news from AP.
http://www.ap.org
NORC at the University of Chicago is an independent research institution that delivers reliable data and rigorous analysis to guide critical programmatic, business, and policy decisions. Since 1941, NORC has conducted groundbreaking studies, created and applied innovative methods and tools, and advanced principles of scientific integrity and collaboration. Today, government, corporate, and nonprofit clients around the world partner with NORC to transform increasingly complex information into useful knowledge.
http://www.norc.org
The two organizations have established The AP-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research to conduct, analyze, and distribute social science research in the public interest on newsworthy topics, and to use the power of journalism to tell the stories that research reveals.
About AmeriSpeak Omnibus
AmeriSpeak Omnibus is a once-a-month, multi-client survey using a probability sample of at least 1,000 nationally representative adults age 18 and older. Respondents are interviewed online and by phone from NORC's AmeriSpeak panel--the most scientifically rigorous multi-client household panel in the United States. AmeriSpeak households are selected randomly from NORC's National Sample Frame, the industry leader in sample coverage. The National Frame is representative of over 99 percent of U.S. households and includes additional coverage of hard-to-survey population segments, such as rural and low-income households, that are underrepresented in other sample frames. More information about AmeriSpeak is available at AmeriSpeak.NORC.org.
Contact: For more information, contact Eric Young for NORC at young-eric@norc.org or (703) 217-6814 (cell); Ray Boyer for NORC at boyer-ray@norc.org or (312) 330-6433; or Paul Colford for AP at pcolford@ap.org or info@apnorc.org.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-26
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Aug. 26, 2015 - In mere seconds, a system developed at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory can identify and characterize a solid or liquid sample, providing a valuable tool with applications in material science, forensics, pharmaceuticals, biology and chemistry.
The device and technique, created by Gary Van Berkel and Vilmos Kertesz of ORNL's Chemical Sciences Division, is described in the journal Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry. The appeal of this open port sampling interface, researchers note, is its elegance, speed and ...
2015-08-26
Monkeys and humans exhibit greater motor recovery than rats after similar spinal cord injury, according to a study conducted in Grégoire Courtine's lab at EPFL. The study results have been published in Science Translational Medicine.
Spontaneous improvement occurs during the first six months after a spinal cord injury, allowing a hemiplegic patient to recover partial motor control. The researchers are using this observation to improve clinical trials and patient therapies. The neuronal mechanisms underlying this extensive recovery in primates are nearly absent in ...
2015-08-26
Scientists have developed a blood test for breast cancer able to identify which patients will suffer a relapse after treatment, months before tumours are visible on hospital scans.
The test can uncover small numbers of residual cancer cells that have resisted therapy by detecting cancer DNA in the bloodstream.
Researchers at The Institute of Cancer Research, London, and The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust were able to track key mutations that cancer accumulates as it develops and spreads, without the need for invasive biopsy procedures.
They hope that by deciphering ...
2015-08-26
Using DNA sequencing, researchers have accurately painted a clear picture of fish spawning activities in a marine protected area (MPA) and have created a baseline for continuing studies on the effects of climate variability on fish populations.
A group of Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego researchers led by Ron Burton and Alice Harada collected 260 samples off the Ellen Browning Scripps Memorial Pier over a two-year period and used DNA barcoding to accurately identify over 13,000 fish eggs.
This study was also a collaborative effort between the Scripps ...
2015-08-26
DURHAM, N.C. -- You're driving on a busy road and you intend to switch lanes when you suddenly realize that there's a car in your blind spot. You have to put a stop to your lane change -- and quickly.
A new study by Duke University researchers suggests that this type of scenario makes a person less likely to remember what halted the action -- for example, the make and model of the car in the blind spot.
People and non-human primates excel at "response inhibition." Our sophisticated brains allow us to cancel an action even when it's something engrained, like driving ...
2015-08-26
ITHACA, N.Y. - After hours harvesting forage, managing livestock and milking cows, new Cornell University agricultural economic research shows family members who work on the family dairy farm make $22,000 less annually than comparable hired managers, but are handsomely compensated with "socioemotional" wealth.
"While $22,000 seems like a large penalty, there are nonfinancial rewards they experience working for the family business," said Loren Tauer, professor at Cornell's Charles H. Dyson School of Applied Economics and Management, who with lead author Jonathan Dressler ...
2015-08-26
Compounds found in purple potatoes may help kill colon cancer stem cells and limit the spread of the cancer, according to a team of researchers.
Baked purple-fleshed potatoes suppressed the growth of colon cancer tumors in petri dishes and in mice by targeting the cancer's stem cells. Colon cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the U.S. and responsible for more than 50,000 deaths annually, according to the American Cancer Society.
Attacking stem cells is an effective way to counter cancer, according to Jairam K.P. Vanamala, associate professor ...
2015-08-26
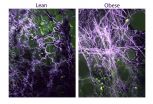
ITHACA, N.Y. - Women who are obese have a higher risk and a worse prognosis for breast cancer, but the reasons why remain unclear. A Cornell study published this month in Science Translational Medicine explains how obesity changes the consistency of breast tissue in ways that are similar to tumors, thereby promoting disease.
The study of mice and women shows obesity leads to a stiffening of a meshwork of material that surrounds fat cells in the breast, called the extracellular matrix, and these biomechanical changes create the right conditions for tumor growth.
The findings ...
2015-08-26
A new study conducted by the Media Insight Project, a collaboration between the American Press Institute and The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research, found that while the similarities to the rest of their generation are numerous, there are some distinct differences in the way that Hispanic and African American Millennials use technology to access news and information. The source of their information is one area of difference: these young adults are more likely to use YouTube and Instagram for news than Millennials in general, though all groups rely ...
2015-08-26
Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) scientists have discovered how the most common genetic defect in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis kills nerve cells. Their study suggests that the pores that allow molecules into and out of a cell's nucleus get jammed, a finding that could speed the search for other genes that promote this fatal illness.
In people who have amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), the motor neurons that operate the muscles deteriorate. Over time, the disease deprives patients of the ability to walk, swallow, and breathe, and they usually die within three ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New survey on Americans' views on papal encyclical on climate change
Catholics mirror non-Catholic Americans in key attitudes about global warming