(Press-News.org) The amount of water flowing in streams and rivers has been significantly altered in nearly 90 percent of waters that were assessed in a new nationwide USGS study. Flow alterations are a primary contributor to degraded river ecosystems and loss of native species.
"This USGS assessment provides the most geographically extensive analysis to date of stream flow alteration," said Bill Werkheiser, USGS Associate Director for Water. "Findings show the pervasiveness of stream flow alteration resulting from land and water management, the significant impact of altered stream flow on aquatic organisms, and the importance of considering this factor for sustaining and restoring the health of the Nation's streams and ecosystems."
Flows are altered by a variety of land- and water-management activities, including reservoirs, diversions, subsurface tile drains, groundwater withdrawals, wastewater inputs, and impervious surfaces, such as parking lots, sidewalks and roads.
"Altered river flows lead to the loss of native fish and invertebrate species whose survival and reproduction are tightly linked to specific flow conditions," said Daren Carlisle, USGS ecologist and lead scientist on this study. "These consequences can also affect water quality, recreational opportunities and the maintenance of sport fish populations."
For example, in streams with severely diminished flow, native trout, a popular sport fish that requires fast-flowing streams with gravel bottoms, are replaced by less desirable non-native species, such as carp. Overall, the USGS study indicated that streams with diminished flow contained aquatic communities that prefer slow moving currents more characteristic of lake or pond habitats.
"Management practices related to water demand continue to alter stream flows in many places," said Jeff Ostermiller, Water Quality Manager with the Utah Division of Water Quality. "Understanding the ecological effects of these flow alterations helps water managers develop effective strategies to ensure that water remains sufficiently clean and abundant to support fisheries and recreation opportunities, while simultaneously supporting economic development."
Annual and seasonal cycles of water flows — particularly the low and high flows — shape ecological processes in rivers and streams. An adequate minimum flow is important to maintain suitable water conditions and habitat for fish and other aquatic life. High flows are important because they replenish floodplains and flush out accumulated sediment that can degrade habitat.
"While this study provided the first, national assessment of flow alteration, focused studies within specific geographic regions will provide a better understanding of the ecological effects of altered stream flows, which can be more effectively applied to local water management challenges," said Carlisle.
The severity and type of stream flow alteration varies among regions, due to natural landscape features, land practices, degree of development, and water demand. Differences are especially large between arid and wet climates. In wet climates, watershed management is often focused on flood control, which can result in lower maximum flows and higher minimum flows. Extremely low flows are the greatest concern in arid climates, in large part due to groundwater withdrawals and high water use for irrigation.
The study identified over 1,000 unimpaired streams to use as reference points to create stream flow models. The models were applied to estimate expected flows for 2,888 additional streams where the USGS had flow monitoring gauges from 1980-2007. The estimated values for the 2,888 streams were compared to actual, measured flows to determine the degree to which streams have been altered.
INFORMATION:
This study was conducted by the USGS National Water-Quality Assessment Program (http://water.usgs.gov/nawqa), which has assessed the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of streams and rivers across the nation since 1991.
For more than 125 years, the USGS has served as the Nation's water monitoring agency, including flow and quality in selected streams and rivers across the United States. USGS continues to work closely with the Environmental Protection Agency and other federal agencies, states and local watersheds to assure that USGS monitoring and assessments provide useful information for managing and protecting streams throughout the Nation.
Water-quality data from more than 1,300 locations, much of it in real-time, are available through USGS Water Quality Watch (http://waterwatch.usgs.gov/wqwatch/). Additional information about surface water, groundwater and water quality is available at the National Water Information System Web Interface (http://waterdata.usgs.gov/nwis/). You can also receive instant, customized updates about water conditions by subscribing to WaterAlert (http://water.usgs.gov/wateralert).
USGS provides science for a changing world. Visit USGS.gov, and follow us on Twitter @USGS and our other social media channels.
Subscribe to our news releases via e-mail, RSS or Twitter.
Links and contacts within this release are valid at the time of publication.
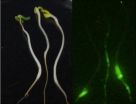
Photosynthesis is arguably the most impressive feat of nature, where plants harvest light energy and convert it into the building blocks of life at fantastically high efficiency. Indeed modern civilization became possible only with the cultivation of plants for food, shelter and clothing.
While scientists have been able to discover details of the fascinating process by which plants store solar energy as chemical energy, how developing plants build and regulate their solar reactors is still poorly understood. How many genes are involved, and which are the most important? ...
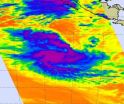
Bands of strong thunderstorms are wrapping around the center of Tropical Storm Anggrek in the Southern Indian Ocean, according to satellite imagery. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared look at those strong thunderstorms today.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Anggrek on Nov. 3 at 07:05 UTC (3:05 a.m. EDT) and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument onboard captured an infrared image of the cold thunderstorms within the system. The image showed that strong, high thunderstorm cloud tops tightly circled the storm's center. There was also strong convection ...
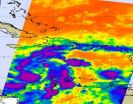
NASA infrared satellite data from this morning revealed that Tropical Storm Tomas has weakened into a tropical depression.
Tomas is in the central Caribbean Sea headed for Haiti this weekend, and forecasters are calling for a re-intensification before it makes landfall.
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) in Miami, Fla. reported at 5 a.m. EDT on Nov. 3 that hurricane hunter aircraft found an "ill-defined and elongated circulation with no tropical storm-force winds at the flight level or the surface." Thus, the status of Tomas was changed from a tropical storm to a ...
Scientists have long known that large volcanic explosions can affect the weather by spewing particles that block solar energy and cool the air. Some suspect that extended "volcanic winters" from gigantic blowups helped kill off dinosaurs and Neanderthals. In the summer following Indonesia's 1815 Tambora eruption, frost wrecked crops as far off as New England, and the 1991 blowout of the Philippines' Mount Pinatubo lowered average global temperatures by 0.7 degrees F—enough to mask the effects of manmade greenhouse gases for a year or so.
Now, scientists have shown ...
TORONTO, Ont., Nov. 3, 2010 – Existing headgear and mouth guards have limited or no benefit in reducing concussions in rugby players, according to Dr. Michael Cusimano, a neurosurgeon at St. Michael's Hospital.
However, educational injury prevention programs that promote proper playing techniques and enforcement of the rules do result in a significant reduction in concussions and head, neck and spinal injuries, Cusimano concluded after a review of existing studies on the topic.
Cusimano still recommends rugby players wear mouth guards and protective headgear ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Physical defects in plants can be predicted based on chromosome imbalances, a finding that may shed light on how the addition or deletion of genes and the organization of the genome affects organisms, according to a study involving a Purdue University researcher.
The findings identify easily measured characteristics that vary with imbalances of specific chromosomes, said Brian Dilkes, a Purdue assistant professor of horticulture. Understanding why and how those imbalances result in certain characteristics could open the door to correcting those ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - E. coli can live for weeks around the roots of produce plants and transfer to the edible portions, but the threat can be minimized if growers don't harvest too soon, a Purdue University study shows.
Purdue scientists added E. coli to soil through manure application and water treated with manure and showed that the bacteria can survive and are active in the rhizosphere, or the area around the plant roots, of lettuce and radishes. E. coli eventually gets onto the aboveground surfaces of the plants, where it can live for several weeks. Activity in ...
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL, Minn. (Nov. 2, 2010) – The vaccine that protects against the potentially cancer-causing human papillomavirus (HPV) enjoys wide support in the medical and public health communities. Yet state laws to require young girls to be vaccinated as a requirement for middle school attendance have aroused controversy with parents, politicians, and even medical and public health experts disagreeing about whether such laws are appropriate. News coverage about HPV vaccine requirements tends to amplify this controversy, possibly leading to negative attitudes among ...
With the demand for organically produced food increasing, scientists are reporting new evidence that organically grown onions, carrots, and potatoes generally do not have higher levels of healthful antioxidants and related substances than vegetables grown with traditional fertilizers and pesticides. Their study appears in ACS' bi-weekly Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.
In the study, Pia Knuthsen and colleagues point out that there are many reasons to pay a premium for organic food products. The most important reasons for the popularity of organic food products ...
Scientists are reporting the development of a simple, built-in timer intended to improve the accuracy of paper tests and test strips for diagnosing diseases inexpensively at-home and elsewhere. Their study appears in ACS' semi-monthly journal Analytical Chemistry.
Scott Phillips and Hyeran Noh note that so-called point-of-care tests include paper strip tests and others performed at home or bedside instead of in laboratories. They show special promise for improving medical care in developing countries and reducing health care costs elsewhere. When fully developed, these ...