(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
Two spiral galaxies undergo a protracted crash lasting two billion years, eventually merging into a single elliptical galaxy.
Click here for more information.
As scientists and engineers work to make NASA's James Webb Space Telescope a reality, they find themselves wondering what new sights the largest space-based observatory ever constructed will reveal. With Webb, astronomers aim to catch planets in the making and identify the universe's first stars and galaxies, yet these are things no telescope -- not even Hubble -- has ever shown them before.
"It's an interesting problem," said Jonathan Gardner, the project's deputy senior project scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "How do we communicate the great scientific promise of the James Webb Space Telescope when we've never seen what it can show us?"
So the project turned to Donna Cox, who directs the Advanced Visualization Laboratory (AVL) at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA). Located at the University of Illinois in Urbana-Champaign, NCSA provides enormous computing resources to researchers trying to simulate natural processes at the largest and smallest scales, from the evolution of the entire universe to the movement of protein molecules through cell walls.
Cox and her AVL team developed custom tools that can transform a model's vast collection of ones and zeroes into an incredible journey of exploration. "We take the actual data scientists have computed for their research and translate them into state-of-the-art cinematic experiences," she said.
Armed with an ultra-high-resolution 3D display and custom software, the AVL team choreographs complex real-time flights through hundreds of gigabytes of data. The results of this work have been featured in planetariums, IMAX theaters and TV documentaries. "Theorists are the only scientists who have ventured where Webb plans to go, and they did it through complex computer models that use the best understanding of the underlying physics we have today," Cox said. "Our challenge is to make these data visually understandable -- and reveal their inherent beauty."
The new visualizations reflect the broad science themes astronomers will address with Webb. Among them: How did the earliest galaxies interact and evolve to create the present-day universe? How do stars and planets form?
"When we look at the largest scales, we see galaxies packed into clusters and clusters of galaxies packed into superclusters, but we know the universe didn't start out this way," Gardner said. Studies of the cosmic microwave background -- the remnants of light emitted when the universe was just 380,000 years old -- show that the clumpy cosmic structure we see developed much later on. Yet the farthest galaxies studied are already more than 500 million years old.
"Webb will show us what happened in between," Gardner added.
Cox and her AVL team visualized this epoch of cosmic construction from a simulation developed by Renyue Cen and Jeremiah Ostriker at Princeton University in New Jersey. It opens when the universe was 20 million years old and continues to the present-day, when the universe is 13.7 billion years old.
AVL team members Robert Patterson, Stuart Levy, Matthew Hall, Alex Betts and A. J. Christensen visualized how stars, gas, dark matter and colliding galaxies created clusters and superclusters of galaxies. Driven by the gravitational effect of dark matter, these structures connect into enormous crisscrossing filaments that extend over vast distances, forming what astronomers call the "cosmic web."
"We worked with nine scientists at five universities to visualize terabytes of computed data in order to take the viewer on a visual tour from the cosmic web, to smaller scales of colliding galaxies, to deep inside a turbulent nebula where stars and disks form solar systems like our own," Cox said. "These visuals represent current theories that scientists will soon re-examine through the eyes of Webb."
Closer to home, Webb will peer more deeply than ever before into the dense, cold, dusty clouds where stars and planets are born. Using data from models created by Aaron Boley at the University of Florida in Gainesville and Alexei Kritsuk and Michael Norman at the University of California, San Diego, the AVL team visualized the evolution of protoplanetary disks over tens of thousands of years.
Dense clumps develop far out in a disk's fringes, and if these clumps survive they may become gas giant planets or substellar objects called brown dwarfs. The precise outcome depends on the detailed makeup of the disk. "Dr. Boley was interested in what happened in the disk and did not include the central star," Cox said, "so to produce a realistic view we worked with him to add a young star."
This is astrophysics with a pinch of Hollywood sensibility, work at the crossroads of science and art. "The theoretical digital studies that form the basis of our work are so advanced that cinematic visualization is the most effective way to share them with the public," Cox said. "It's the art of visualizing science."
"What AVL has done for the Webb project is truly amazing and inspiring," Gardner noted. "It really whets our appetites for the science we'll be doing when the telescope begins work a few years from now."
INFORMATION:
Related Links:
› James Webb Space Telescope project website
http://www.jwst.nasa.gov/
› AVL visualizations and more Webb science videos
http://www.jwst.nasa.gov/videos_science.html
› NCSA's Advanced Visualization Laboratory
http://avl.ncsa.illinois.edu/
END
NEW YORK (Nov. 3, 2010) -- Scientists at Weill Cornell Medical College have taken an important step toward a better understanding of prostate cancer by uncovering evidence that it is not one disease, as previously believed, but rather several factors which can be measured and, in the future, destroyed by targeted therapy.
The research team led by of Dr. Mark A. Rubin, the Homer T. Hirst Professor of Oncology in Pathology and vice chair for experimental pathology at Weill Cornell Medical College, identified secondary mutations that cause some types of prostate cancer ...
More than 30 million people in the United States travel to resource-limited areas of the world each year. This global mobility may contribute to the spread of infectious diseases – such as influenza, measles, and meningitis – and may also put individual travelers at risk for malaria, typhoid, dengue fever and hepatitis. Despite these potential risks, a recent study conducted by the Division of Infectious Diseases at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and published in the Journal of Travel Medicine found that 46 percent of travelers to resource-limited countries did ...
NEW YORK (Nov. 3, 2010) -- Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a type of aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma that accounts for approximately 40 percent of lymphomas among adults. If left untreated, it is fatal. The existing treatments have a cure rate that is slightly over 50 percent but destroy healthy cells along with the cancer cells.
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medical College have found a combination therapy that is more effective than traditional treatments and is able to kill the cancer cells without harm to surrounding tissues. In a paper published in the ...
CINCINNATI—Researchers at the University of Cincinnati (UC) and the Cincinnati Veterans Affairs (VA) Medical Center have found that about one-third of chronic kidney disease patients who are prescribed therapies for high blood pressure do not often adhere to treatments.
This report was published in the Nov. 2 online edition of the American Journal of Nephrology.
The study, led by researchers at UC and the Cincinnati VA, showed that treatment of hypertension in patients with chronic kidney disease continues to be a challenge in their care and that by simply improving ...
Researchers at Mount Sinai School of Medicine have found that 98 percent of the U.S. population lives in communities within 60 minutes of a hospice provider, suggesting that disparities in use of hospice are not likely due to a lack of access to a hospice provider. The results are published in the current issue of the Journal of Palliative Medicine.
"Despite a significant increase in the availability of hospice services during the past decade, the majority of Americans die without hospice care," said Melissa D.A. Carlson, PhD, Assistant Professor of Geriatrics and Palliative ...
VIDEO:
Video opens with footage of a common cornstarch and water experiment. Ian Oberst, a visiting student from Portland Community College who participated in the University of Oregon's UCORE program for...
Click here for more information.
Mix two parts cornstarch and one part water. Swirl your fingers in it slowly and the mixture is a smoothly flowing liquid. Punch it quickly with your fist and you meet a rubbery solid -- so solid you can jump up and down on a vat of it.
It ...
Melt water flowing through ice sheets via crevasses, fractures and large drains called moulins can carry warmth into ice sheet interiors, greatly accelerating the thermal response of an ice sheet to climate change, according to a new study involving the University of Colorado at Boulder.
The new study showed ice sheets like the Greenland Ice Sheet can respond to such warming on the order of decades rather than the centuries projected by conventional thermal models. Ice flows more readily as it warms, so a warming climate can increase ice flows on ice sheets much faster ...
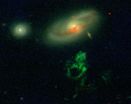
New Haven, Conn.—While sorting through hundreds of galaxy images as part of the Galaxy Zoo citizen science project two years ago, Dutch schoolteacher and volunteer astronomer Hanny van Arkel stumbled upon a strange-looking object that baffled professional astronomers. Two years later, a team led by Yale University researchers has discovered that the unique object represents a snapshot in time that reveals surprising clues about the life cycle of black holes.
In a new study, the team has confirmed that the unusual object, known as Hanny's Voorwerp (Hanny's "object" in ...
Positive psychological changes that occur during meditation training are associated with greater telomerase activity, according to researchers at the University of California, Davis, and the University of California, San Francisco. The study is the first to link positive well-being to higher telomerase, an enzyme important for the long-term health of cells in the body.
The effect appears to be attributable to psychological changes that increase a person's ability to cope with stress and maintain feelings of well-being.
"We have found that meditation promotes positive ...
LOS ALAMOS, New Mexico, NOVEMBER 3, 2010—Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Los Alamos National Laboratory and Brookhaven National Laboratory have fabricated transparent thin films capable of absorbing light and generating electric charge over a relatively large area. The material, described in the journal Chemistry of Materials, could be used in development of transparent solar panels.
"Potentially, with future refinement of this technology, windows in a home or office could generate solar power," said Hsing-Lin Wang, a co-corresponding author of the paper ...