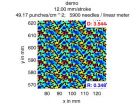
(Press-News.org) Geneva, 8 November 2010. Four days is all it took for the LHC operations team at CERN* to complete the transition from protons to lead ions in the LHC. After extracting the final proton beam of 2010 on 4 November, commissioning the lead-ion beam was underway by early afternoon. First collisions were recorded at 00:30 CET on 7 November, and stable running conditions marked the start of physics with heavy ions at 11:20 CET today.
"The speed of the transition to lead ions is a sign of the maturity of the LHC," said CERN Director General Rolf Heuer. "The machine is running like clockwork after just a few months of routine operation."
Operating the LHC with lead ions – lead atoms stripped of electrons - is completely different from operating the machine with protons. From the source to collisions, operational parameters have to be re-established for the new type of beam. For lead-ions, as for protons before them, the procedure started with threading a single beam round the ring in one direction and steadily increasing the number of laps before repeating the process for the other beam. Once circulating beams had been established they could be accelerated to the full energy of 287 TeV per beam. This energy is much higher than for proton beams because lead ions contain 82 protons. Another period of careful adjustment was needed before lining the beams up for collision, and then finally declaring that nominal data taking conditions, known at CERN as stable beams, had been established. The three experiments recording data with lead ions, ALICE, ATLAS and CMS can now look forward to continuous lead-ion running until CERN's winter technical stop begins on 6 December.
"It's been very impressive to see how well the LHC has adapted to lead ions," said Jurgen Schukraft, spokesperson of the ALICE experiment. "The ALICE detector has been optimised to record the large number of tracks that emerge from ion collisions and has handled the first collisions very well, so we are all set to explore this new opportunity at LHC."
"After a very successful proton run, we're very excited to be moving to this new phase of LHC operation," said ATLAS spokesperson Fabiola Gianotti. "The ATLAS detector has recorded first spectacular heavy-ion events, and we are eager to study them in detail."
"We designed CMS as a multi-purpose detector," said Guido Tonelli, the collaboration's spokesperson, "and it's very rewarding to see how well it's adapting to this new kind of collision. Having data collected by the same detector in proton-proton and heavy-ion modes is a powerful tool to look for unambiguous signatures of new states of matter."
Lead-ion running opens up an entirely new avenue of exploration for the LHC programme, probing matter as it would have been in the first instants of the Universe's existence. One of the main objectives for lead-ion running is to produce tiny quantities of such matter, which is known as quark-gluon plasma, and to study its evolution into the kind of matter that makes up the Universe today. This exploration will shed further light on the properties of the strong interaction, which binds the particles called quarks, into bigger objects, such as protons and neutrons.
Following the winter technical stop, operation of the collider will start again with protons in February and physics runs will continue through 2011.
INFORMATION:
*CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, is the world's leading laboratory for particle physics. It has its headquarters in Geneva. At present, its Member States are Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom. India, Israel, Japan, the Russian Federation, the United States of America, Turkey, the European Commission and UNESCO have Observer status.
END
UPTON, NY In theory, plants could be the ultimate green factories, engineered to pump out the kinds of raw materials we now obtain from petroleum-based chemicals. But in reality, getting plants to accumulate high levels of desired products has been an elusive goal. Now, in a first step toward achieving industrial-scale green production, scientists from the U.S. Department of Energys (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and collaborators at Dow AgroSciences report engineering a plant that produces industrially relevant levels of compounds that could potentially be used ...
The messenger interleukin-27 plays an important role when the human body blocks inflammations. This was discovered by an international research team, of which the Kiel Professors Joachim Grötzinger and Stefan Rose-John, as well as the doctoral candidate, Björn Spudy, are a part of. The research findings of the scientists from Kiel, the US and Great Britain were published yesterday, Sunday (7 November 2010), in the online advance edition of Nature Immunology.
The human immune system reacts to bodily injuries and infections with inflammation. This is important for the healing ...
Cars and trucks race down the highway, turn off into town, wait at traffic lights and move slowly through side streets. Electricity flows in a similar way – from the power plant via high voltage lines to transformer substations. The flow is controlled as if by traffic lights. Cables then take the electricity into the city centre. Numerous switching points reduce the voltage, so that equipment can tap into the electricity at low voltage. Thanks to this highly complex infrastructure, the electricity customer can use all kinds of electrical devices just by switching them on. ...
BOSTON, November 8, 2010 – California pistachios took center stage at this year's American Dietetic Association's annual Food & Nutrition Conference & Expo (FNCE), the industry's premier conference where thousands of registered dietitians gather to learn about innovative nutrition research and emerging health trends.
Pistachios led with a strong presence with new research on the importance of mindful eating and, for the first time ever, participating in a session on emerging green food issues and solutions designed to sustain the environment along with good health.
The ...
Learning a hobby or other complex task in childhood with assistance from a trusted adult may help guard against the emergence of a personality disorder (PD) later on in life, reports a study in the current issue of the journal, Development and Psychopathology.
Spending time with a child by reading with them, helping with homework or teaching them organizational skills helps to foster better psychological health in adulthood.
"The strong interpersonal connectedness and social skills that children learn from having active, healthy engagements with adults fosters positive ...
What do diapers, wiping cloths, wall paneling, sticking plasters and Ultrasuede covers for upholstered furniture have in common? All these products are made of nonwovens. There is hardly any other fabric that is as versatile. Last summer the operators of the Zugspitze railroad even used sheets of nonwovens to prevent the snow melting away on Germany's highest mountain. The quality of this textile, however, varies considerably. It is generally true to say that the firmer, the smoother and the freer of marks the nonwoven is, the higher the quality. In the search for the perfect ...
A team of Italian scientists has fired a laser beam into a hunk of glass to create what they believe is an optical analogue of the Hawking radiation that many physicists expect is emitted by black holes. Although the laser experiment superficially bears little resemblance to ultra-dense black holes, the mathematical theories used to describe both are similar enough that confirmation of laser-induced Hawking radiation would bolster confidence that black holes also emit Hawking radiation.
When Stephen Hawking first predicted the radiation bearing his name in 1974, he hypothesized ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. - Door-to-balloon time has dropped dramatically as hospitals rush heart attack patients into treatment, but a five-year study released Monday shows quicker hospital care has not saved more lives.
Heart attacks are a medical emergency and hospitals race against the clock to open the clogged artery causing the attack in 90 minutes or less.
Door-to-balloon time is the amount of time between a heart attack patient's arrival at the hospital to the time he or she receives an intervention, such as a balloon angioplasty, to open the artery.
The study published ...
A new study shows how an amphibious fish stays alive for up to two months on land. It's all in the skin.
Mangrove killifish are small fish—only about an inch or two long—that live in temporary pools in the coastal mangrove forests of Central and South America and Florida. During dry seasons when their pools disappear, the fish hole up in leaf litter or hollow logs. As long as they stay moist, they can survive for extended periods out of water by breathing air through their skin. But oxygen isn't the only thing a fish out of water needs to worry about, according to Professor ...
Chapel Hill - A new discovery by UNC scientists describes how cells infected by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) produce small vesicles or sacs called exosomes, changing their cellular "cargo" of proteins and RNA. This altered exosome enters cells and can change the growth of recipient cells from benign to cancer-producing.
In this way, virus-infected cells can have wide-ranging effects and potentially manipulate other cells throughout the body. The findings are reported in the November 8, 2010 early online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Nancy ...